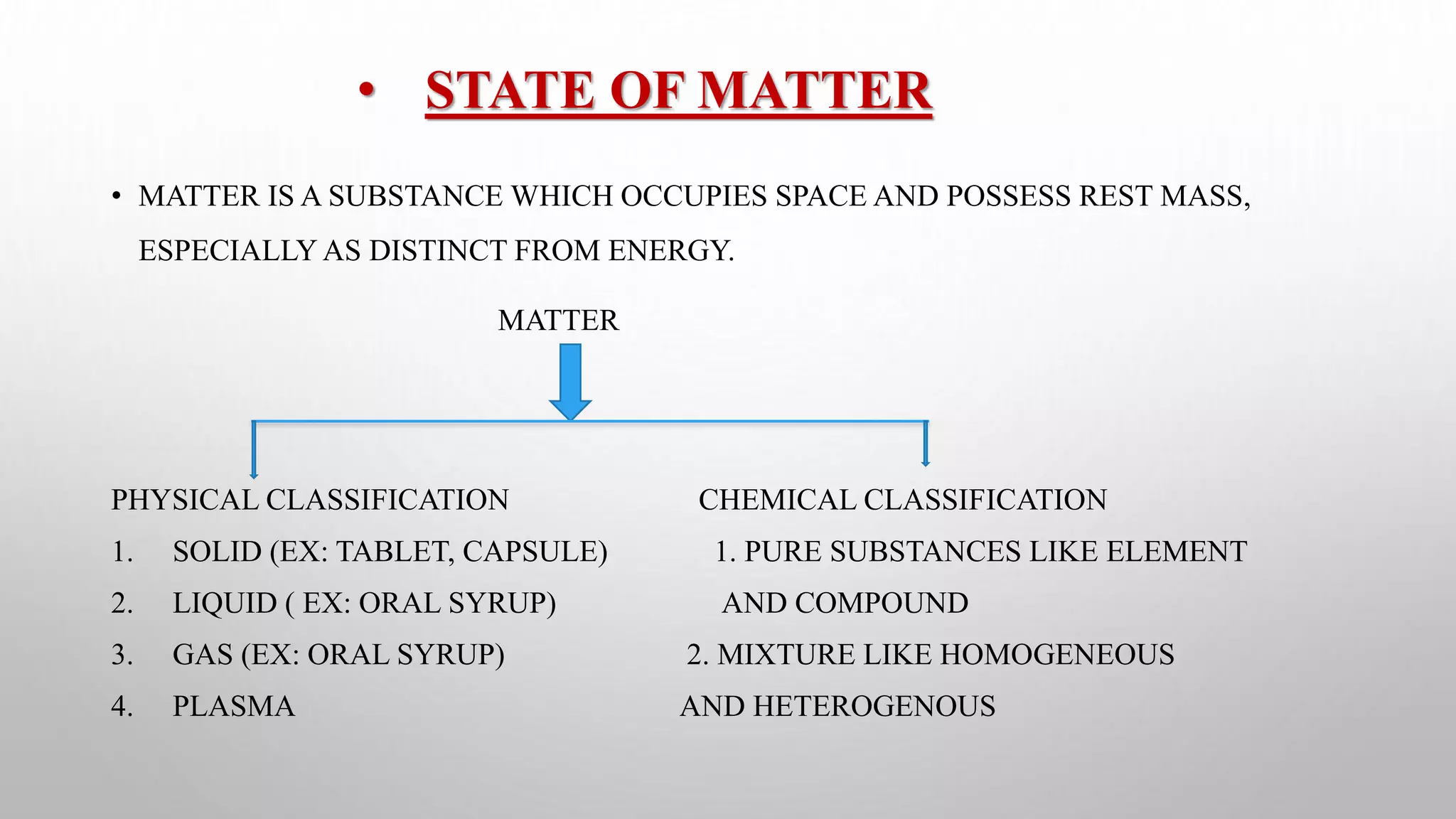
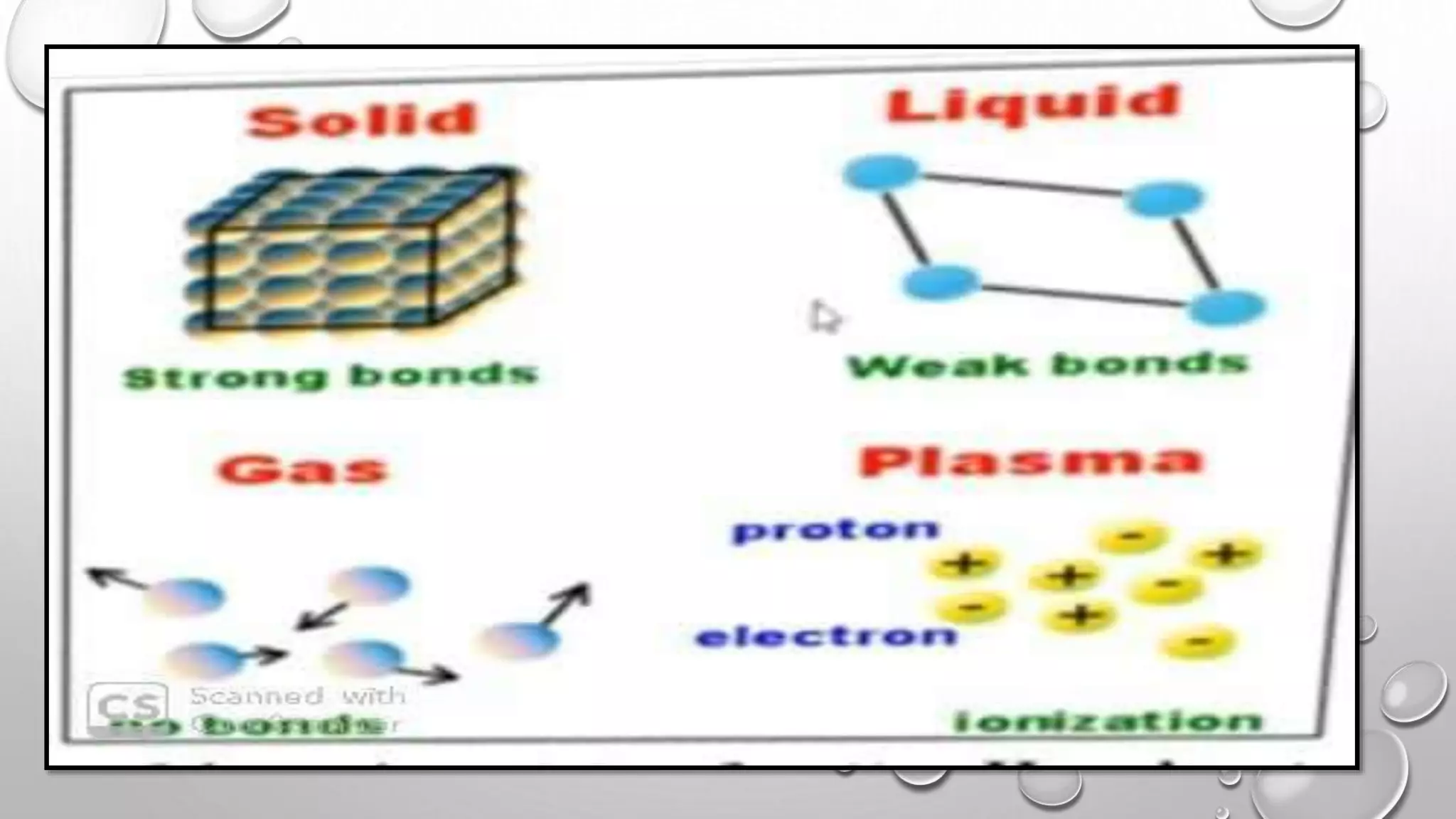
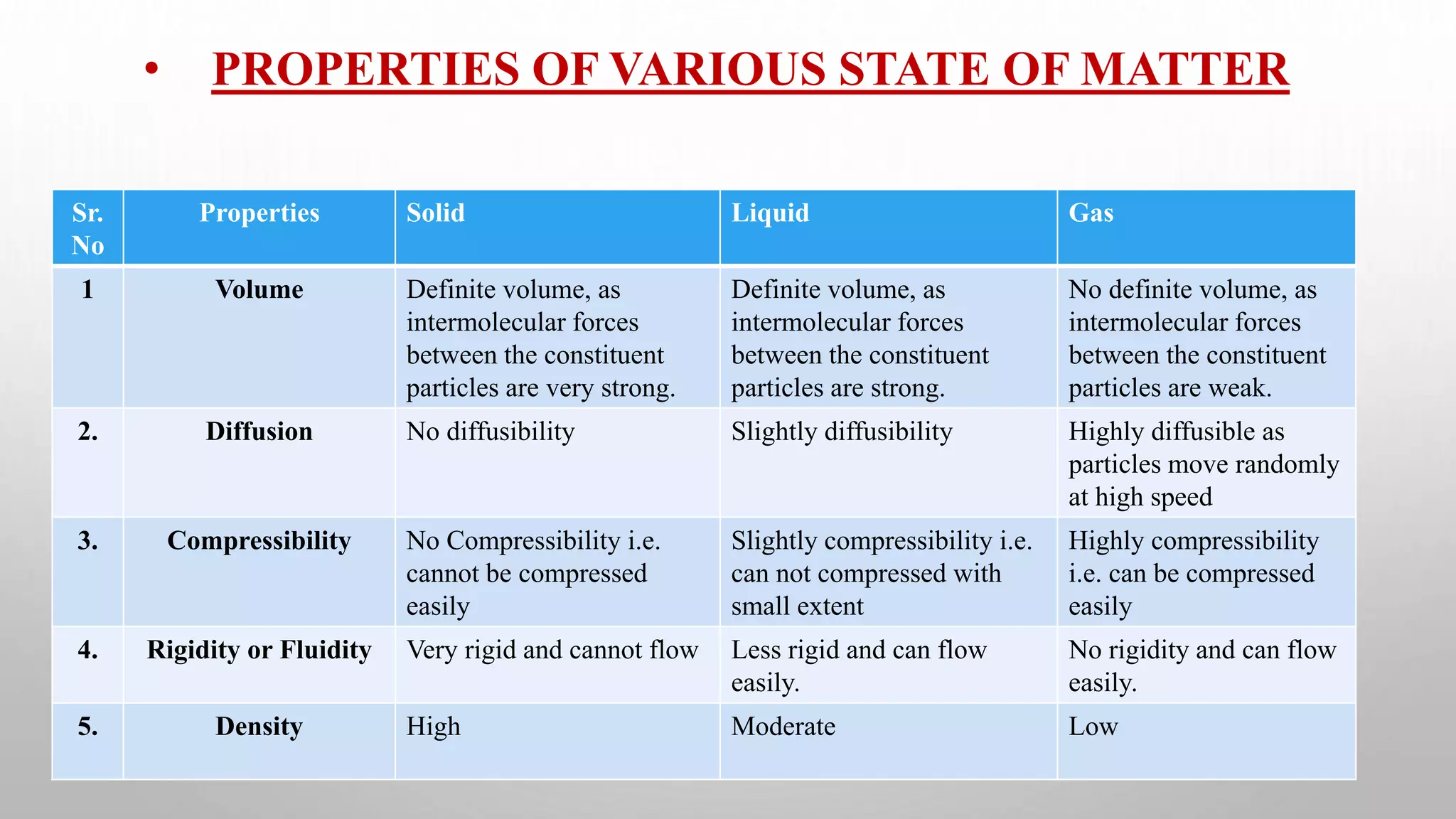
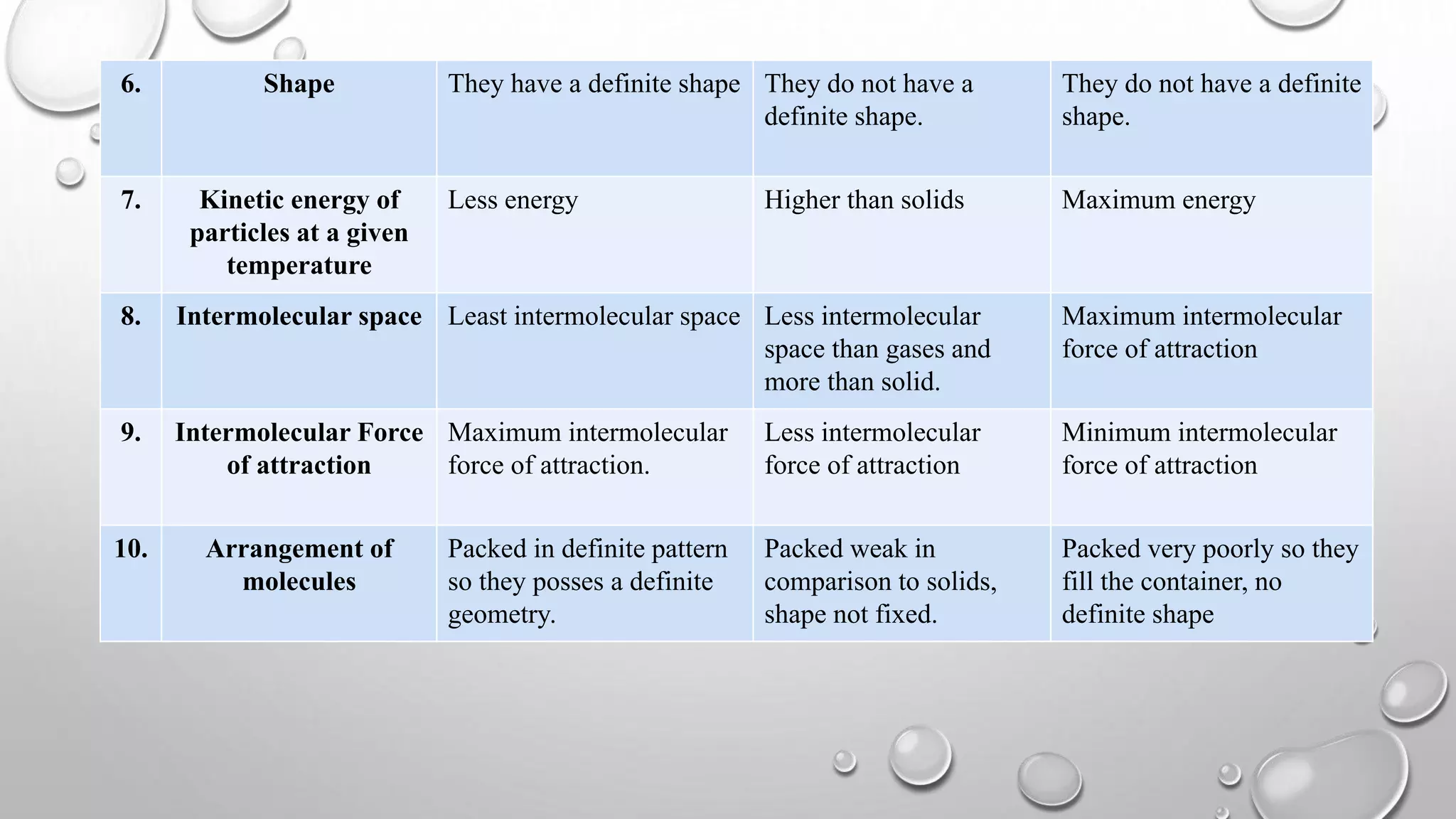
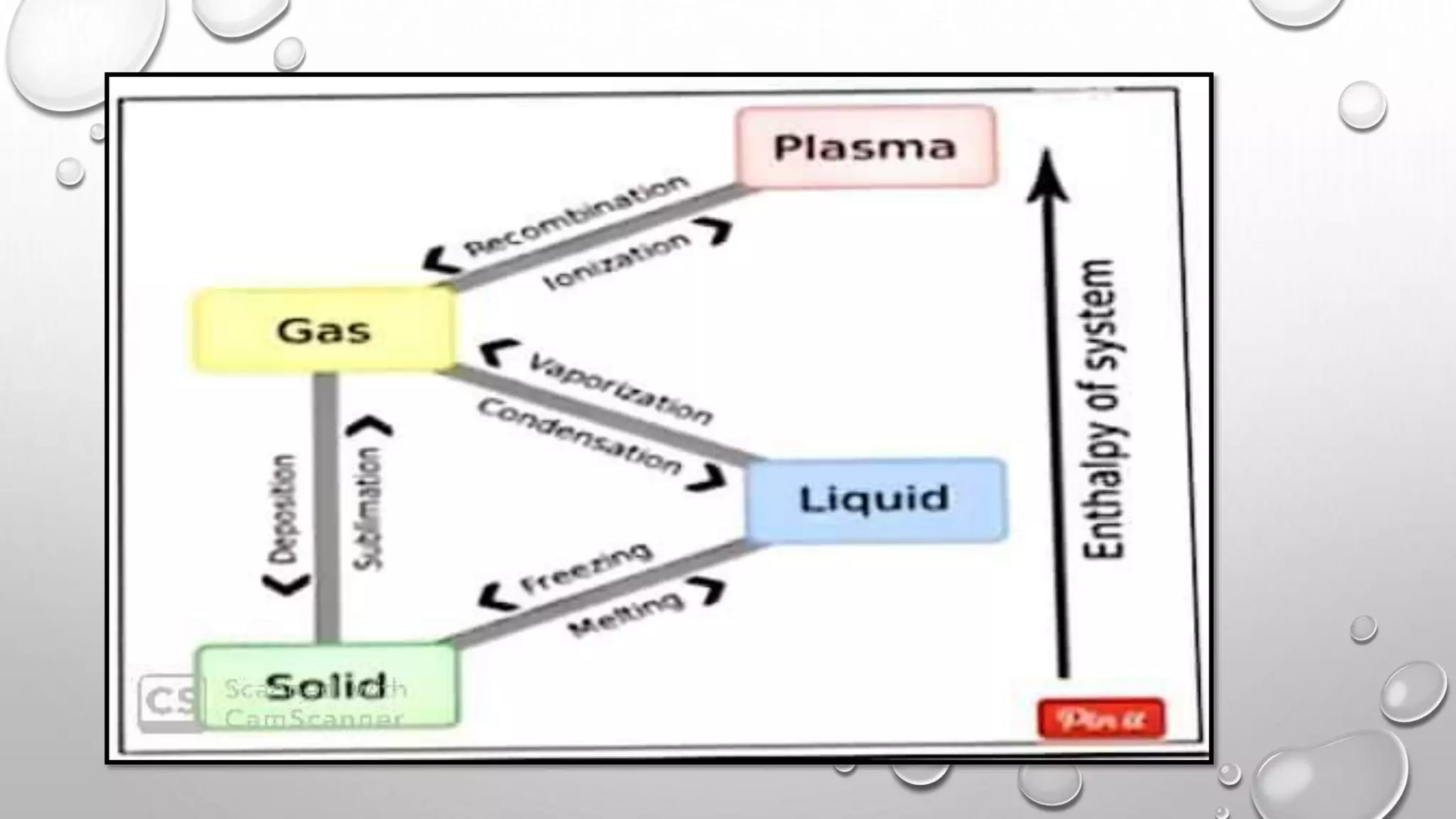
The document discusses the states of matter and their properties, including solids, liquids, gases, and plasma, highlighting key differences in volume, diffusibility, compressibility, and molecular arrangement. It defines various phase transitions such as freezing, melting, deposition, sublimation, vaporization, and condensation while explaining the concepts of enthalpy and entropy. Additionally, it introduces the concept of the triple point for substances, particularly noting that for water it occurs at 273.16K and 611.2Pa.