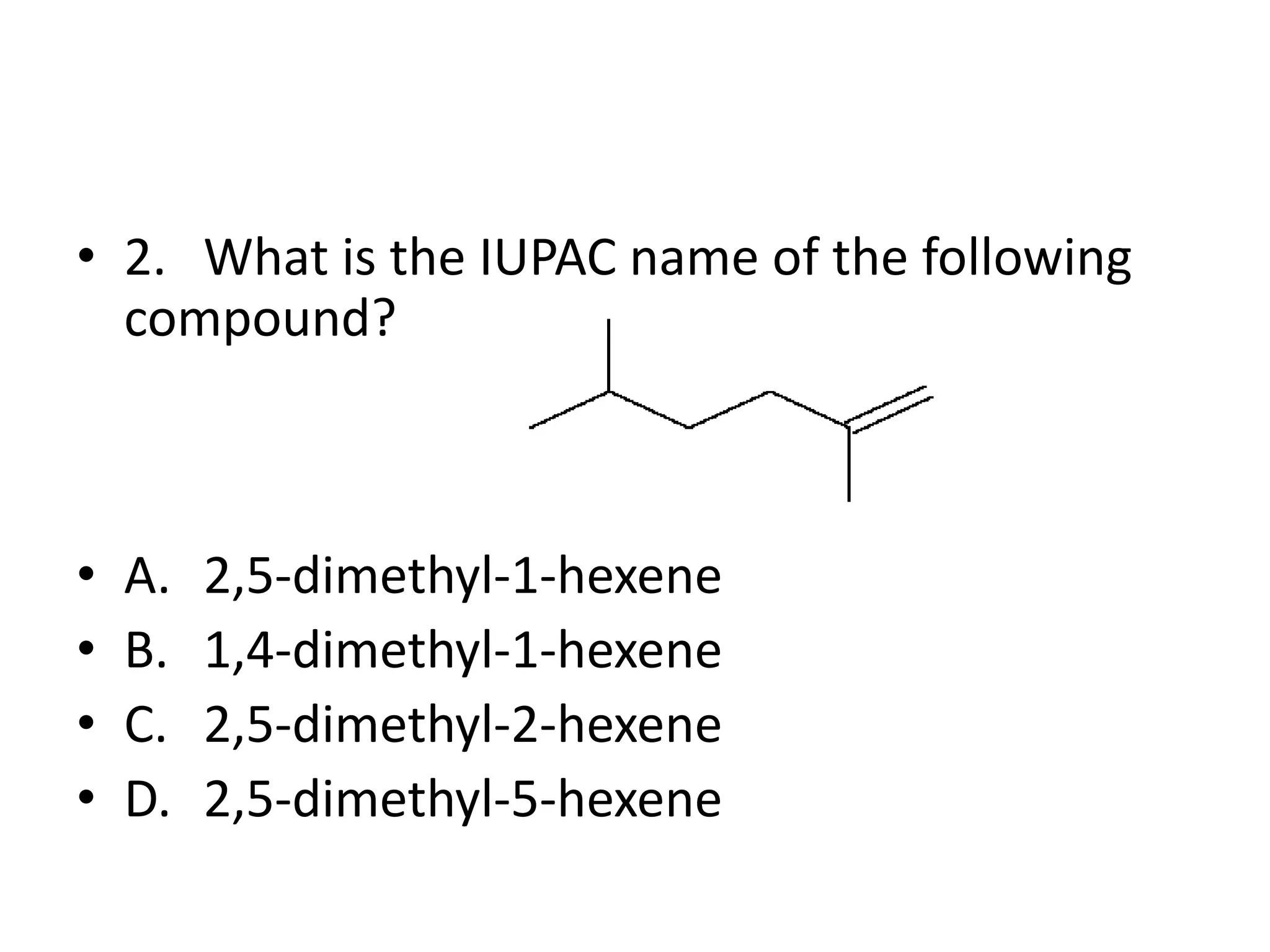
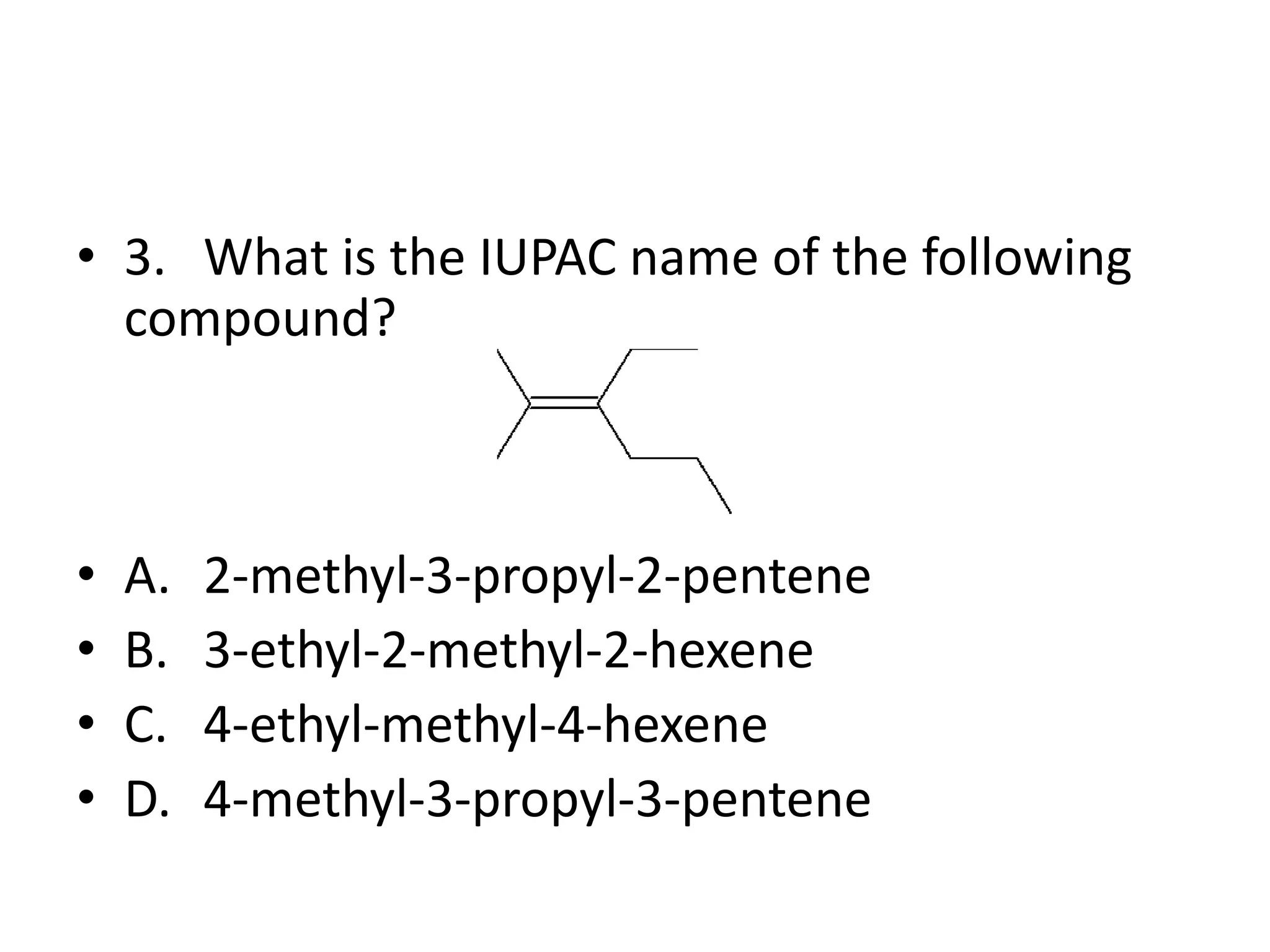
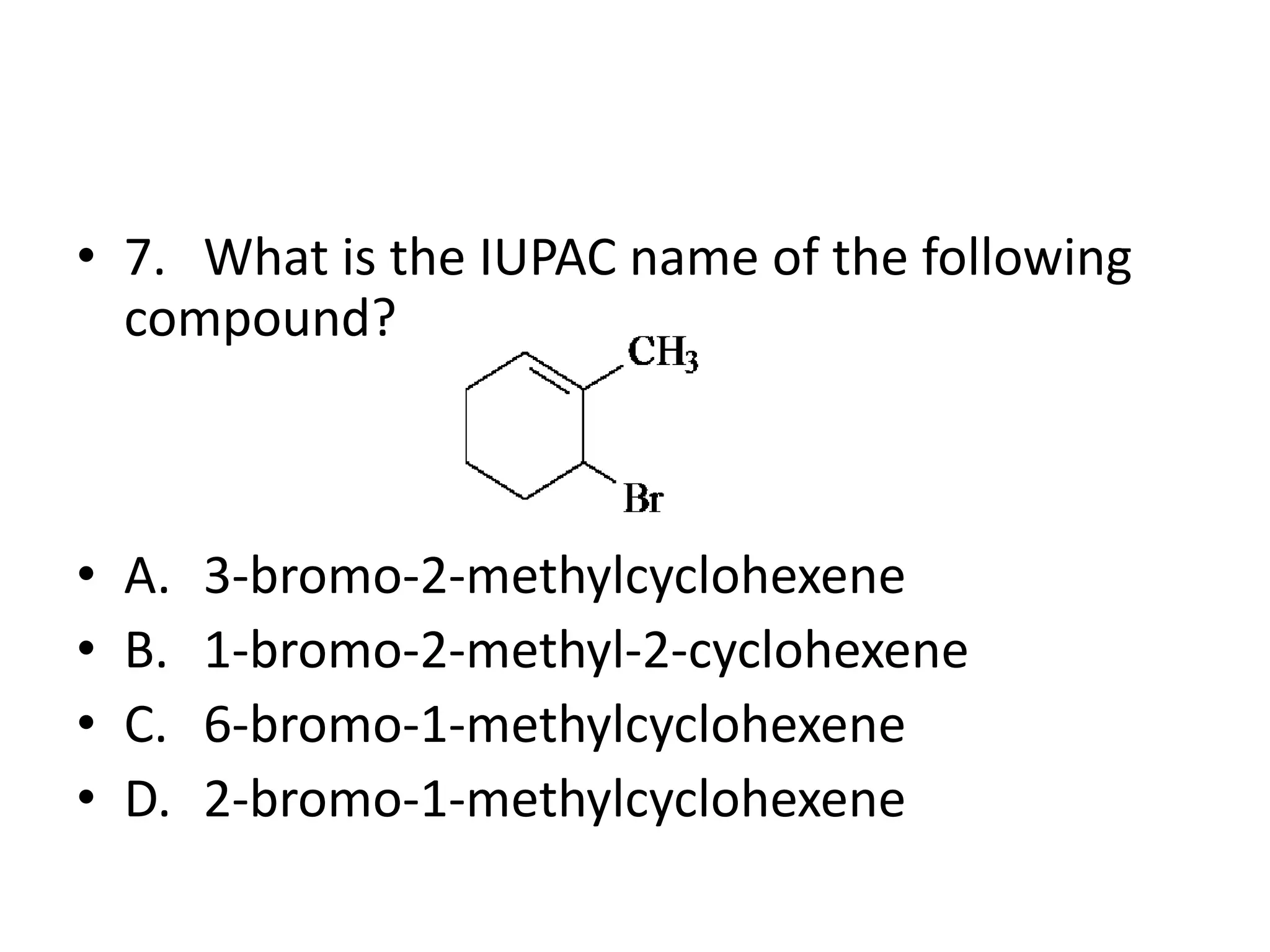
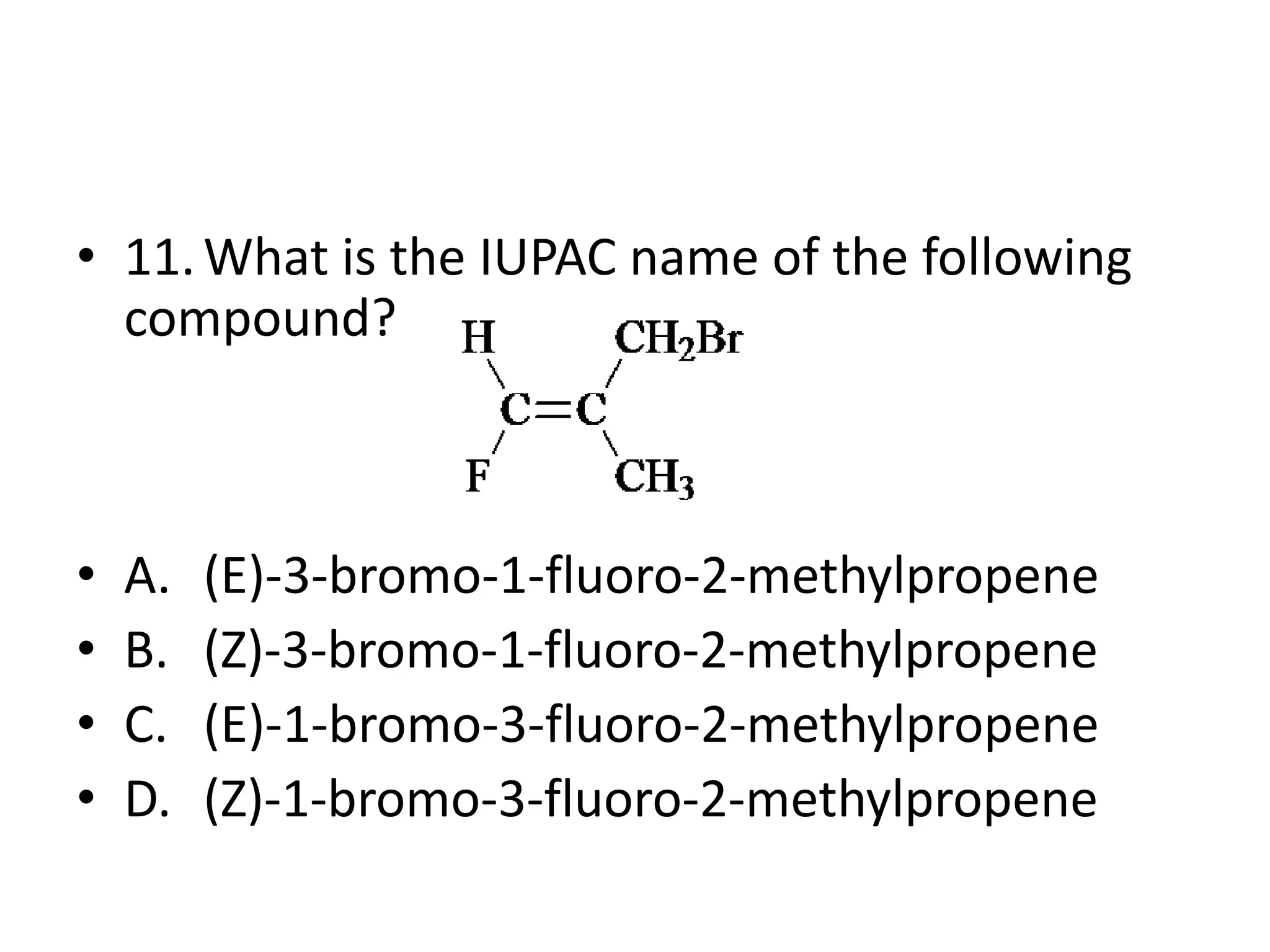
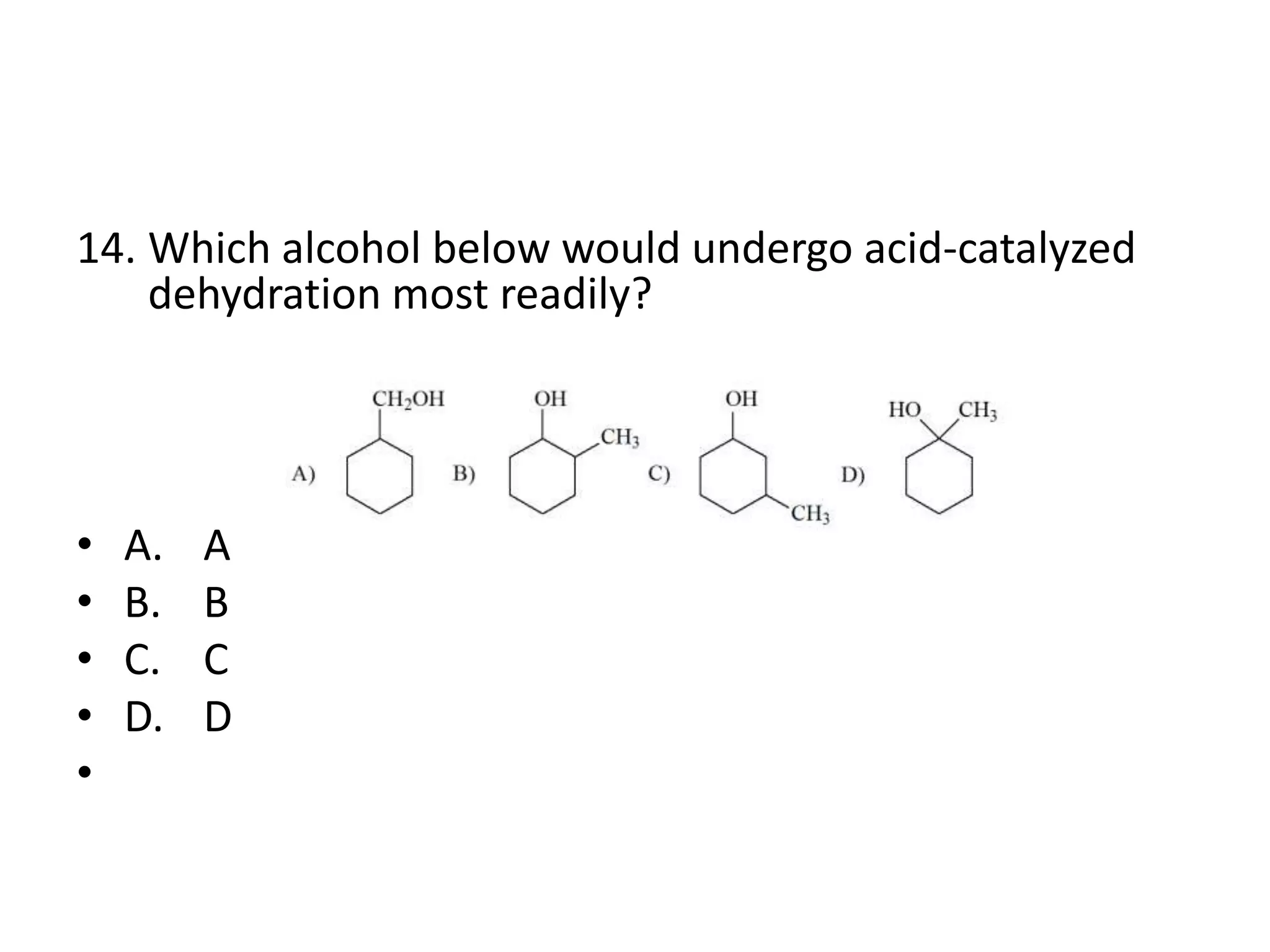
Chapter 5 discusses the structure and preparation of alkenes, particularly focusing on elimination reactions and the unique properties of carbon-carbon double bonds. It includes a series of questions related to IUPAC naming, isomerism, and mechanisms involved in the acid-catalyzed dehydration of alcohols. The chapter also addresses factors influencing carbocation stability and rearrangements.