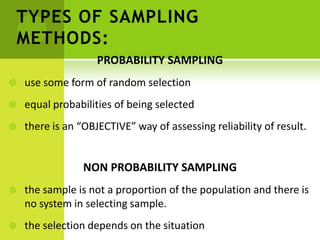
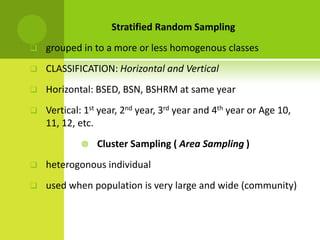
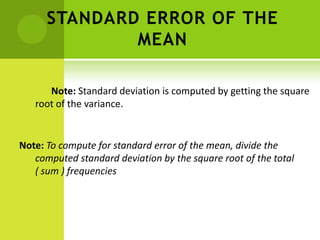
This document discusses sampling methods and statistics. It describes population, sample, and target population. There are four basic reasons for using samples: greater speed, reduced cost, greater accuracy, and greater scope. Two main types of sampling methods are described: probability sampling, which uses random selection, and non-probability sampling, which has no system for selection. Several specific probability and non-probability sampling techniques are defined. The document also covers sampling error, standard error of the mean, confidence intervals, and confidence levels. It provides examples of how to construct confidence intervals.