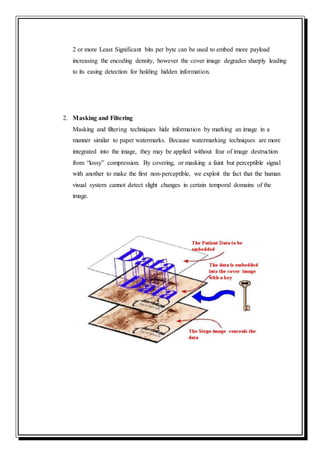
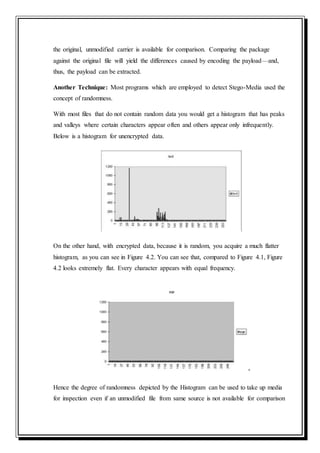
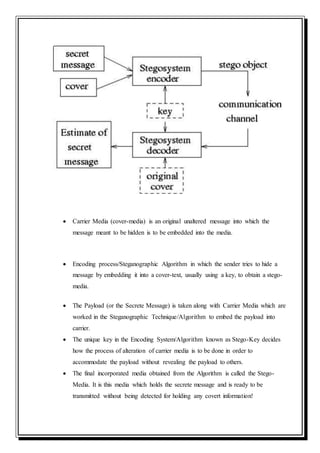
This document is a self-study seminar report on steganography presented by Abhishek Singh. It includes an introduction to steganography, its importance, and a literature review on different steganographic techniques. The introduction defines steganography as hidden writing and discusses why it is important for secret communications. The literature review covers steganography methods in text, audio, images, and networks. It also discusses steganalysis, applications of steganography, and how it compares to cryptography.









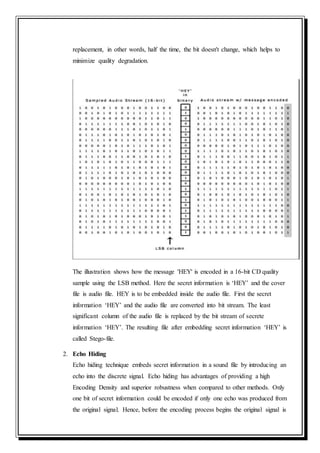
![broken down into blocks. Once the encoding process is done, the blocks are
concatenated back together to create the final signal [5, 20]. Echo Hiding is shown
in the illustration:
3. Phase Coding
The phase coding technique works by replacing the phase of an initial audio
segment with a reference phase that represents the secret information. The
remaining segments phase is adjusted in order to preserve the relative phase
between segments.
STEGANOGRAPHYIN IMAGES
To a computer, an image is an array of numbers that represent light intensities at
various points, or pixels. The 8-bit color images is more preferably used to hide
information. In 8-bit color images, each pixel is represented as a single byte. Each pixel
merely points to a color index table, or palette, with 256 possible colors. The pixel's value,
then, is between 0 and 255.
The challenge of using steganography in computer images is to hide as much data as
possible with the least noticeable difference in the image. Many Steganography experts
recommend using images featuring 256 shades of gray as the palette, for reasons that will
become apparent. Grey-scale images are preferred because the shades change very
gradually between palette entries. This increases the image's ability to hide information!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/steganography-150101230036-conversion-gate01/85/Steganography-13-320.jpg)