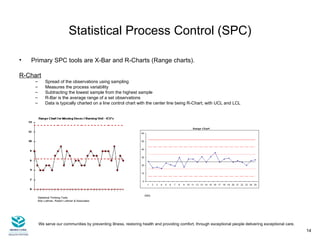
The document discusses statistical process control (SPC) in healthcare. It provides an overview of SPC, including its history and key elements like control charts. Control charts are the primary SPC tool and help determine whether a process is stable or experiencing special cause variations that require investigation and process improvement. The document outlines how SPC can be used to monitor various healthcare processes, detect problems early, and drive process improvement.
![Statistical Process Control in Healthcare Thursday, July 10, 2008 Christy Dean-Benson, BSCIS, MCSE, HCM Manager, Clinical Informatics and Analysis Moses Cone Health System (MCHS) [email_address] 336-832-8724](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/VHASPCWebinar-123135003075-phpapp01/85/Vha-Spc-Webinar-1-320.jpg)