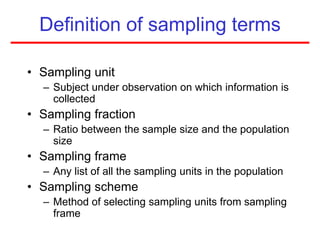
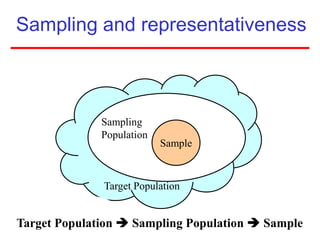
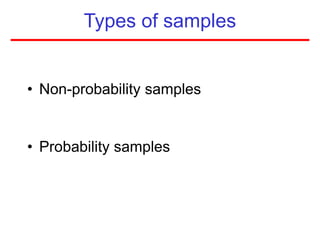
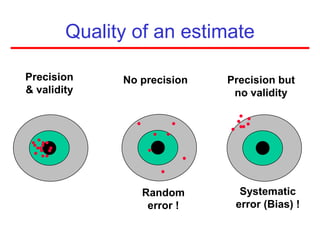
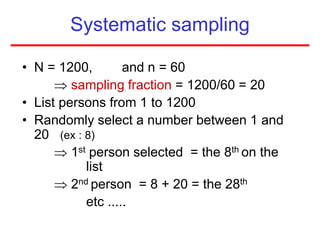
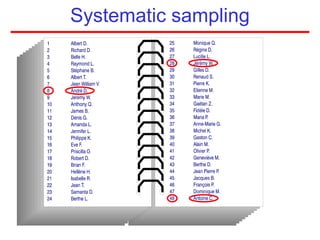
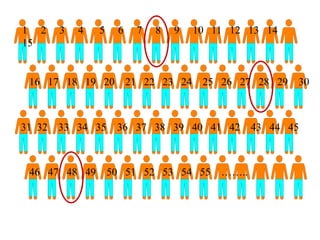
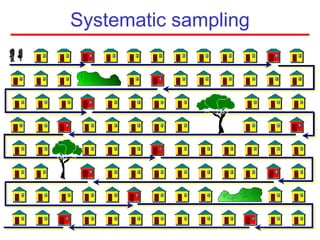
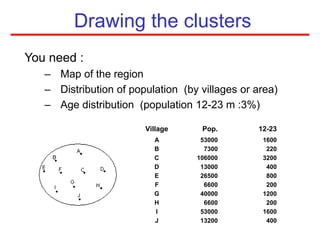
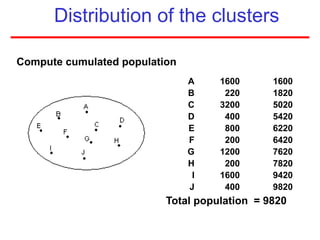
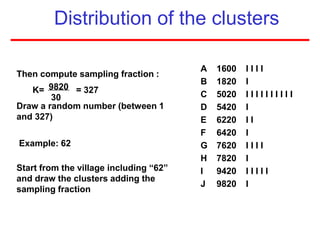
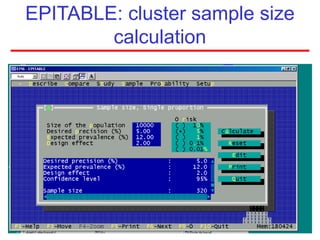
This document defines sampling and discusses key concepts for selecting samples. It defines sampling as selecting some members of a population to represent the whole. Probability and non-probability sampling methods are covered, including simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and multistage sampling. The importance of representativeness is emphasized. Sample size calculations and factors like design effect are also addressed. The goal of sampling is to obtain information about large populations with minimal cost, maximum speed and precision.