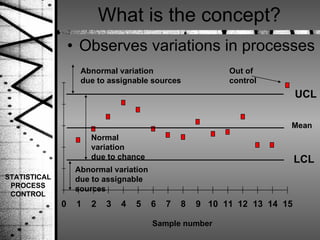
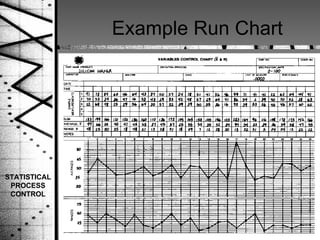
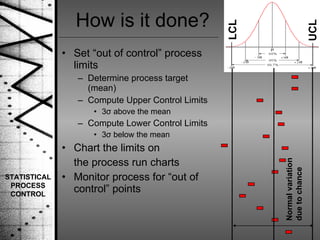
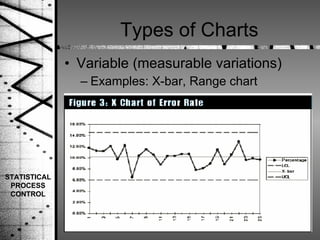
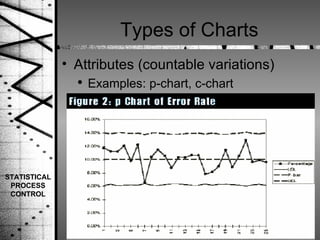
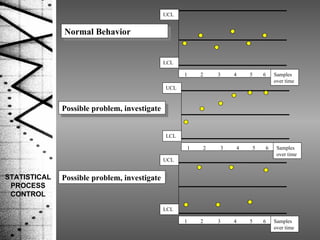
Statistical process control (SPC) is a method of quality control that monitors processes by identifying correctable variations from the target mean. SPC was pioneered by Dr. Walter Shewhart and involves setting upper and lower control limits based on the target mean and standard deviation to determine when a process is out of statistical control. SPC uses variable and attribute control charts to monitor processes over time and identify abnormal variations that require investigation and correction.