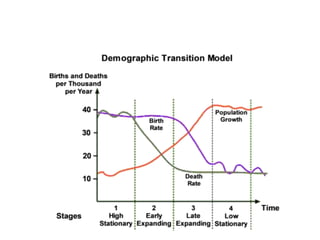
The document explains the demographic transition model through four stages: Stage 1 (high birth and death rates), Stage 2 (high birth rate with declining death rate), Stage 3 (falling birth and death rates), and Stage 4 (both rates low and steady population). Each stage outlines factors influencing birth and death rates, such as healthcare improvements, family planning, and economic conditions. The model illustrates the transition from high to low population growth typical of various countries in different historical contexts.