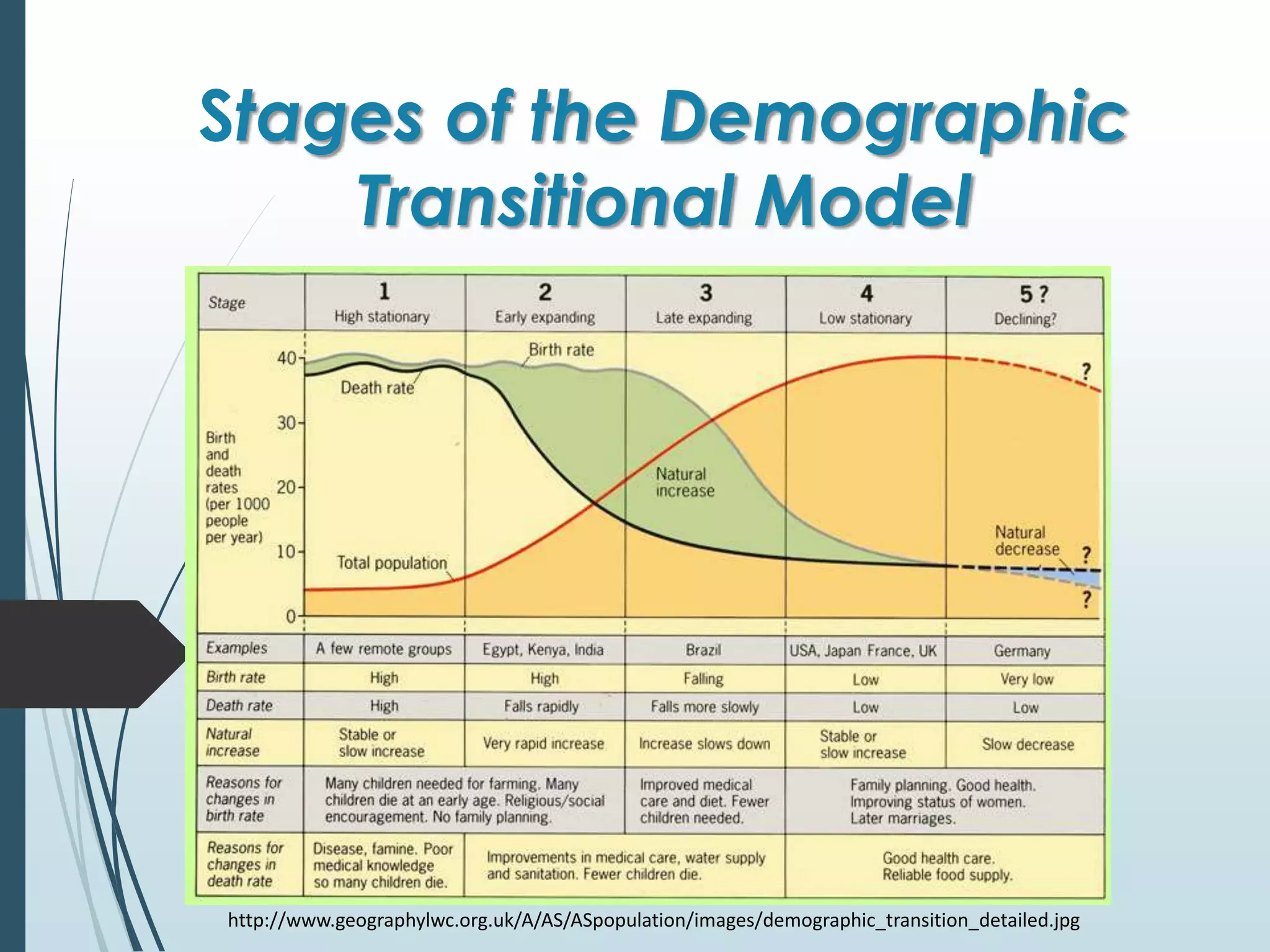
The document outlines the 5 stages of the demographic transitional model:
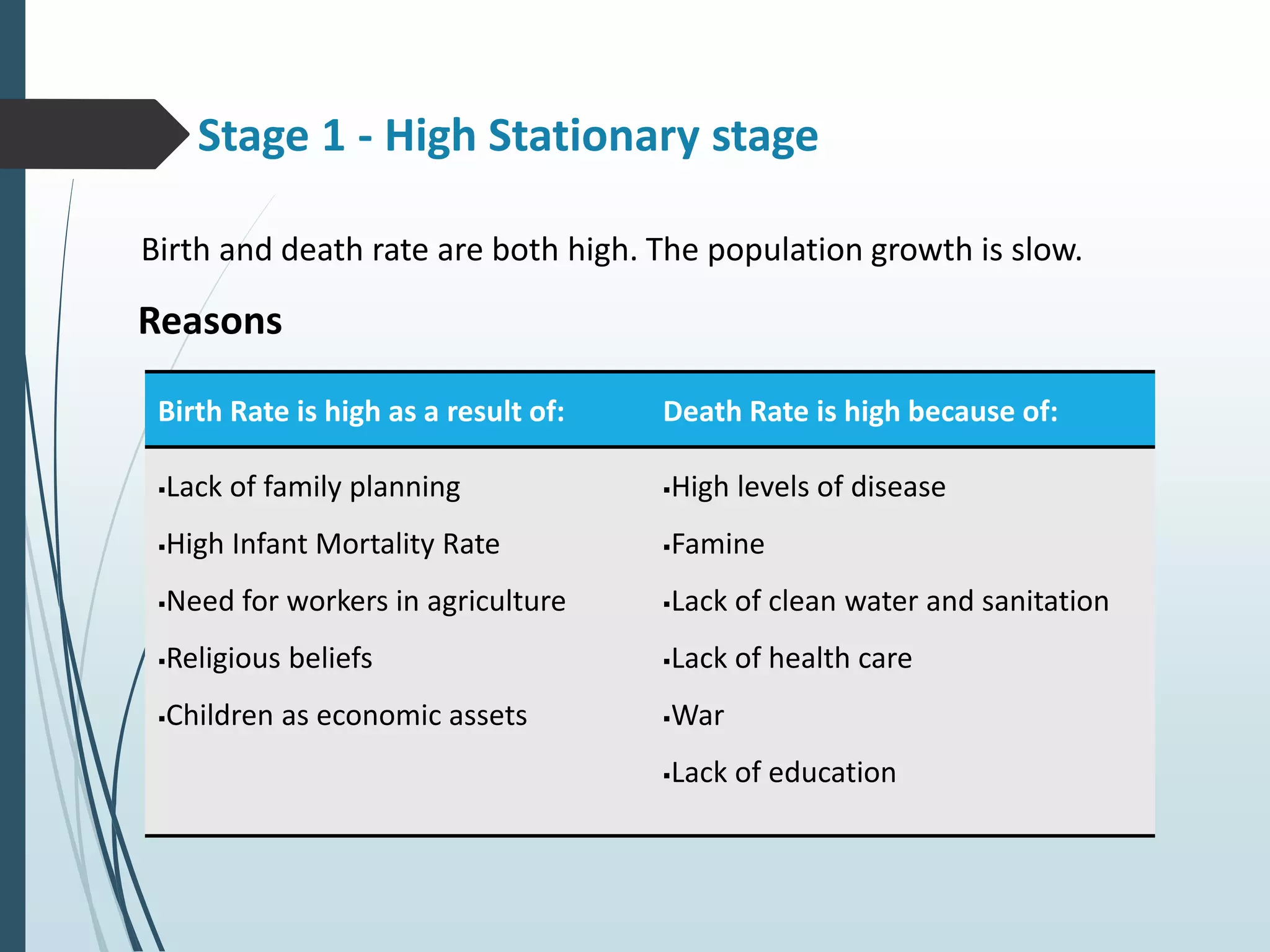
1. High Stationary stage - Both birth and death rates are high resulting in slow population growth due to factors like lack of healthcare and family planning.
2. Early Expanding stage - Birth rate remains high while death rate falls rapidly due to improvements in healthcare and sanitation, causing rapid population increase.
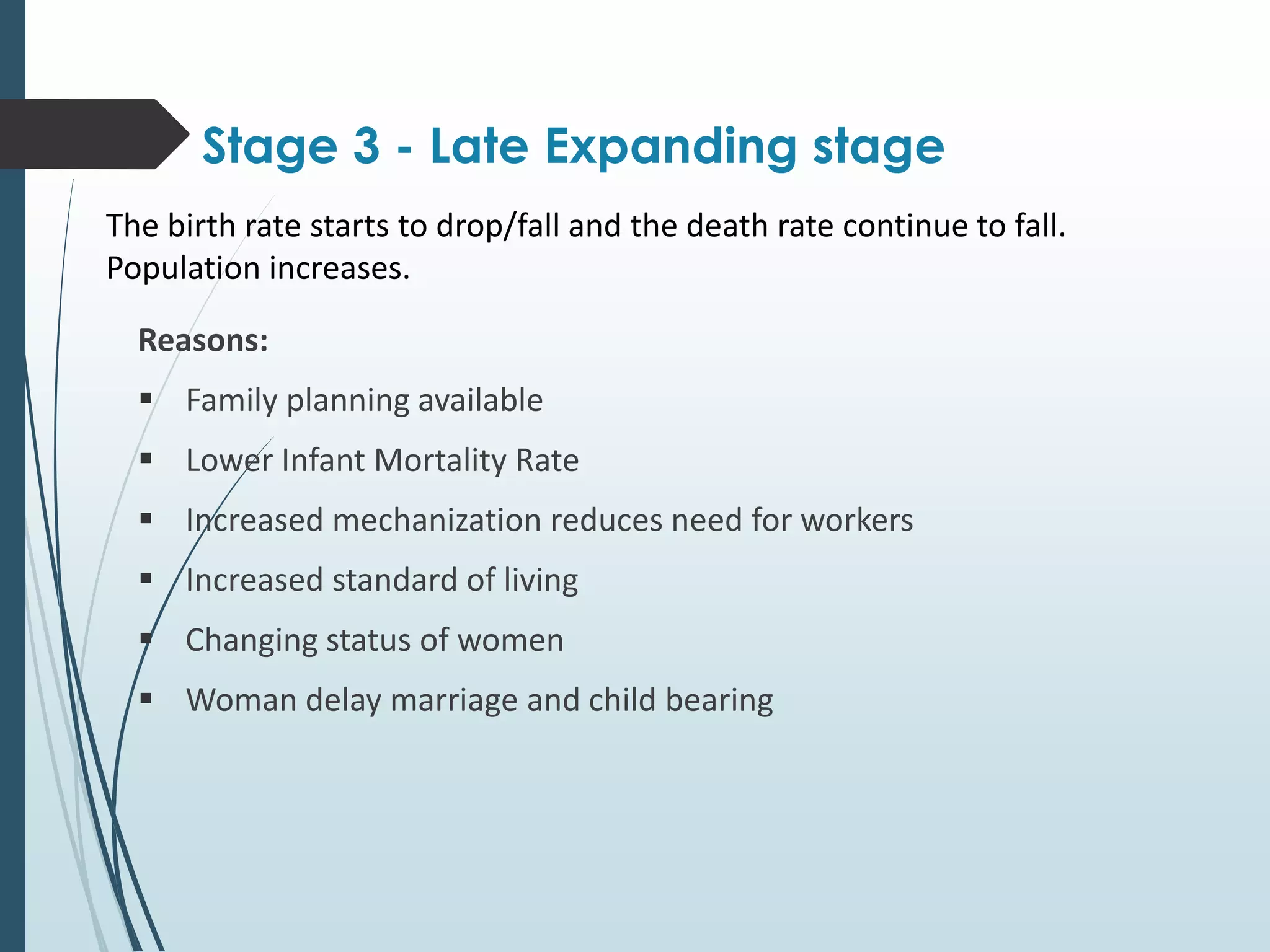
3. Late Expanding stage - Birth rate begins to decline while death rate continues falling, leading to sustained population growth.
4. Low Stationary stage - Both birth and death rates are low, resulting in low steady population growth due to increased education, financial independence, and family planning.
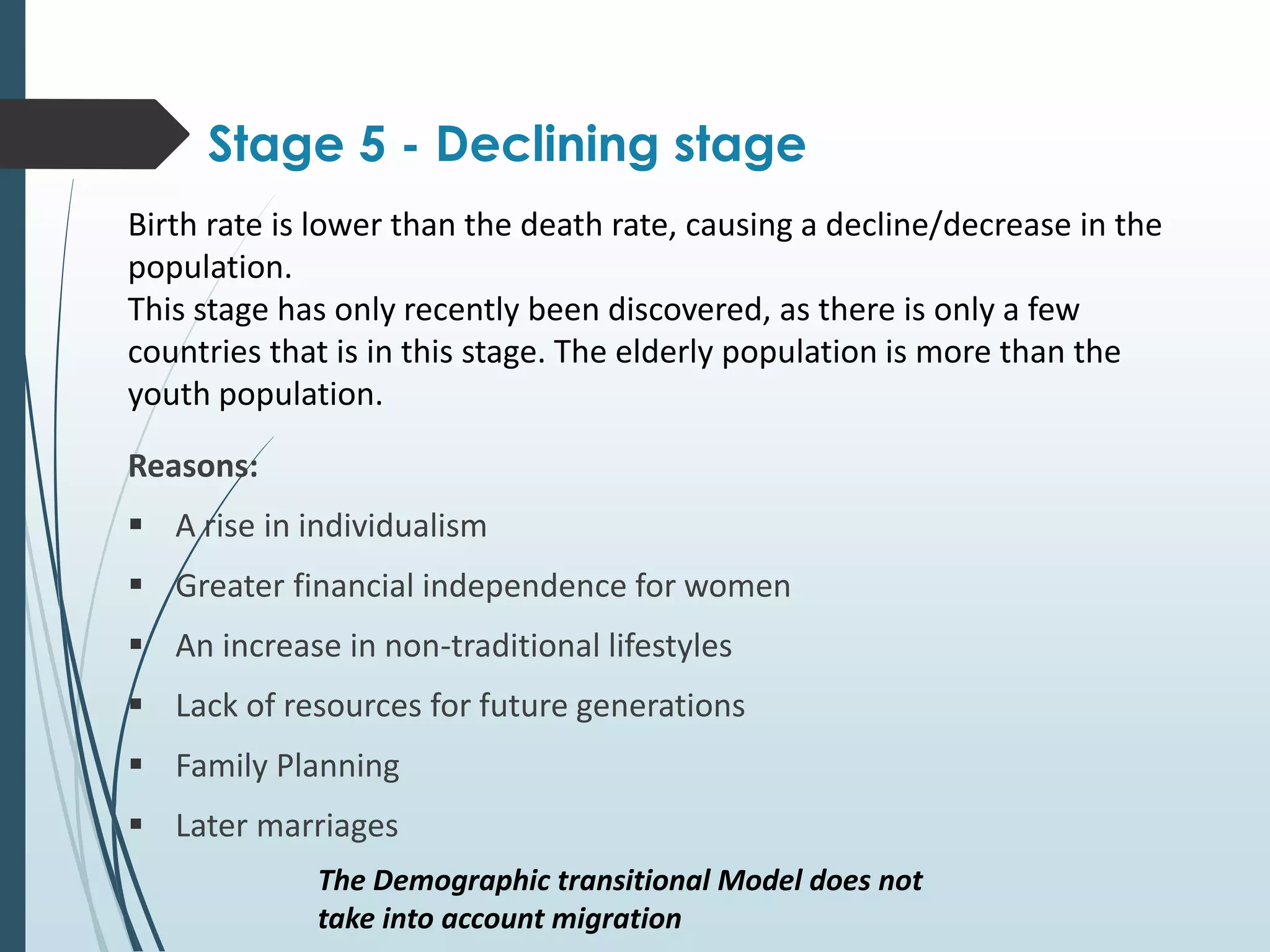
5. Declining stage - Birth