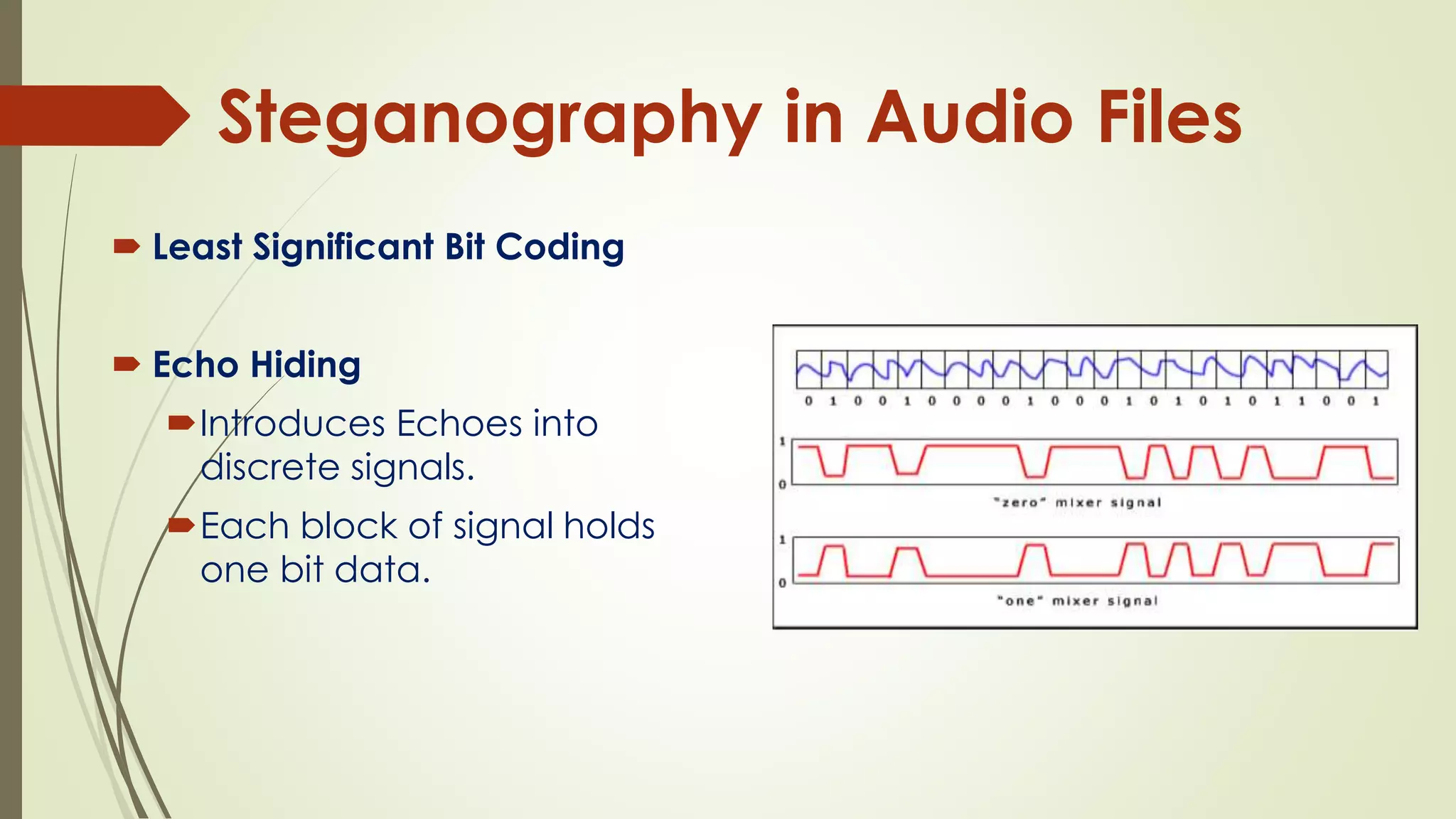
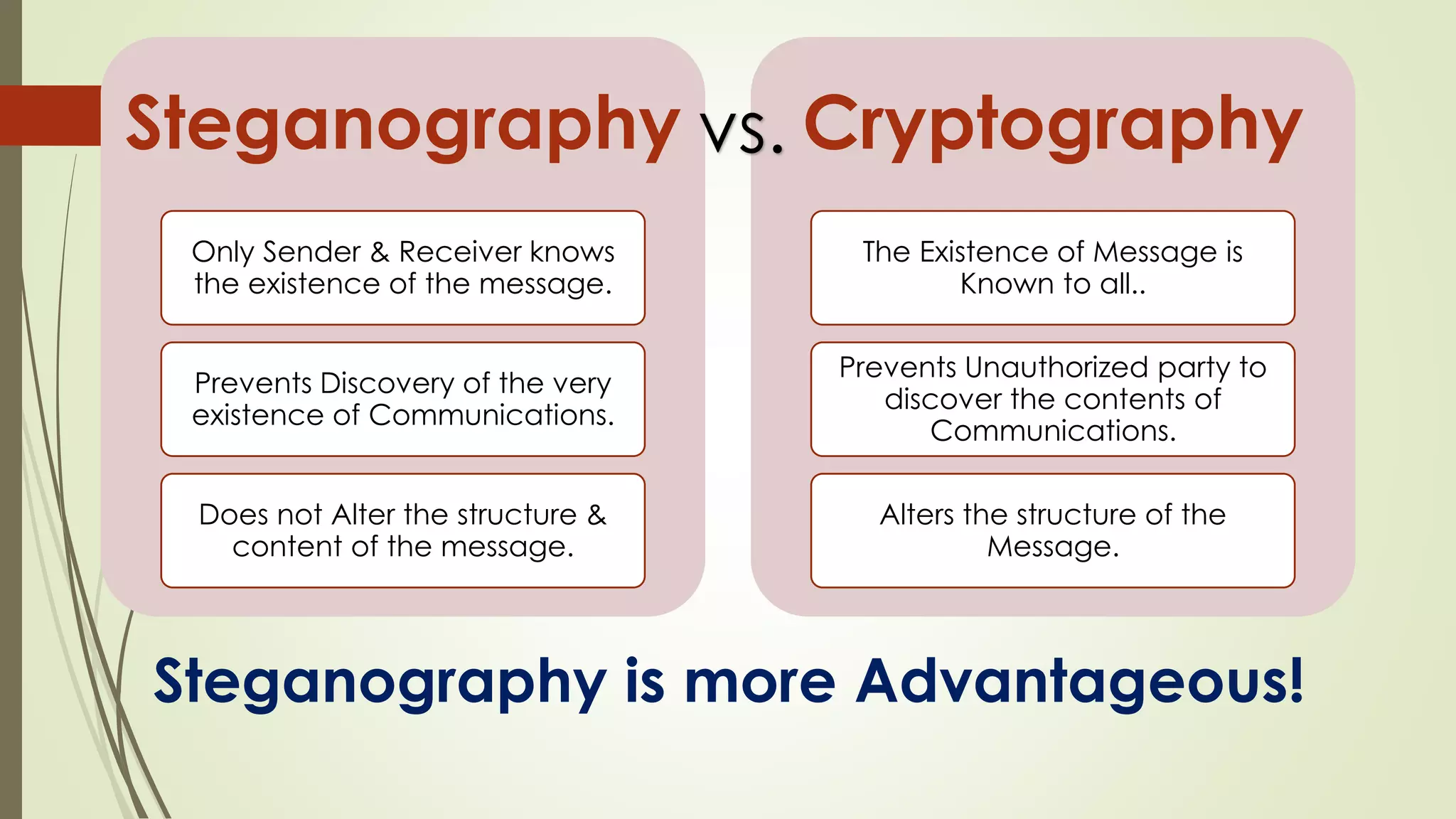
This document provides an overview of steganography. It defines steganography as hiding secret messages within other harmless messages to avoid detection by unauthorized parties. Various steganographic techniques are described, including hiding messages in digital files like images, audio, text and network protocols. Detection of steganography (steganalysis) and applications like digital watermarking and tamper proofing are also discussed. The document concludes by noting the importance of steganography and expectations for further advancement in the field.