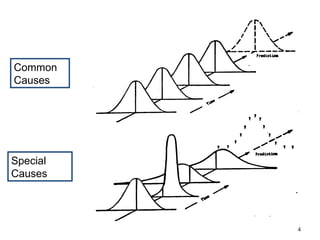
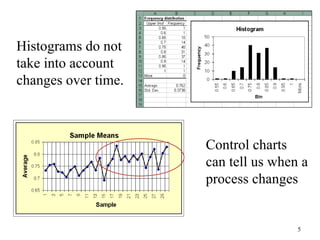
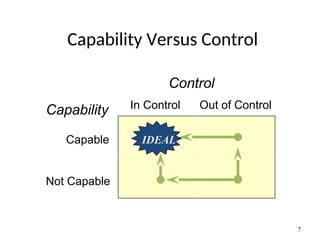
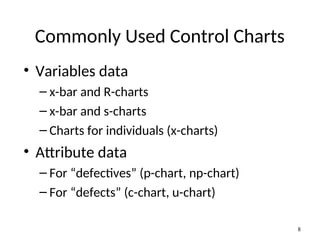
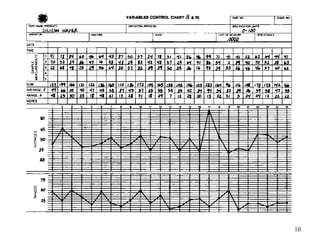
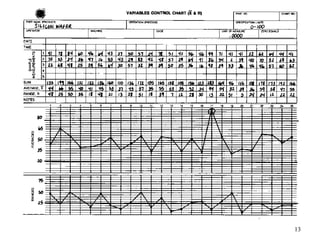
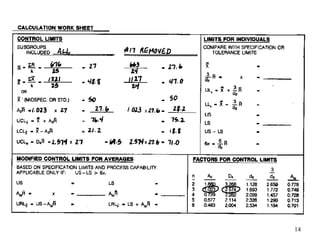
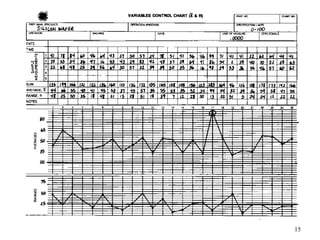
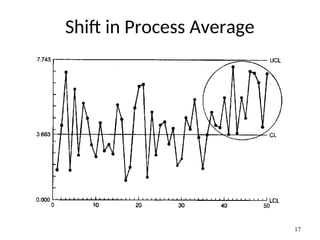
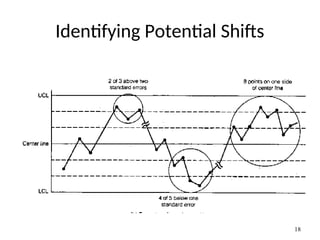
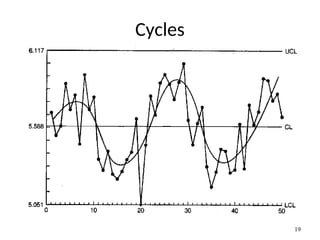
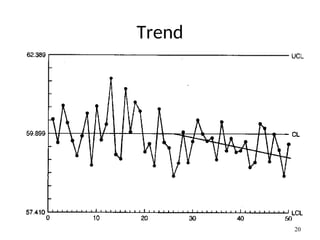
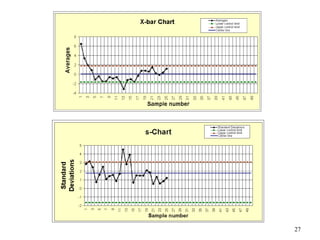
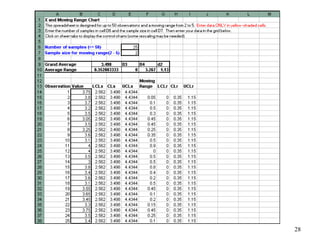
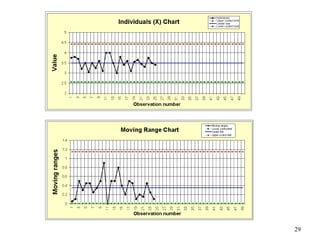
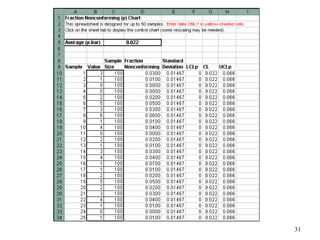
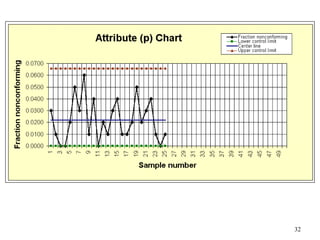
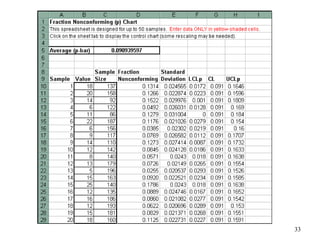
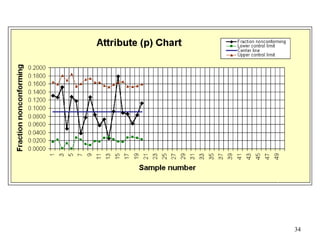
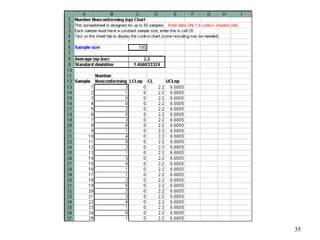
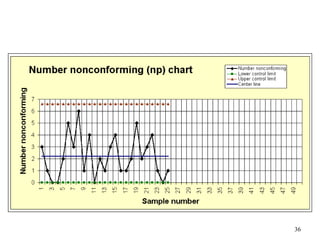
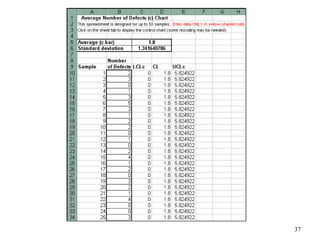
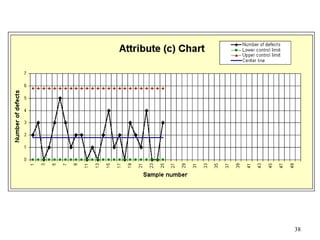
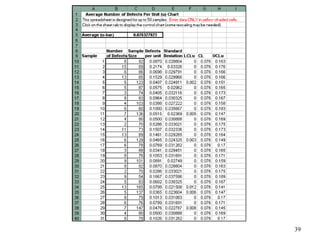
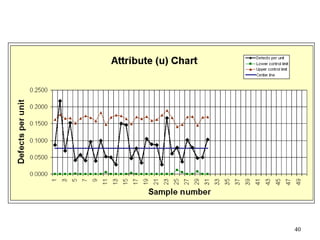
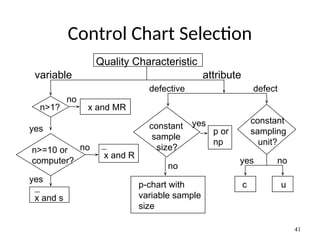
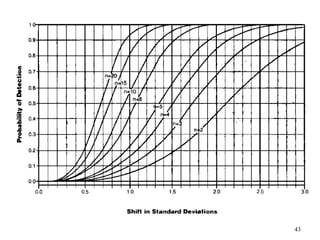
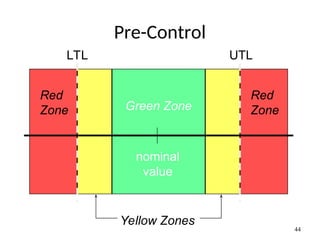
The document discusses Statistical Process Control (SPC), a methodology for monitoring processes to identify variations and maintain quality through control charts. It outlines the concepts of accuracy, precision, control charts for variable and attribute data, and the steps for developing and interpreting these charts. Additionally, it highlights the importance of management commitment and employee training for effective SPC implementation.