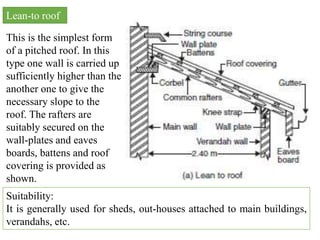
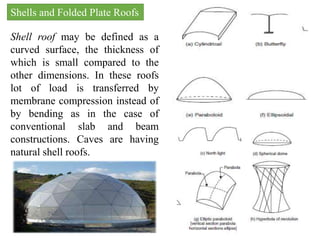
The document discusses different types of roofs for buildings. It begins by defining a roof as the uppermost part of a building that protects it from rain, heat, snow, wind, etc. and typically consists of structural elements like trusses, slabs, and domes that support roof coverings. It then covers requirements for good roofs, classifications of pitched/flat/curved roofs, and provides details on flat roofs, pitched roofs including single, double purlin, and trussed roofs, and finally shell and folded plate roofs.