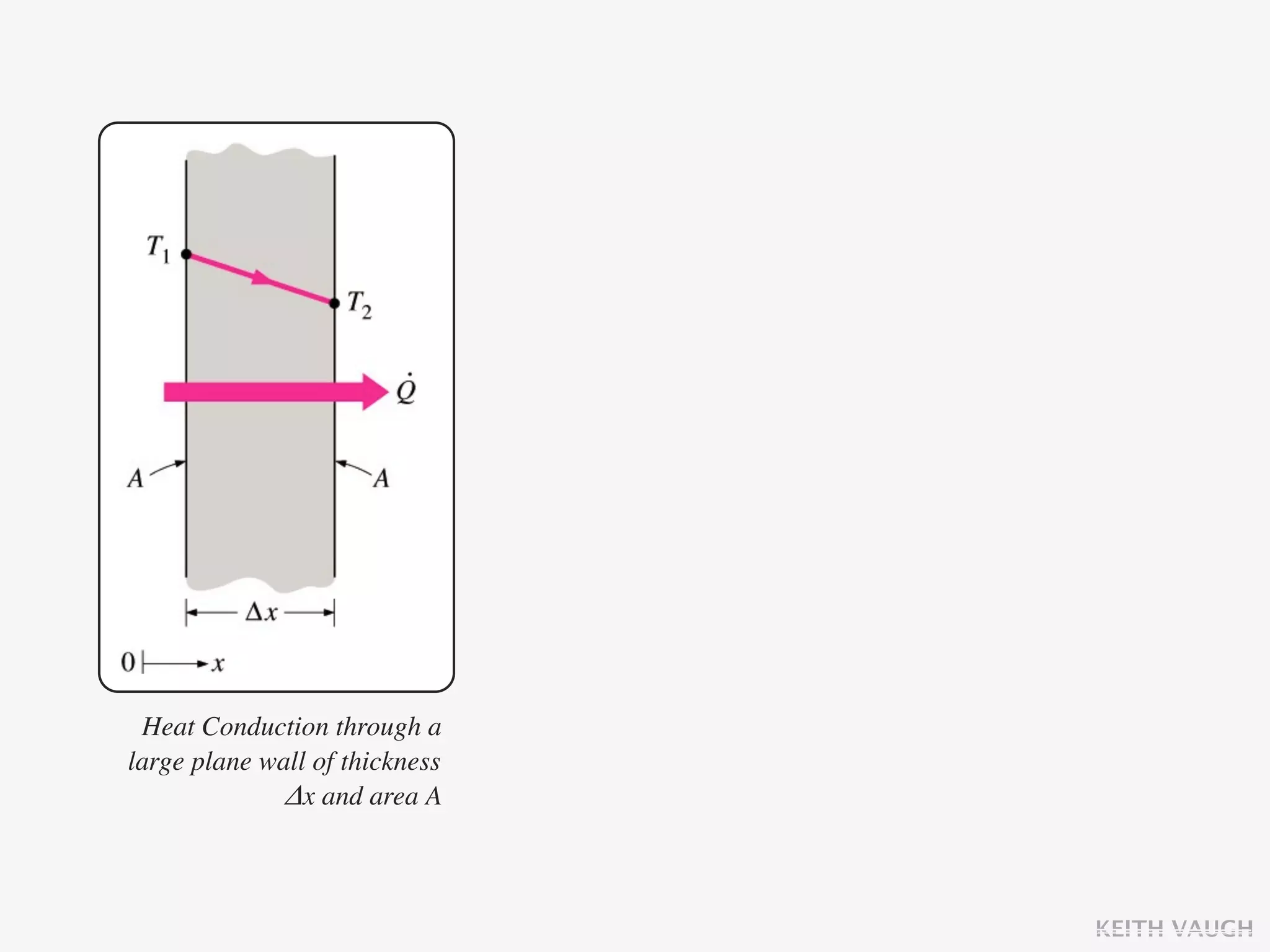
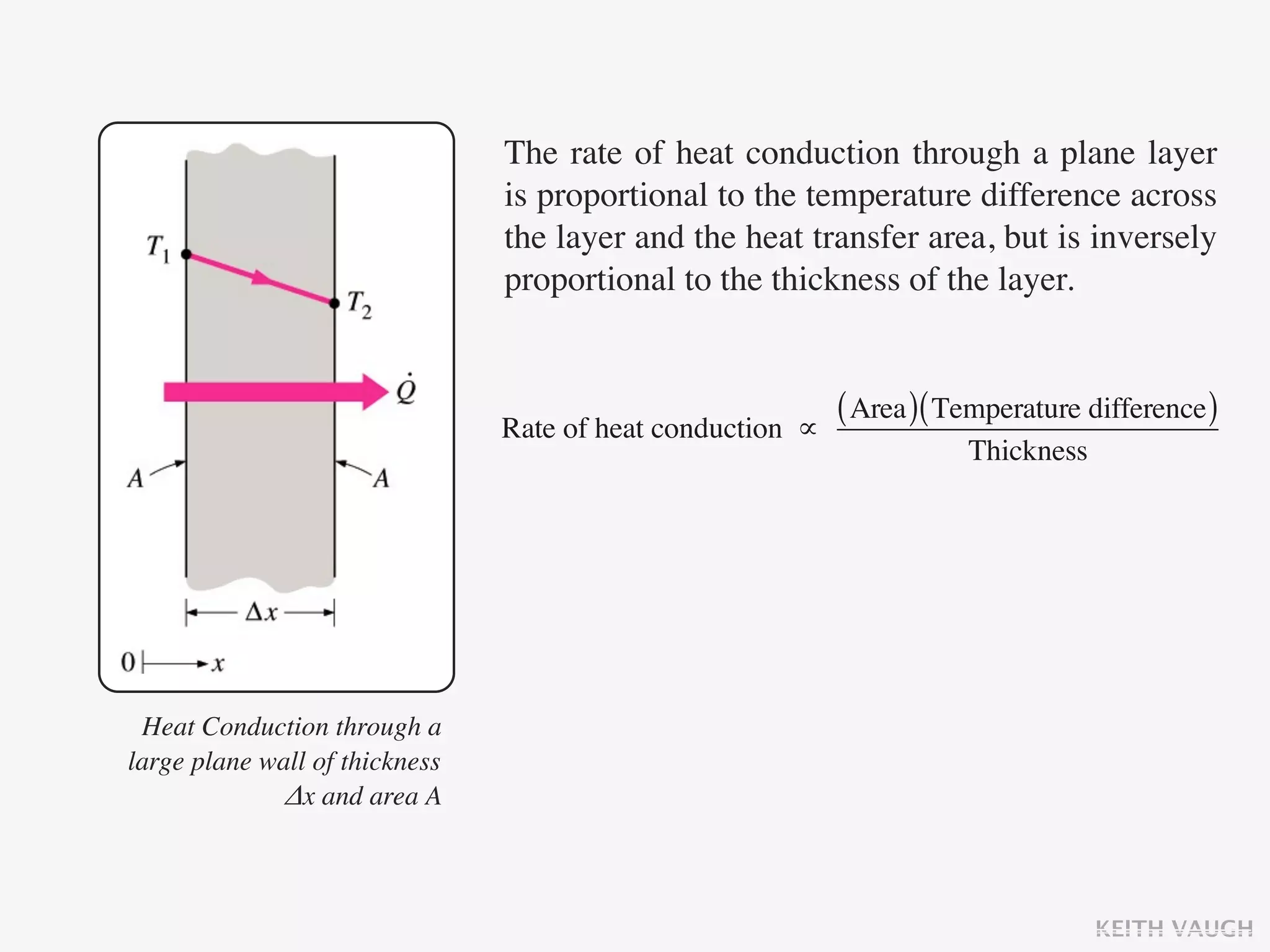
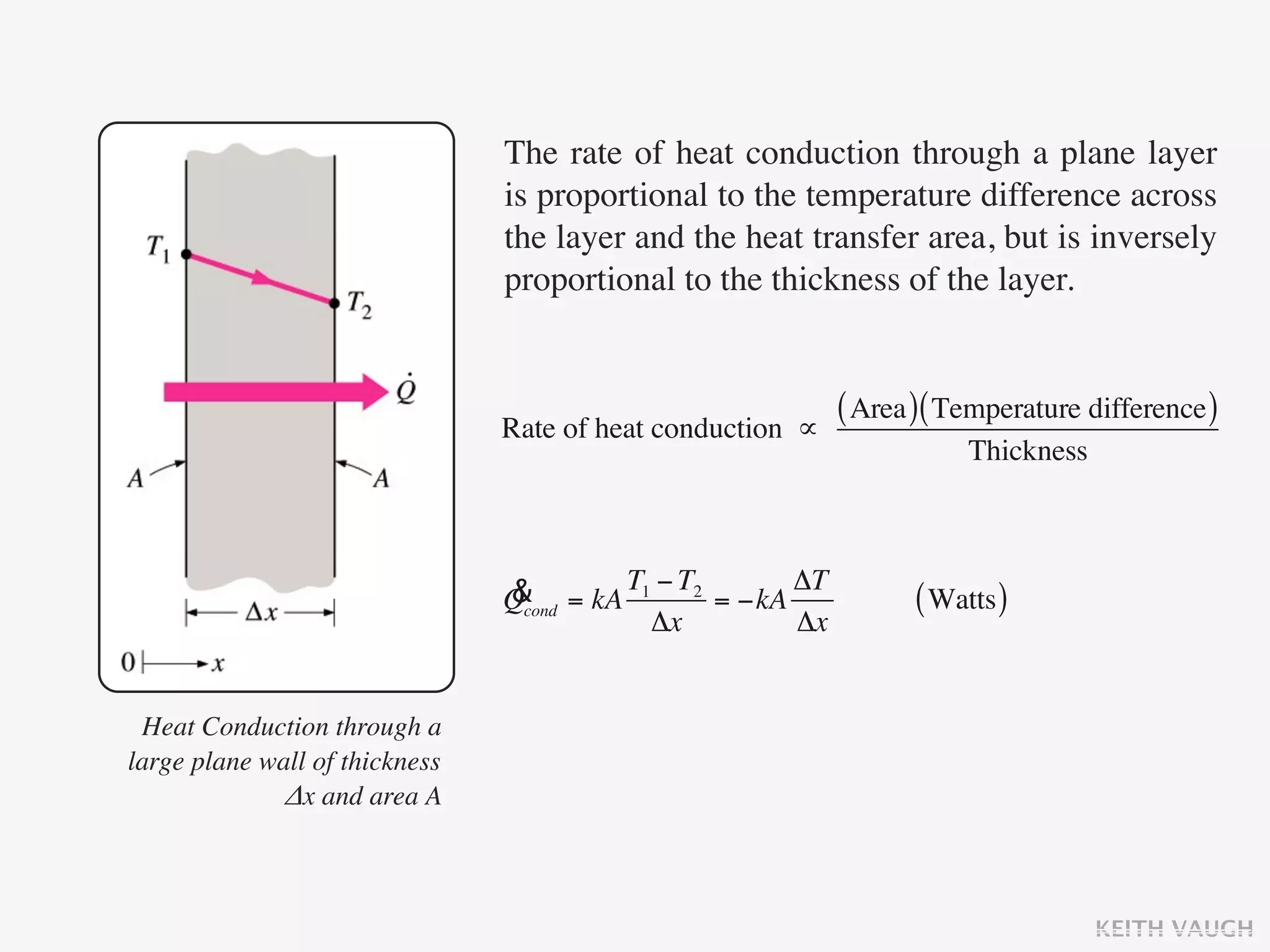
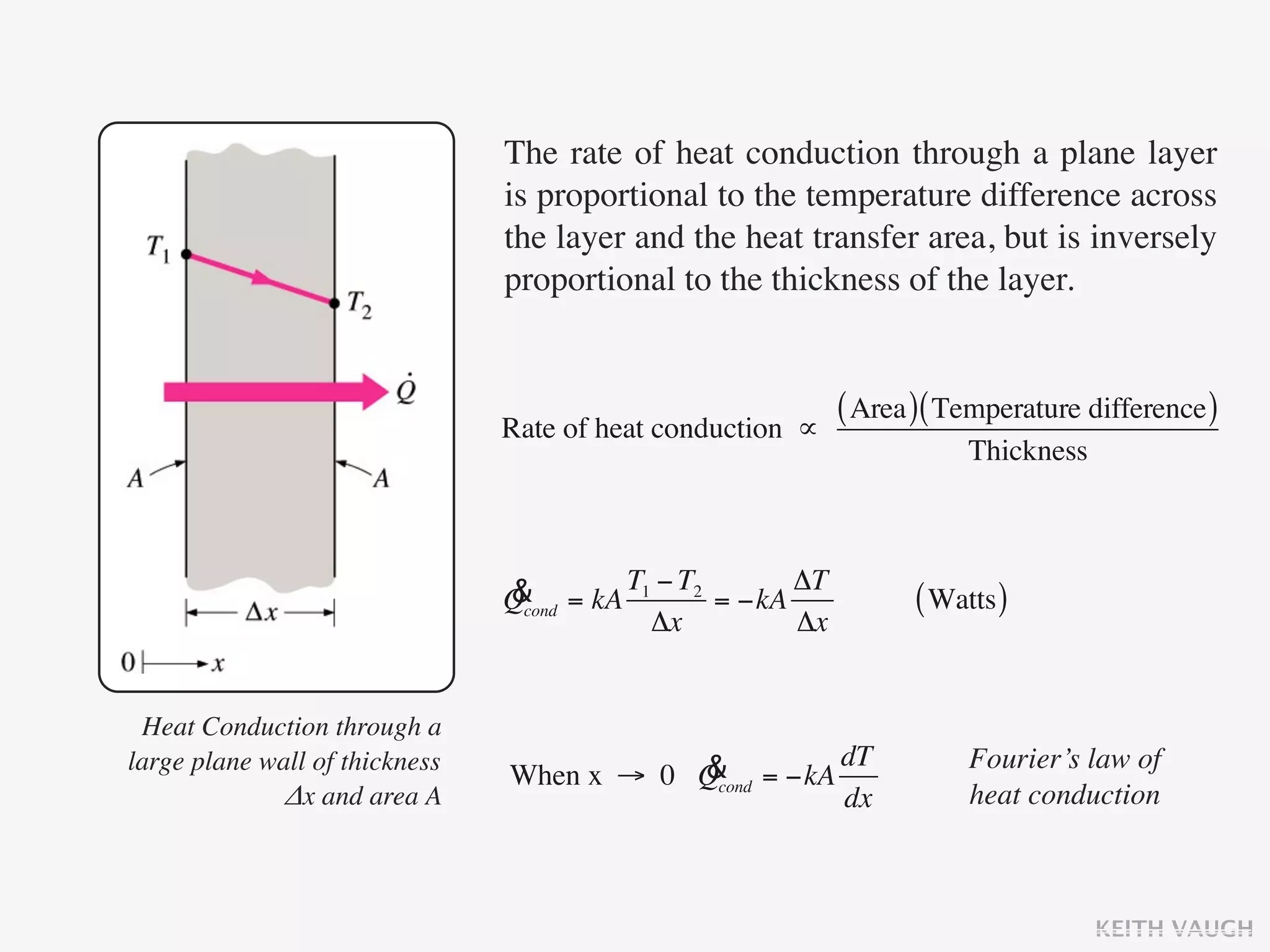
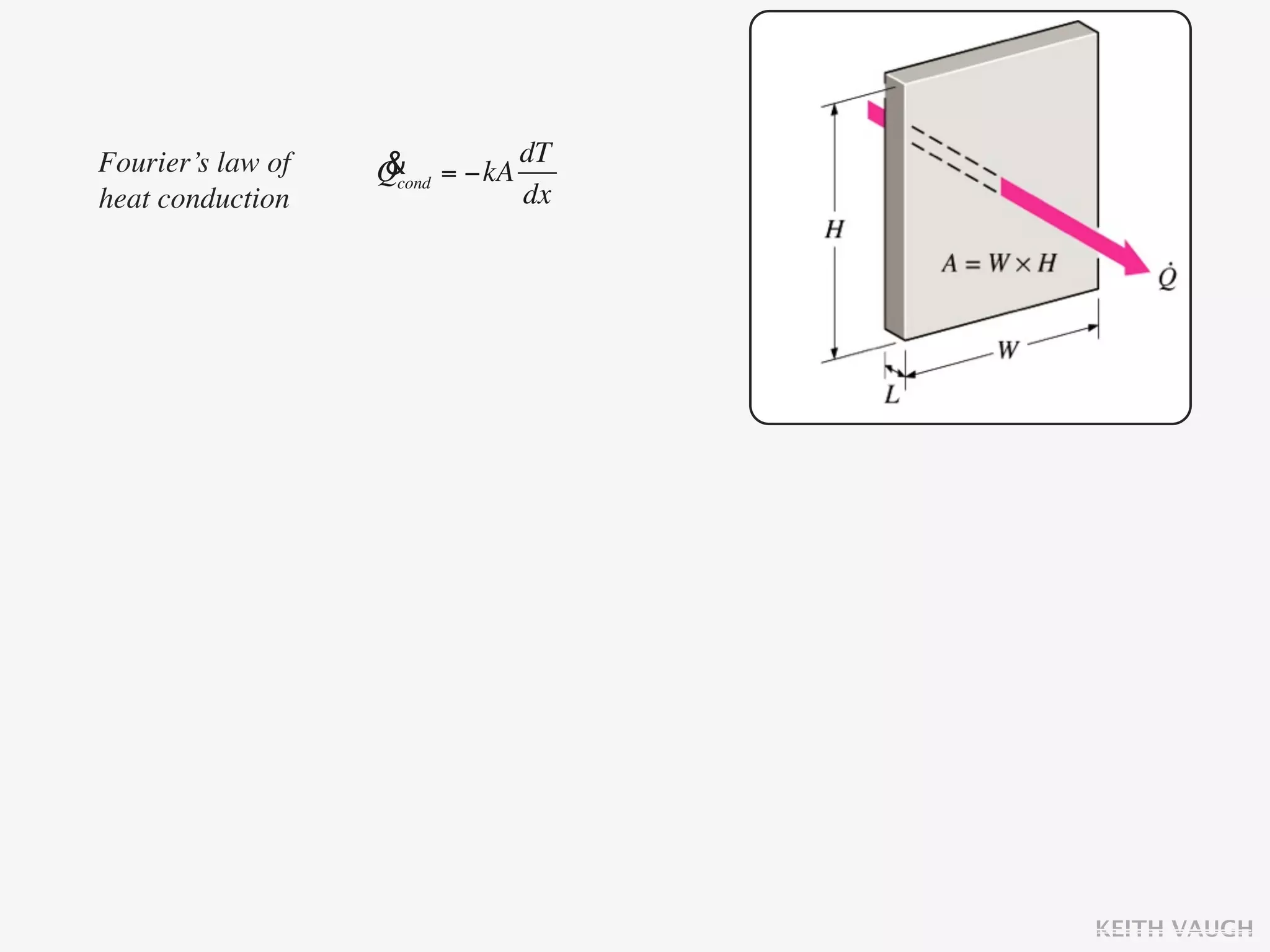
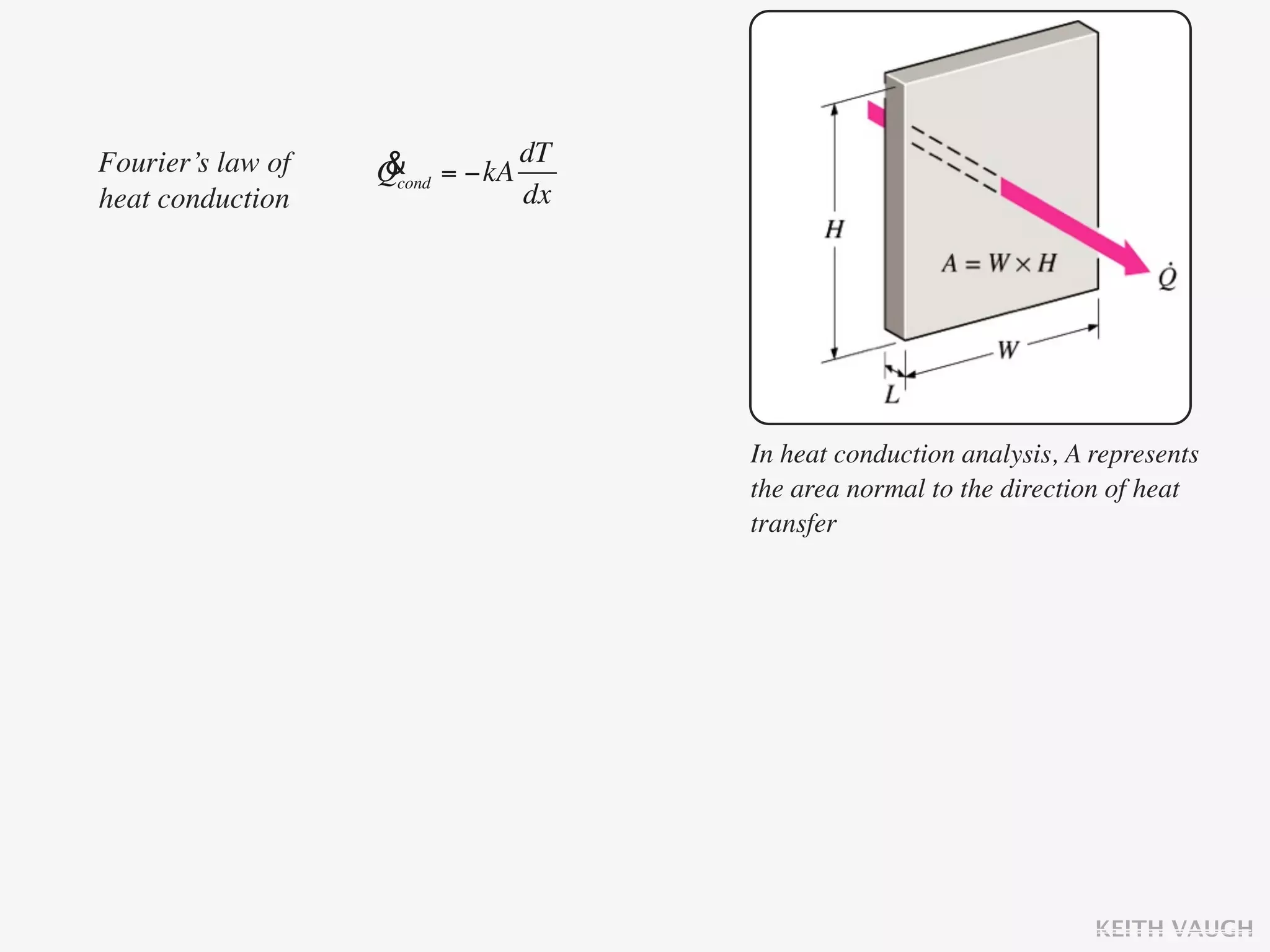
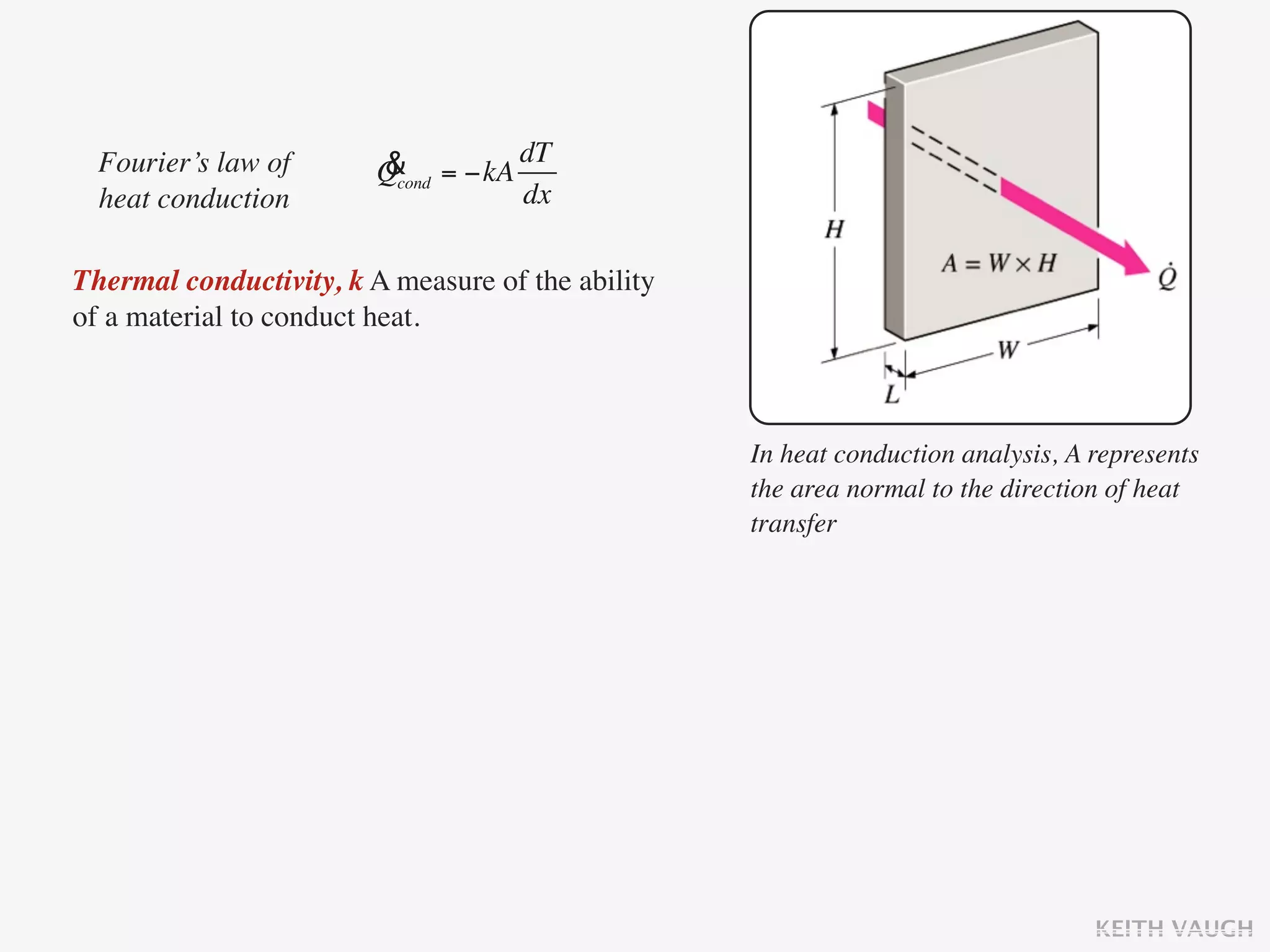
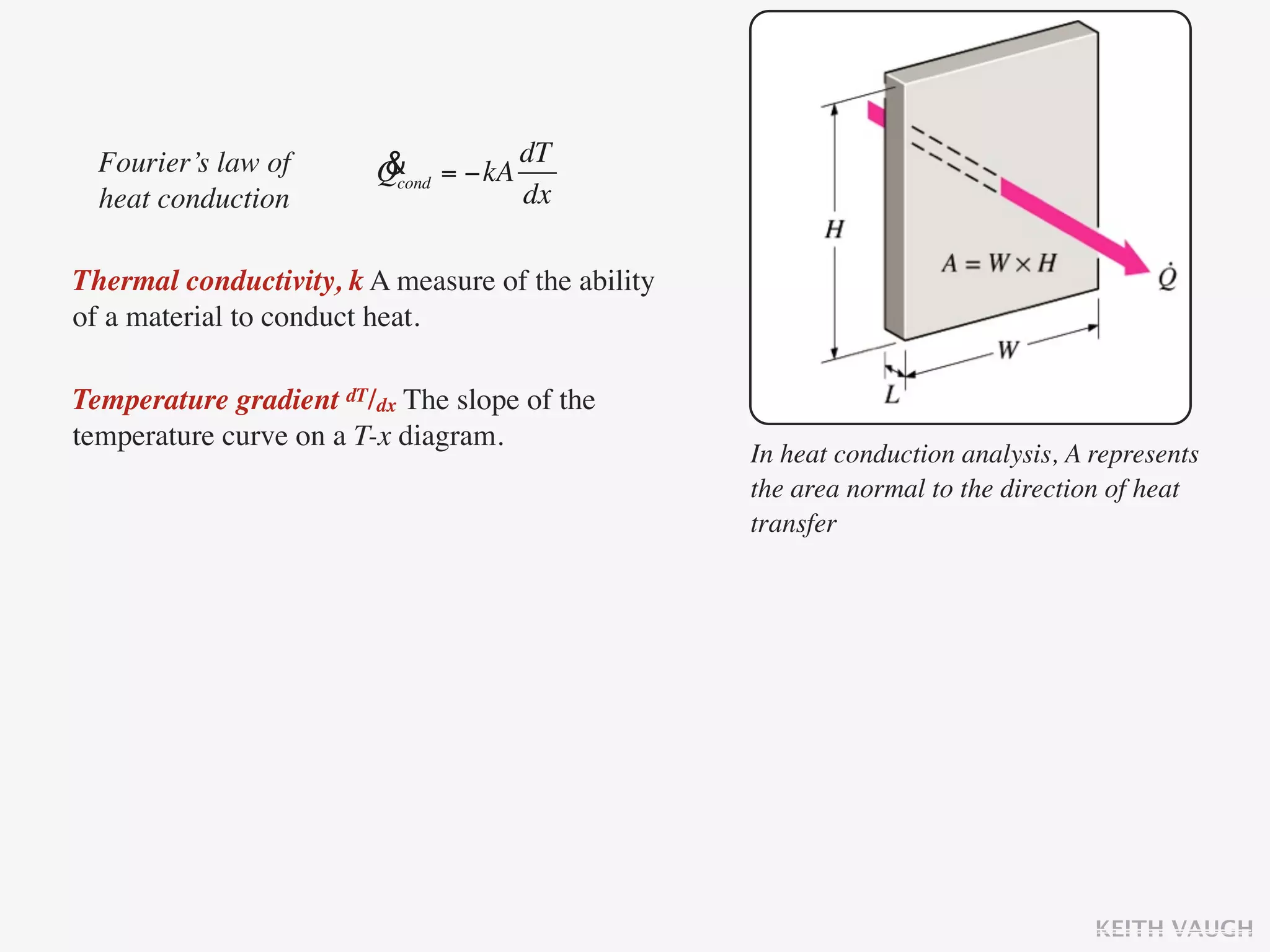
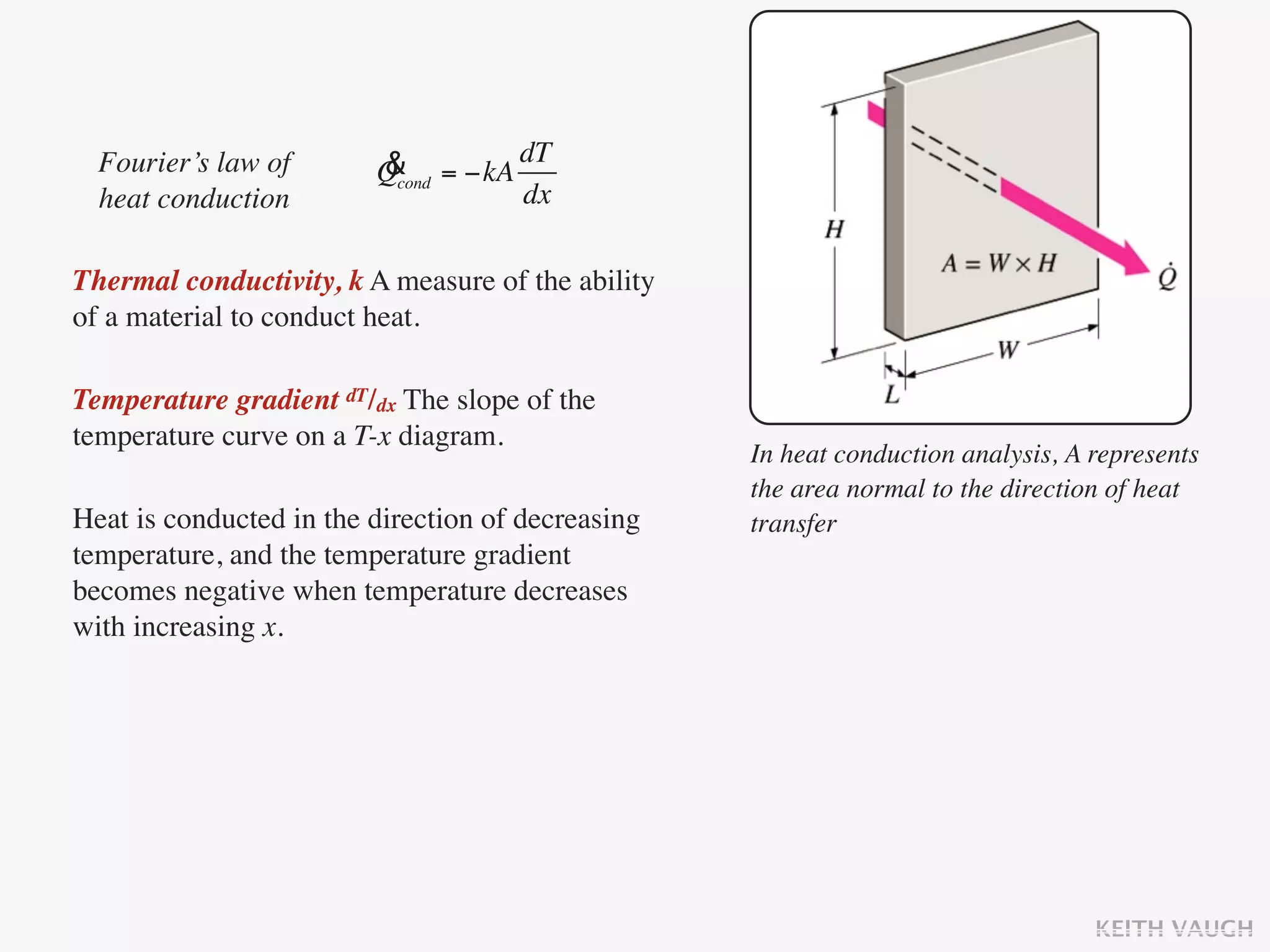
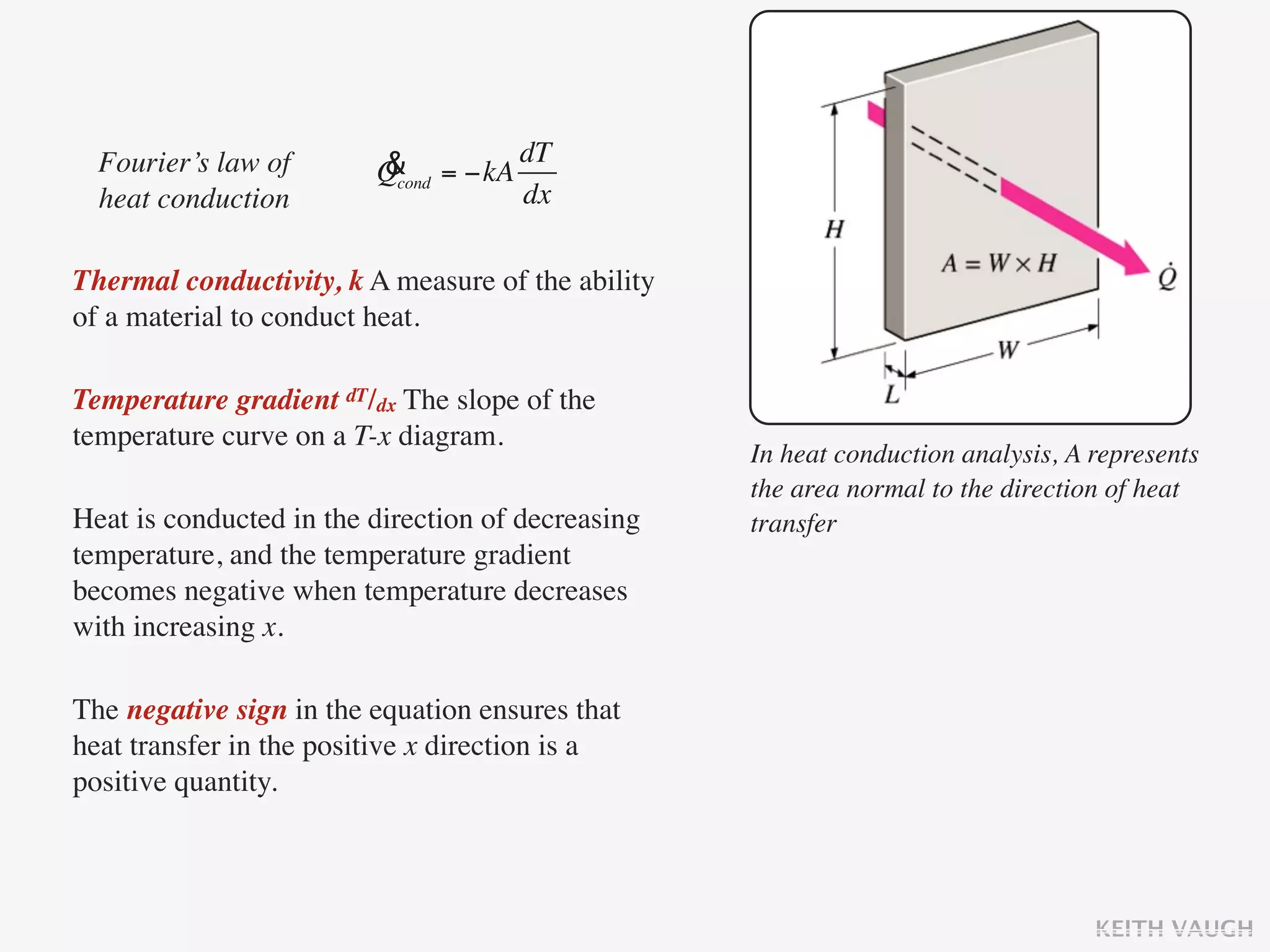
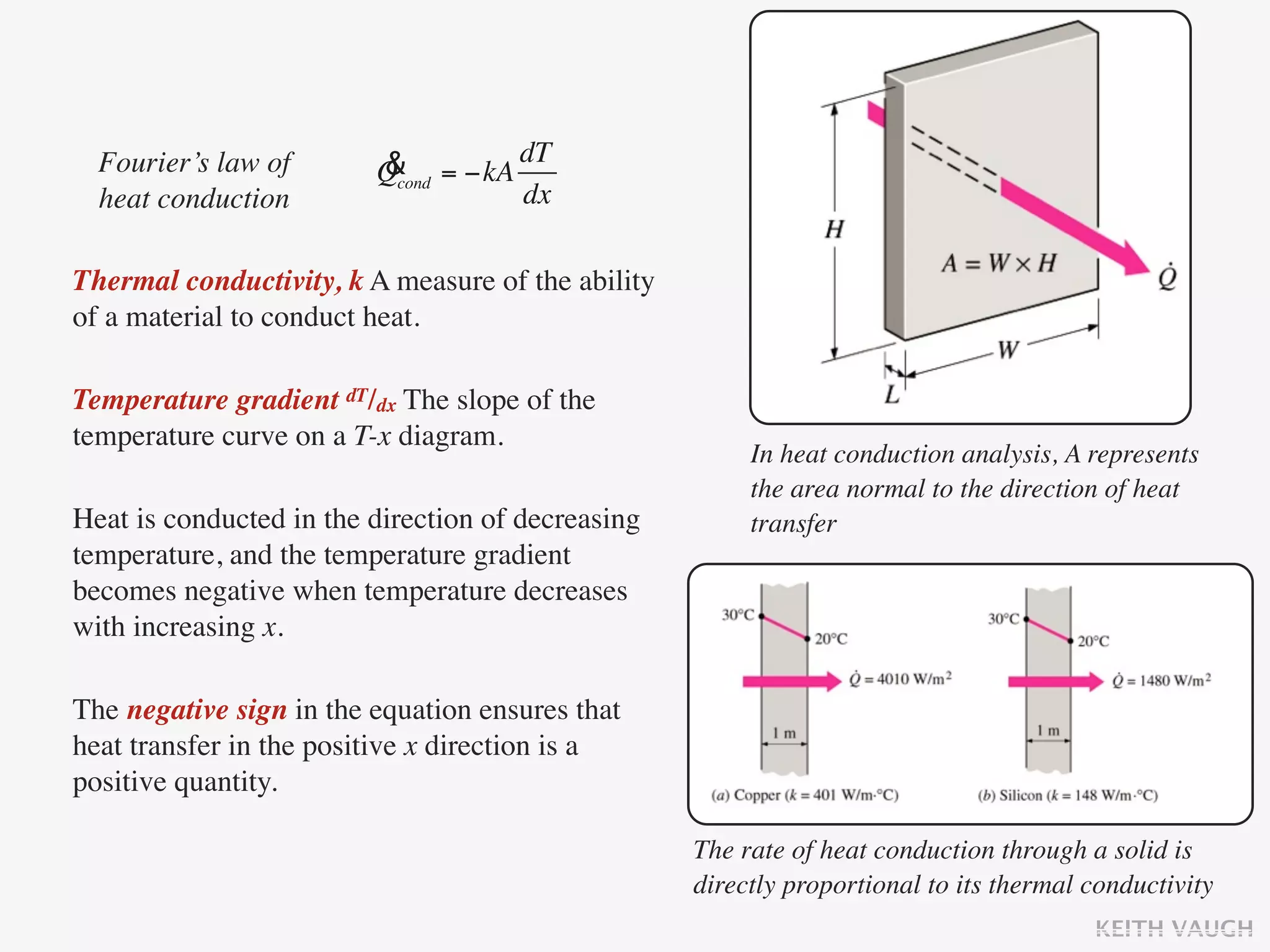
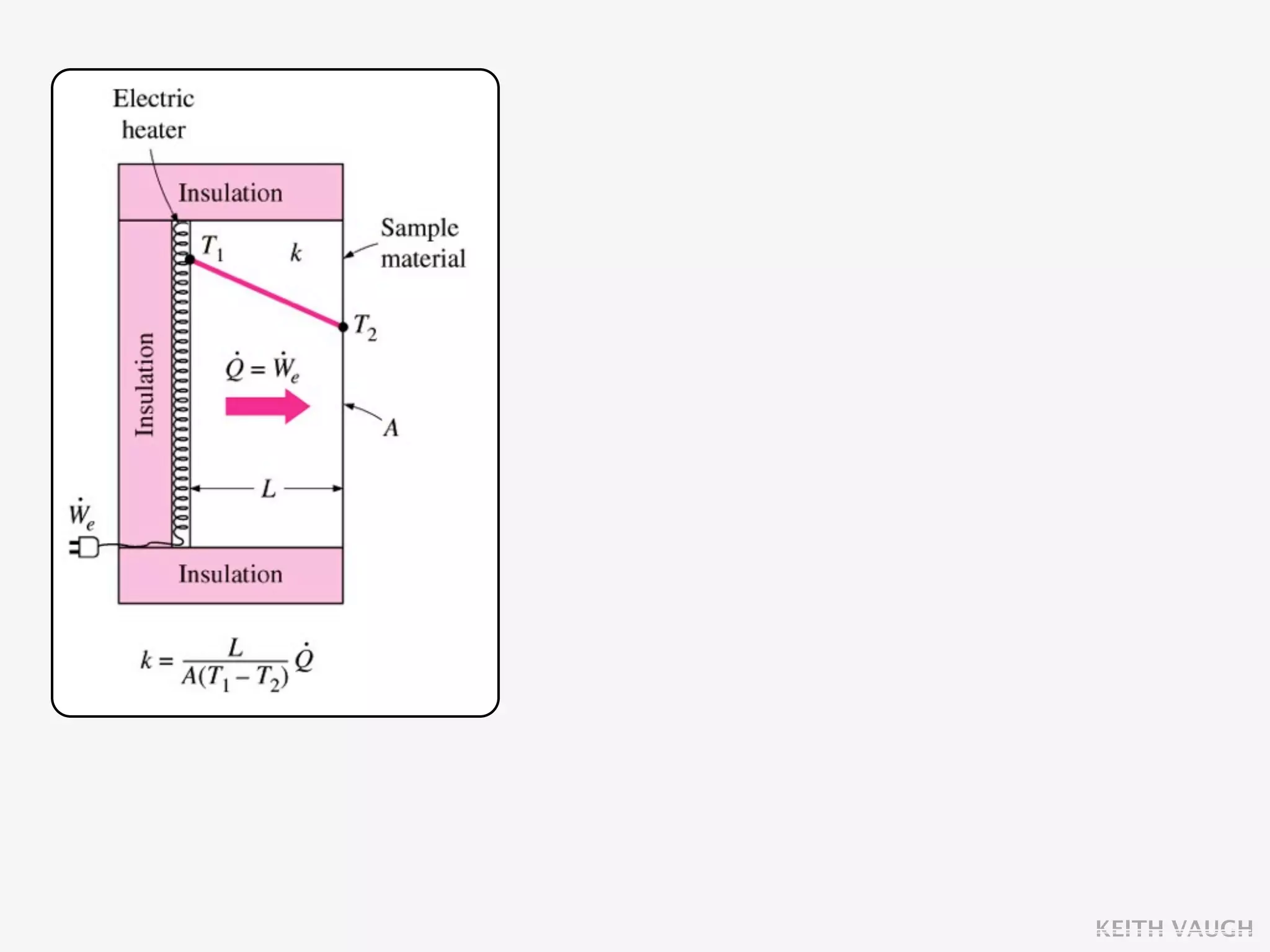
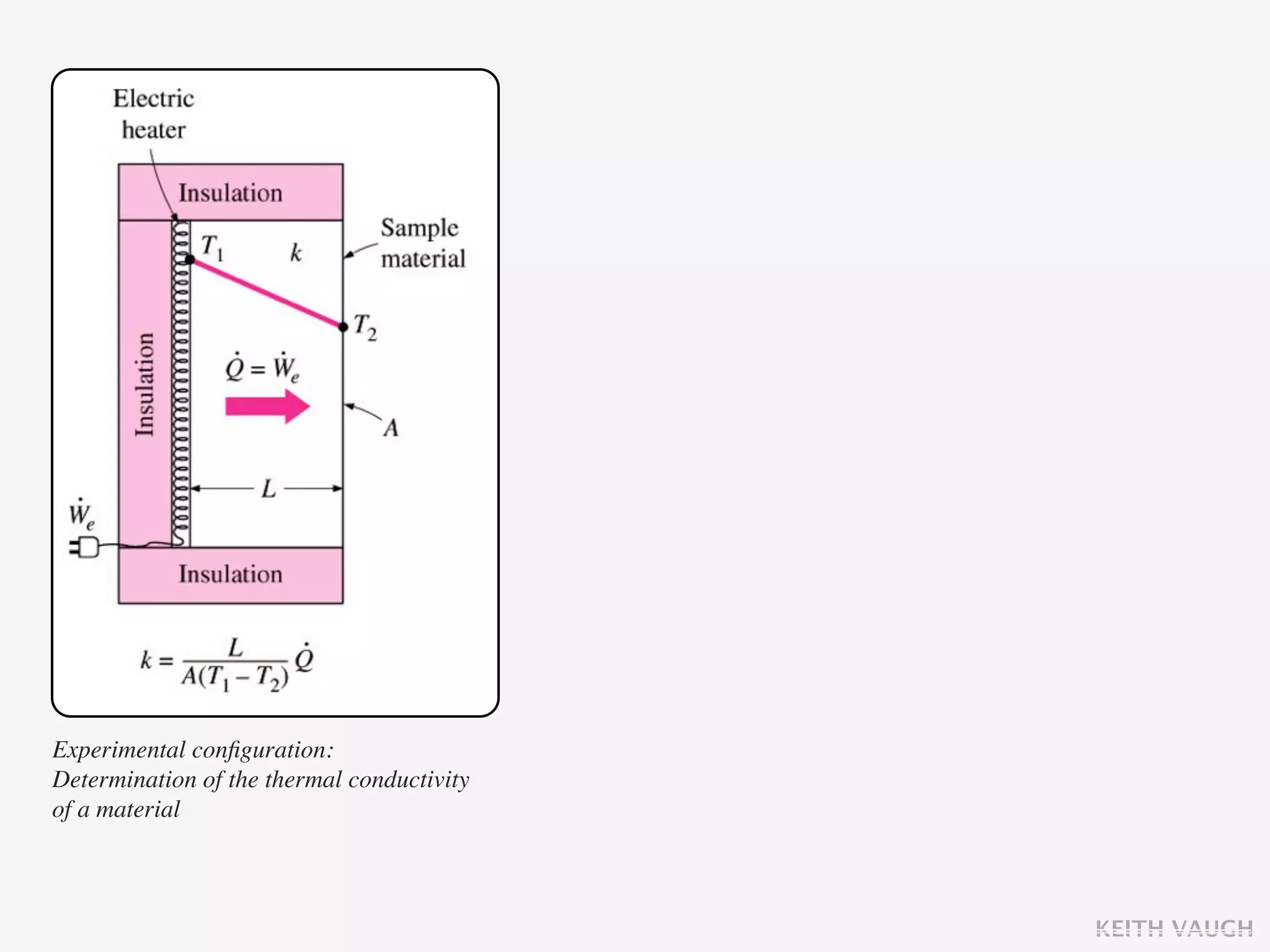
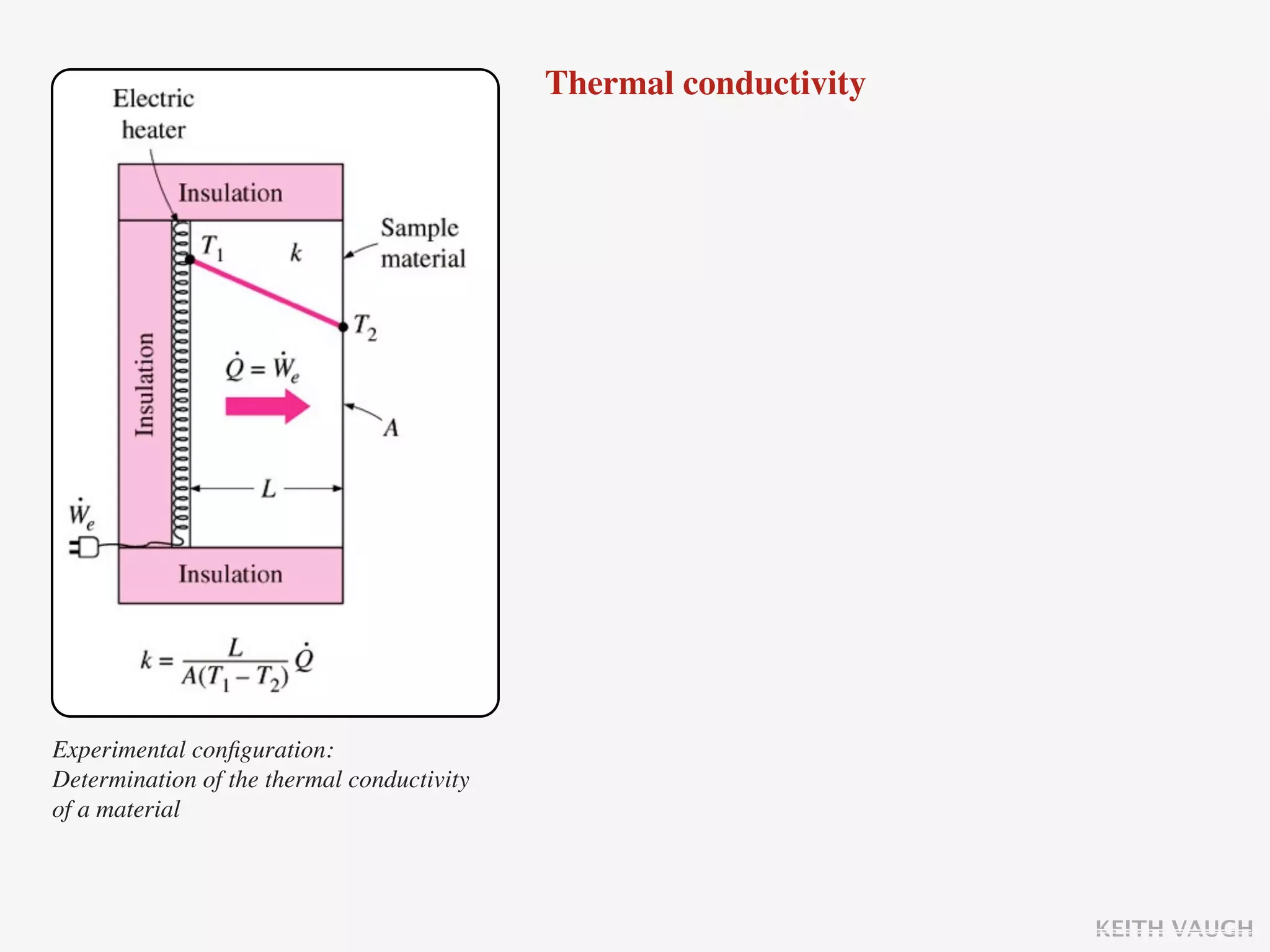
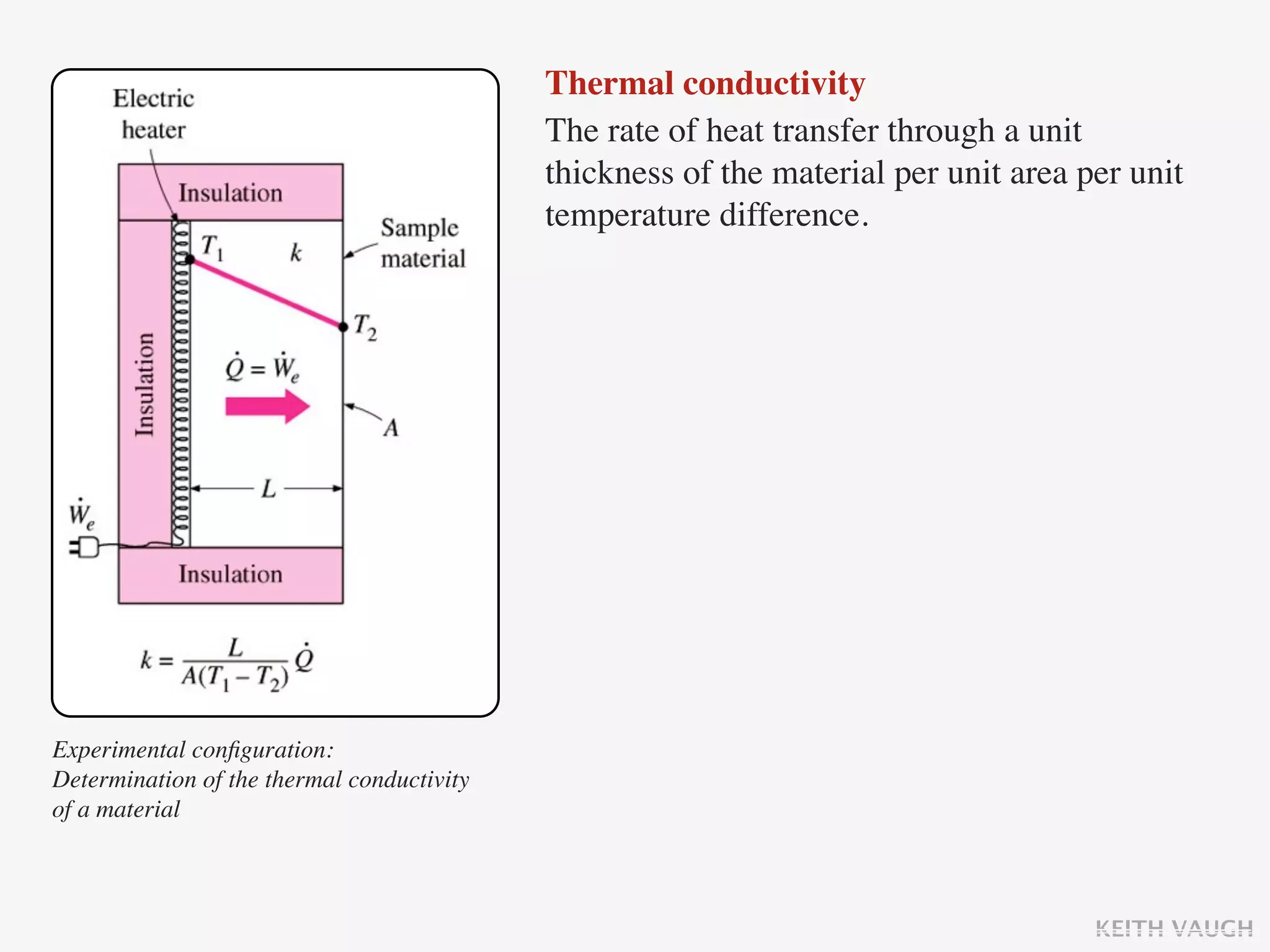
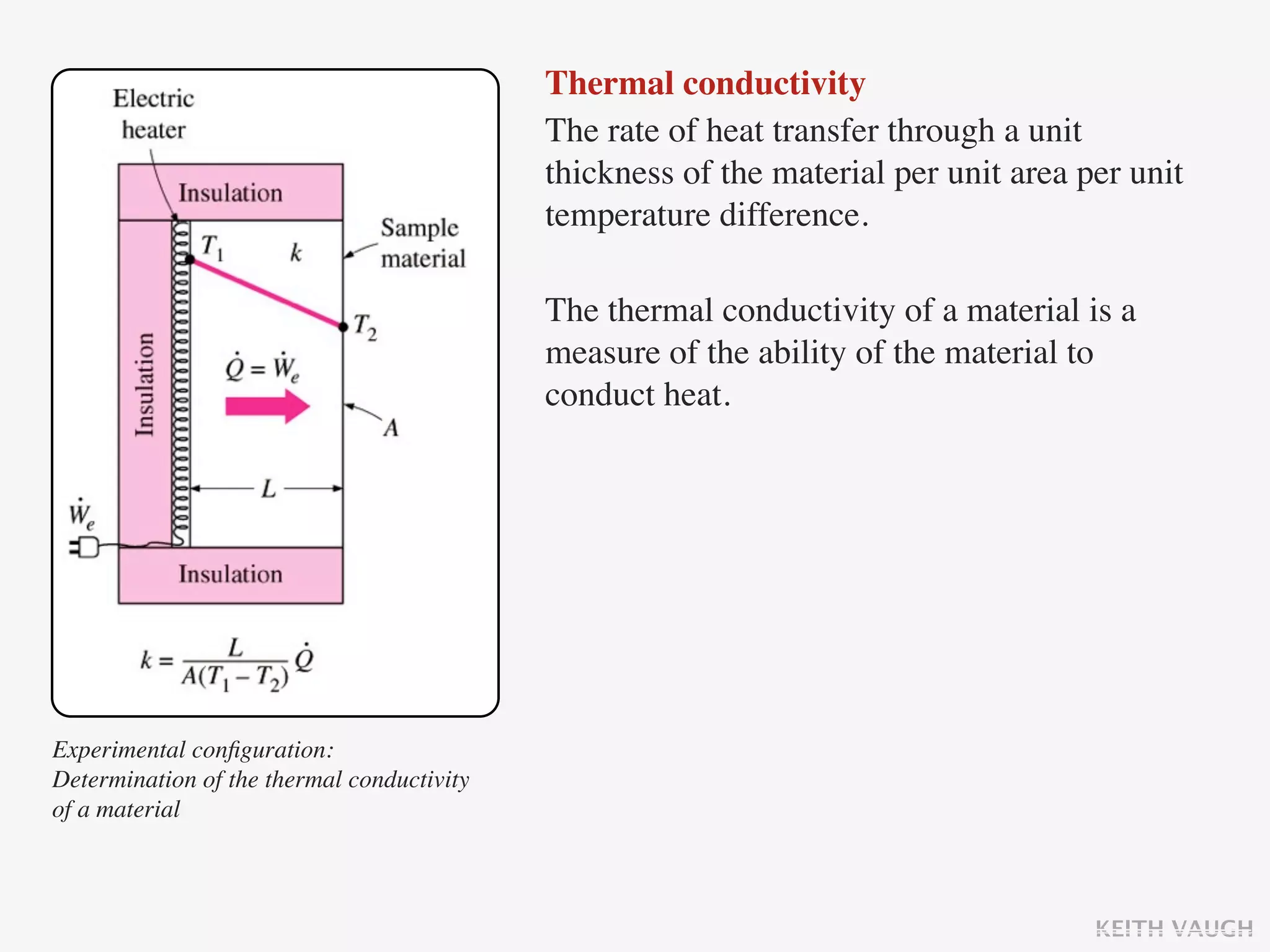
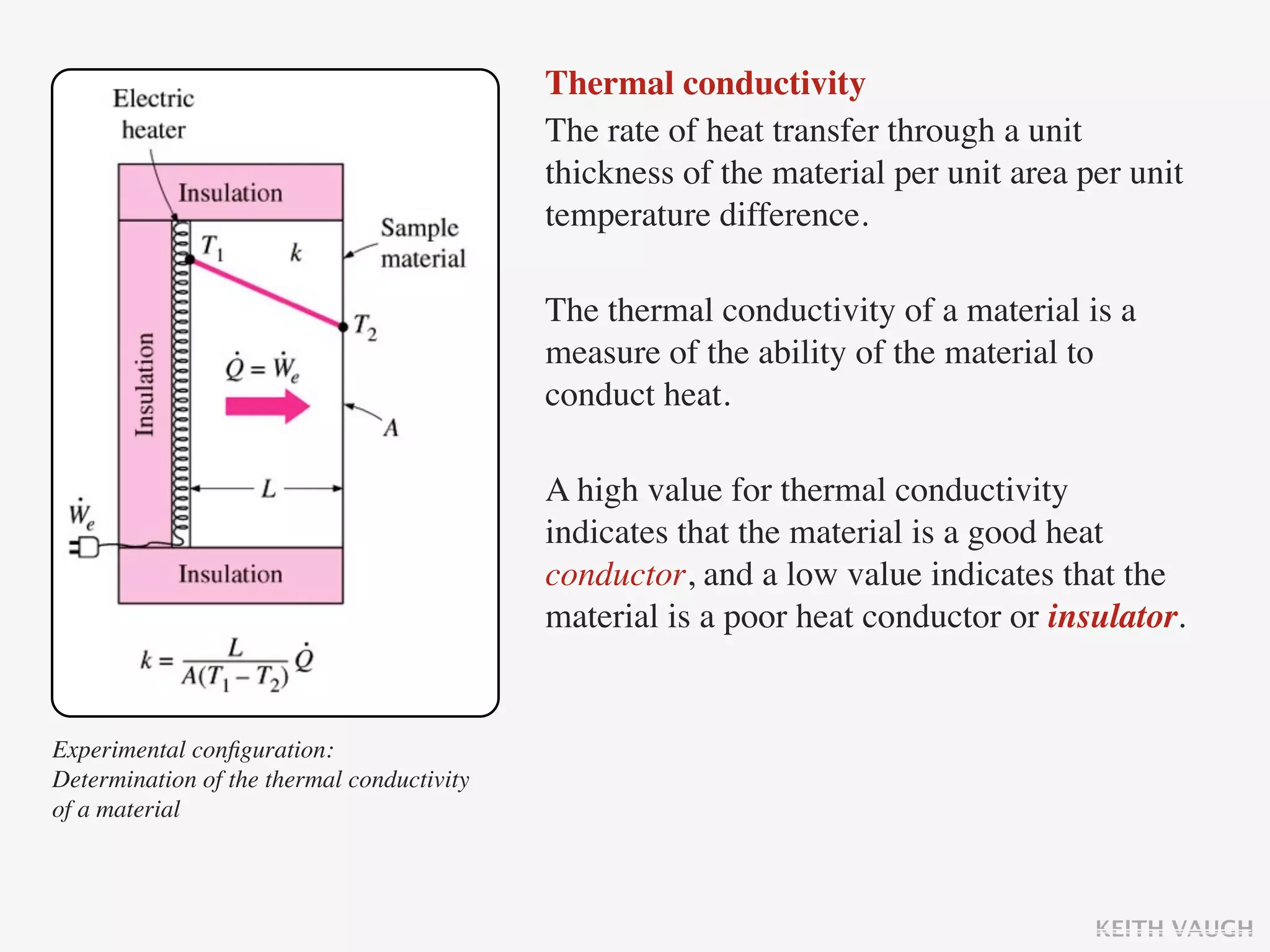
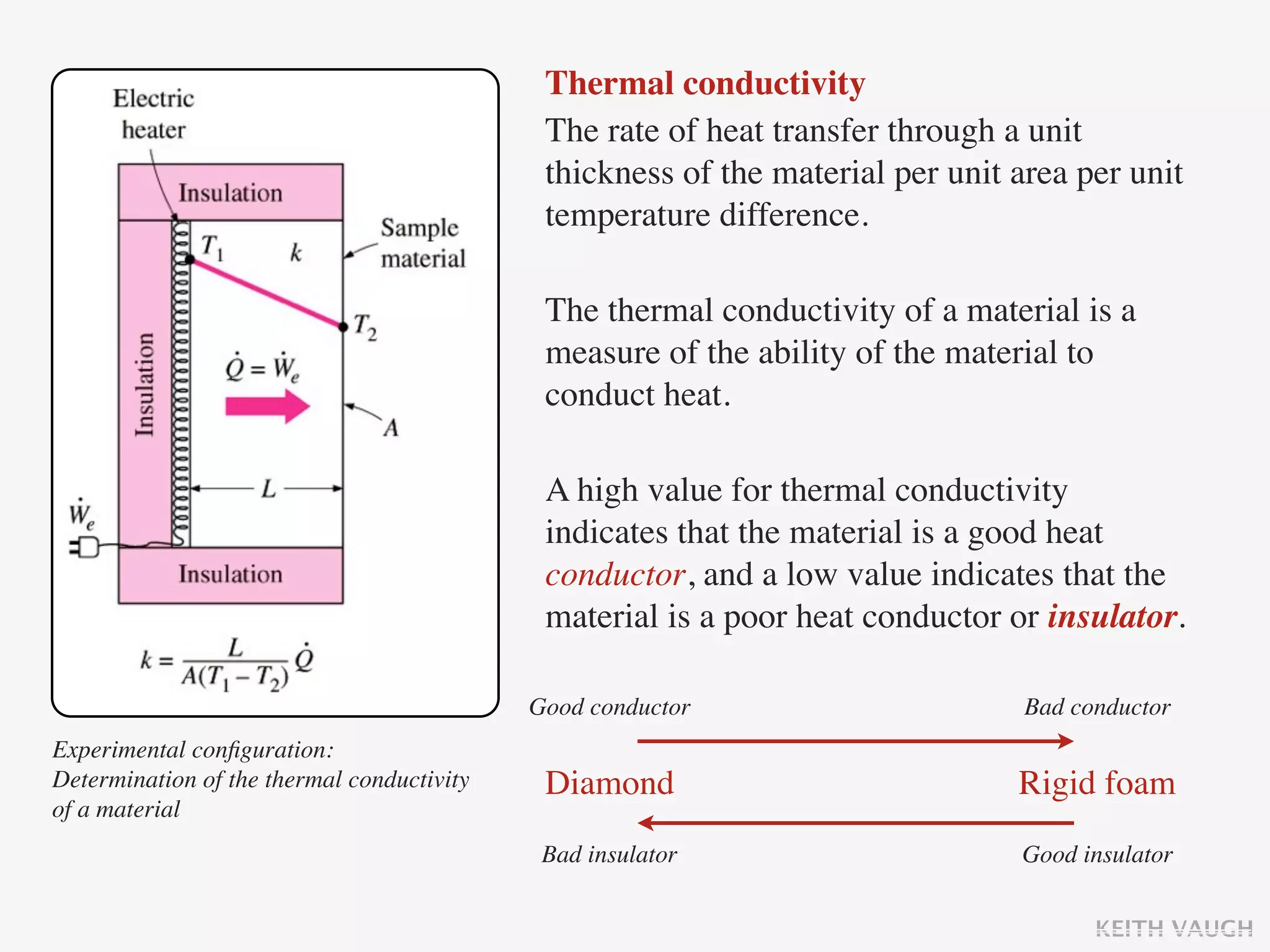
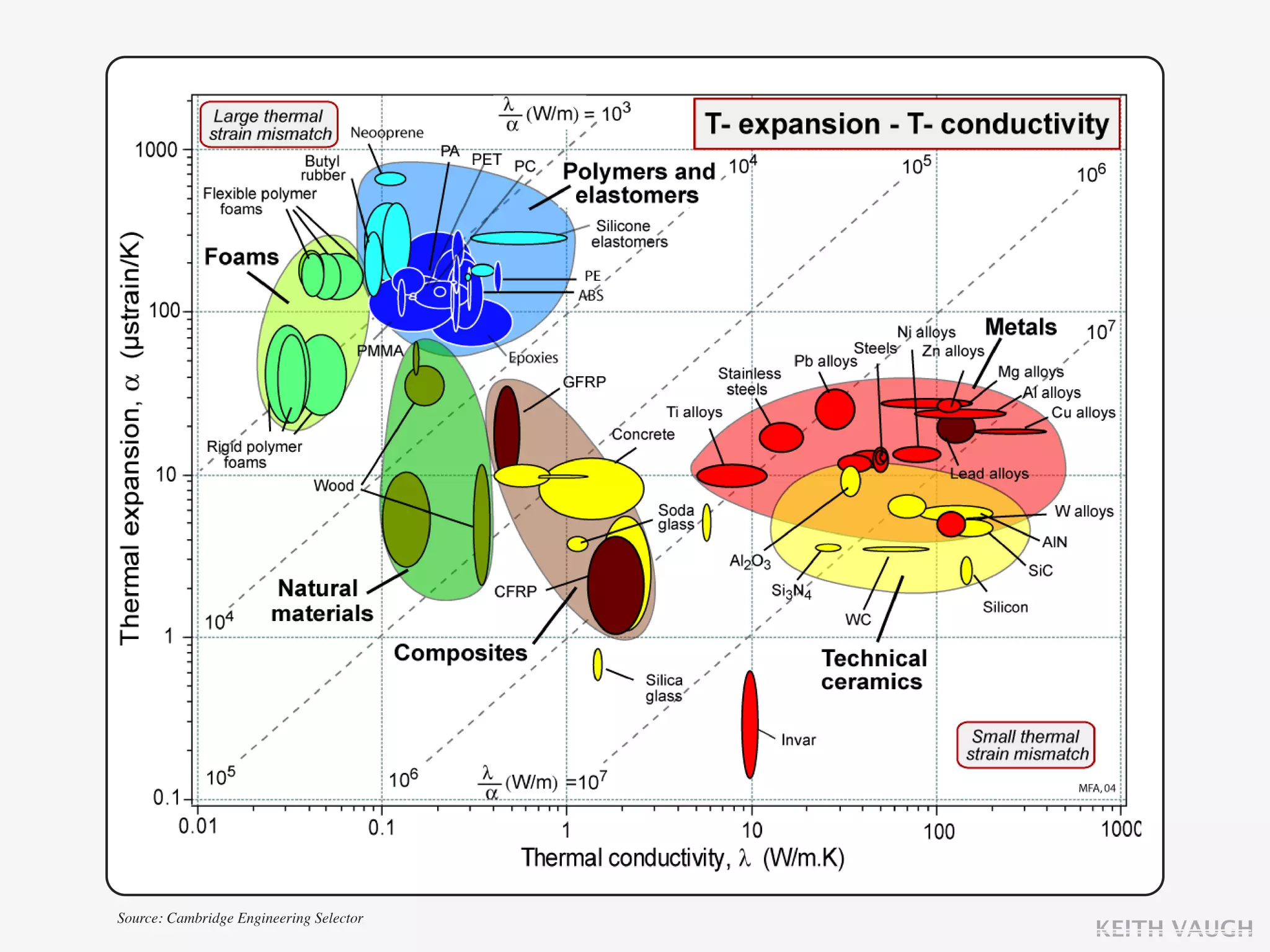
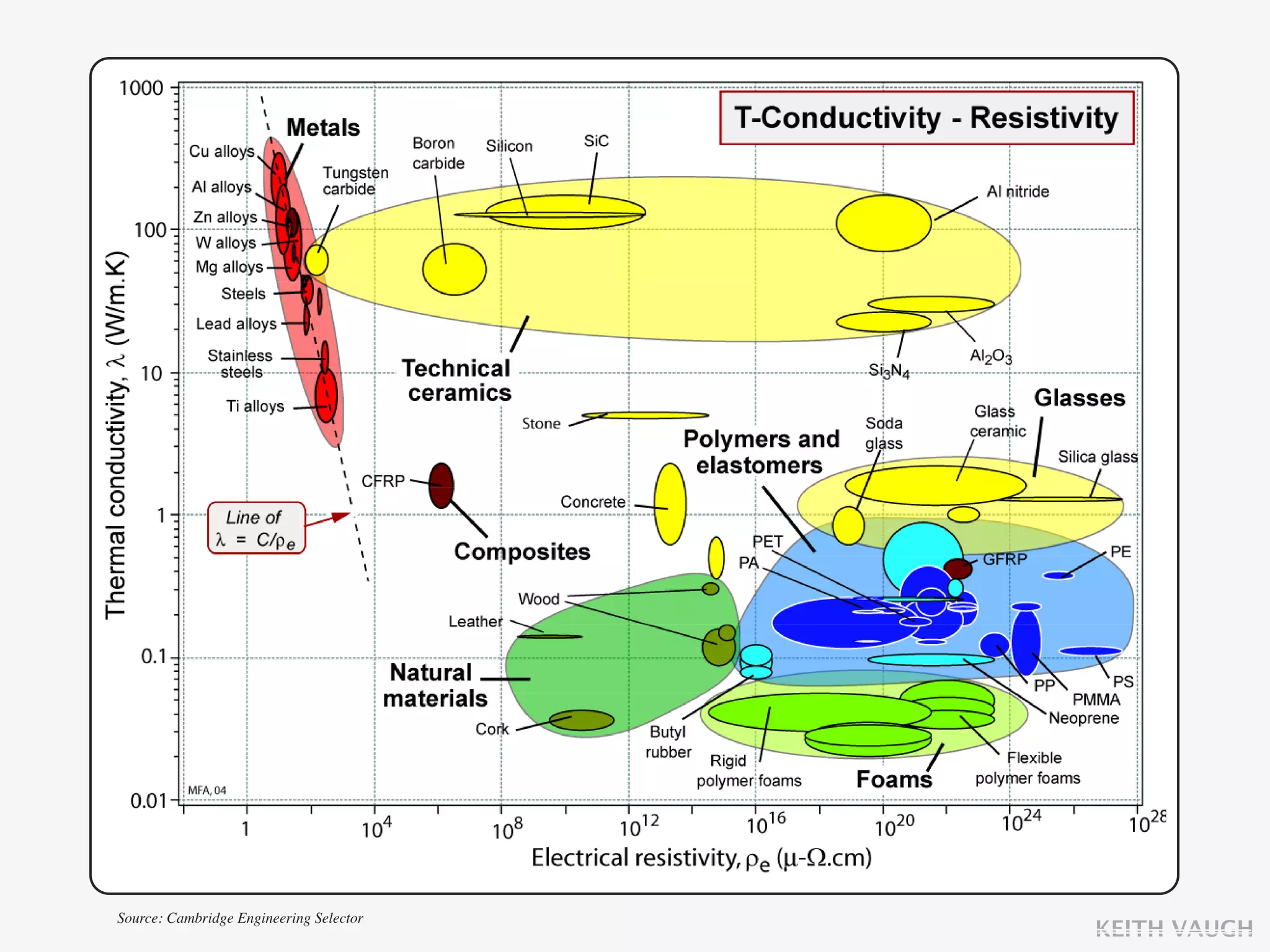
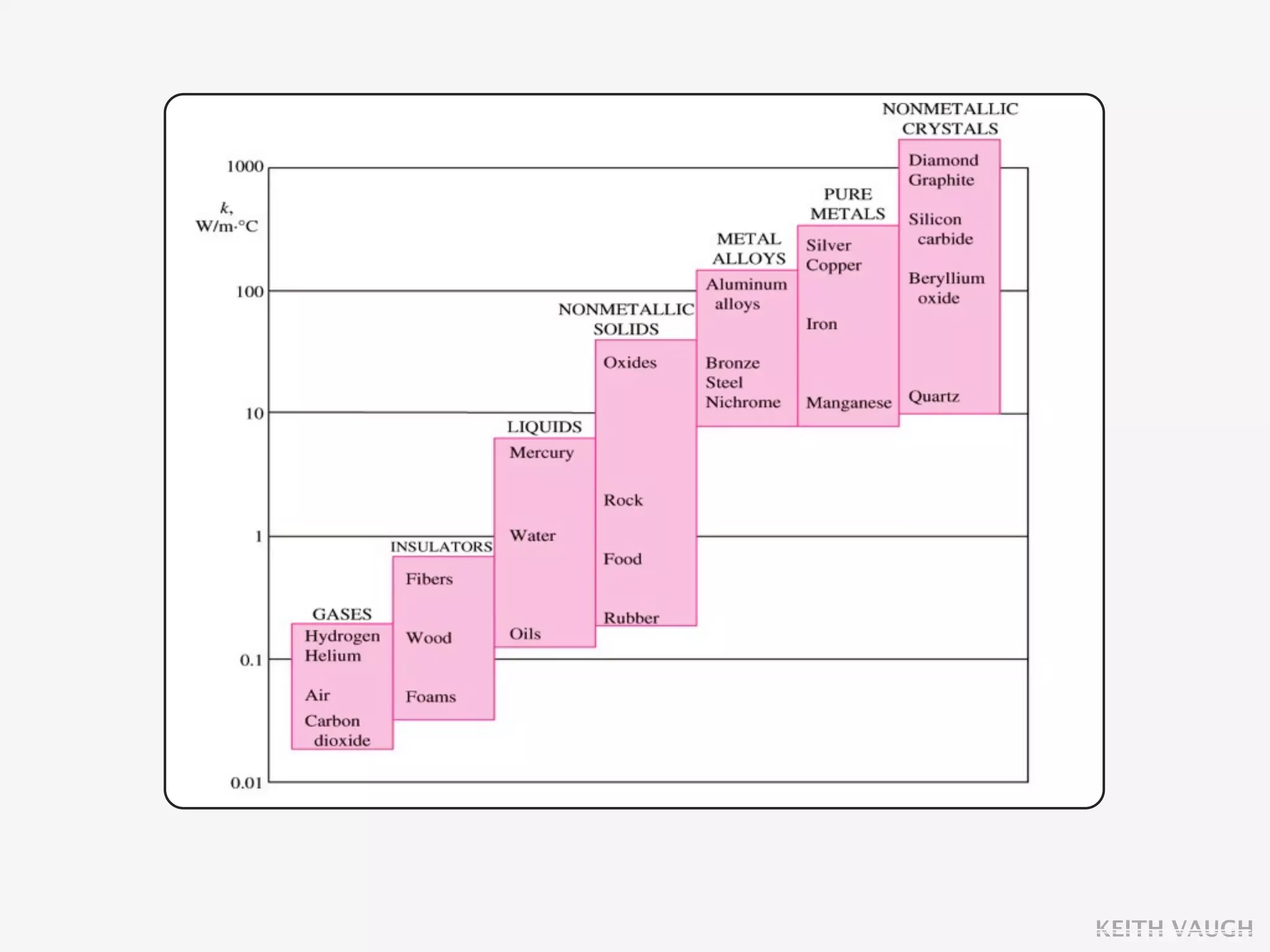
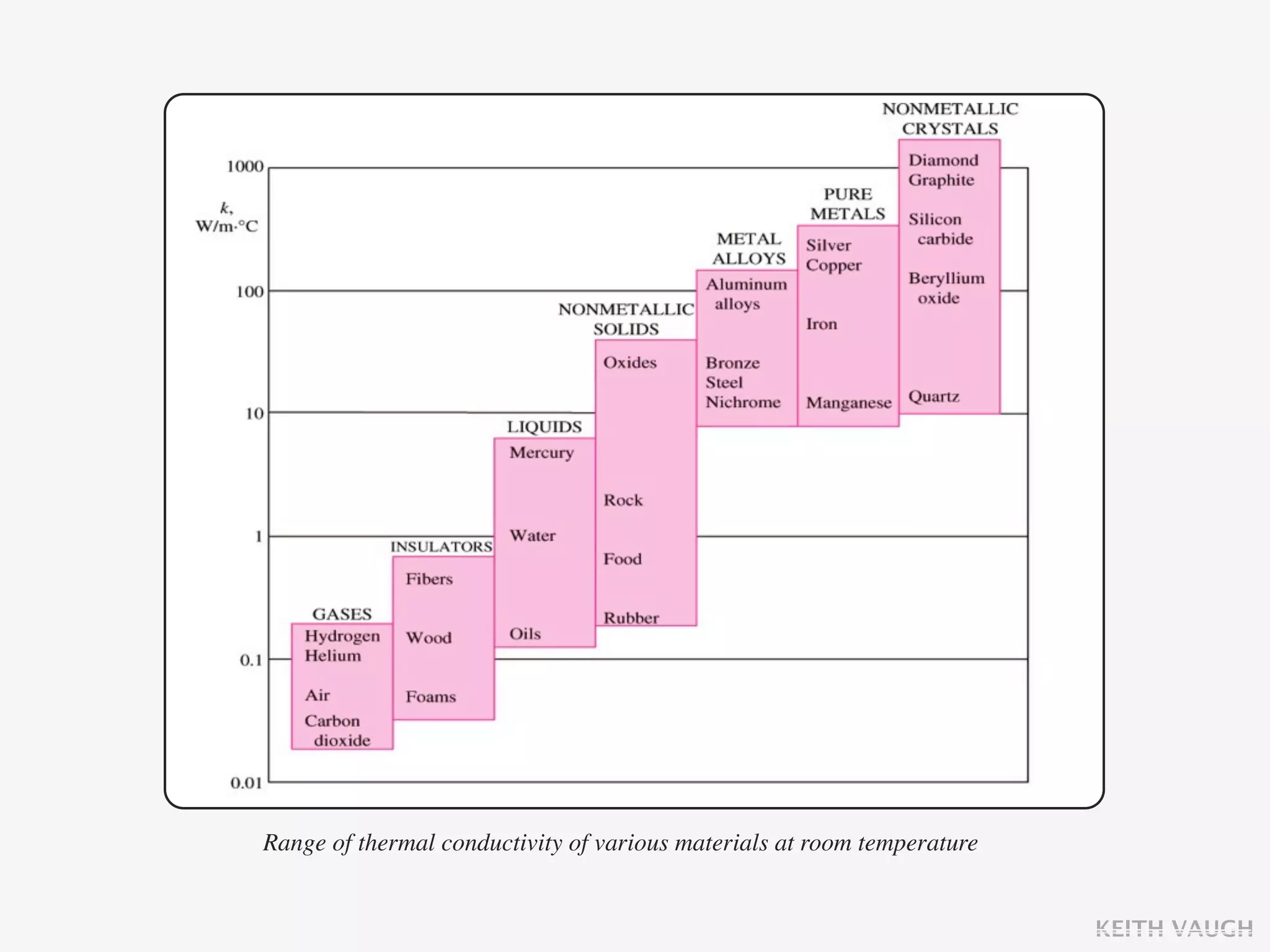
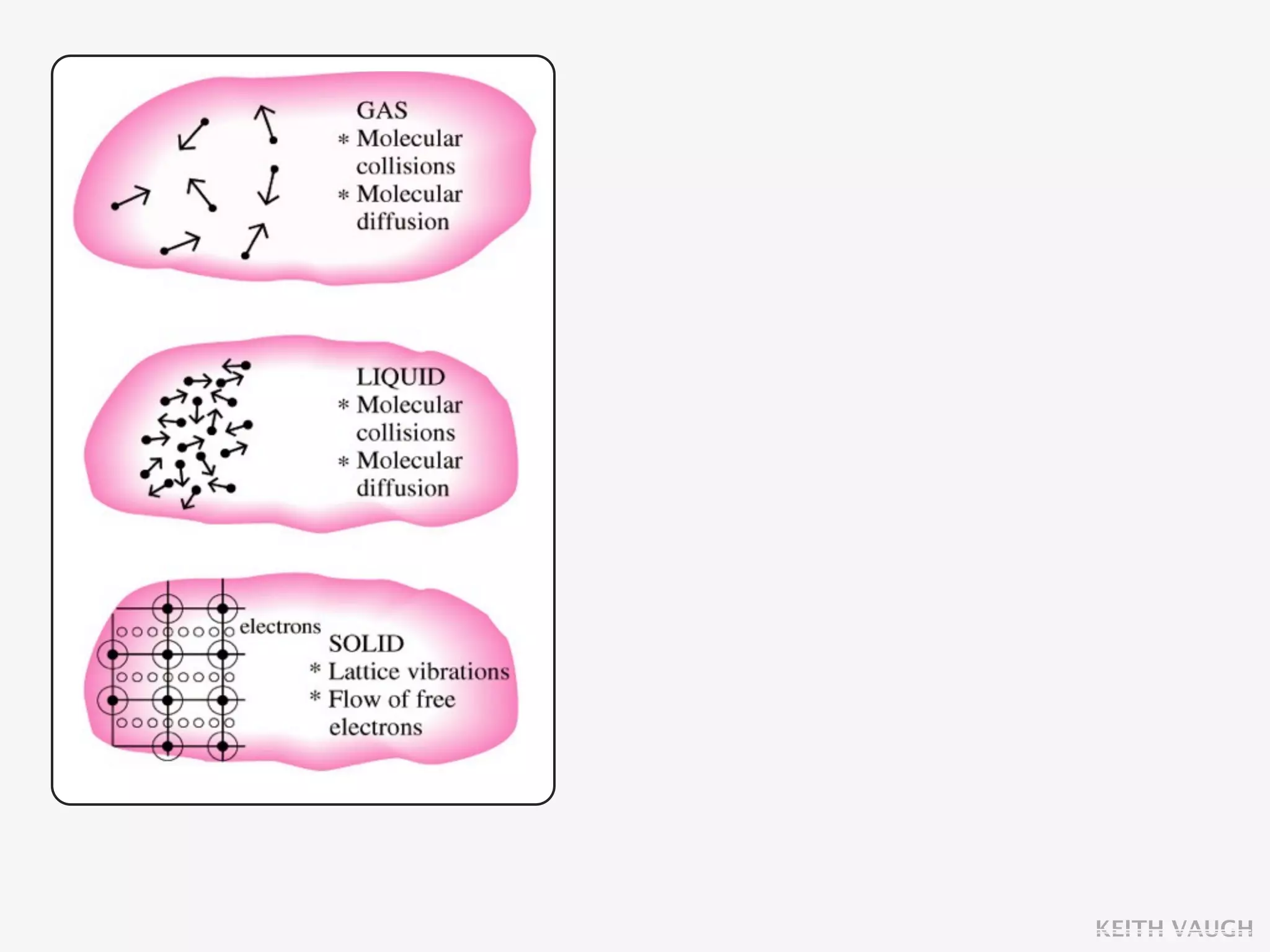
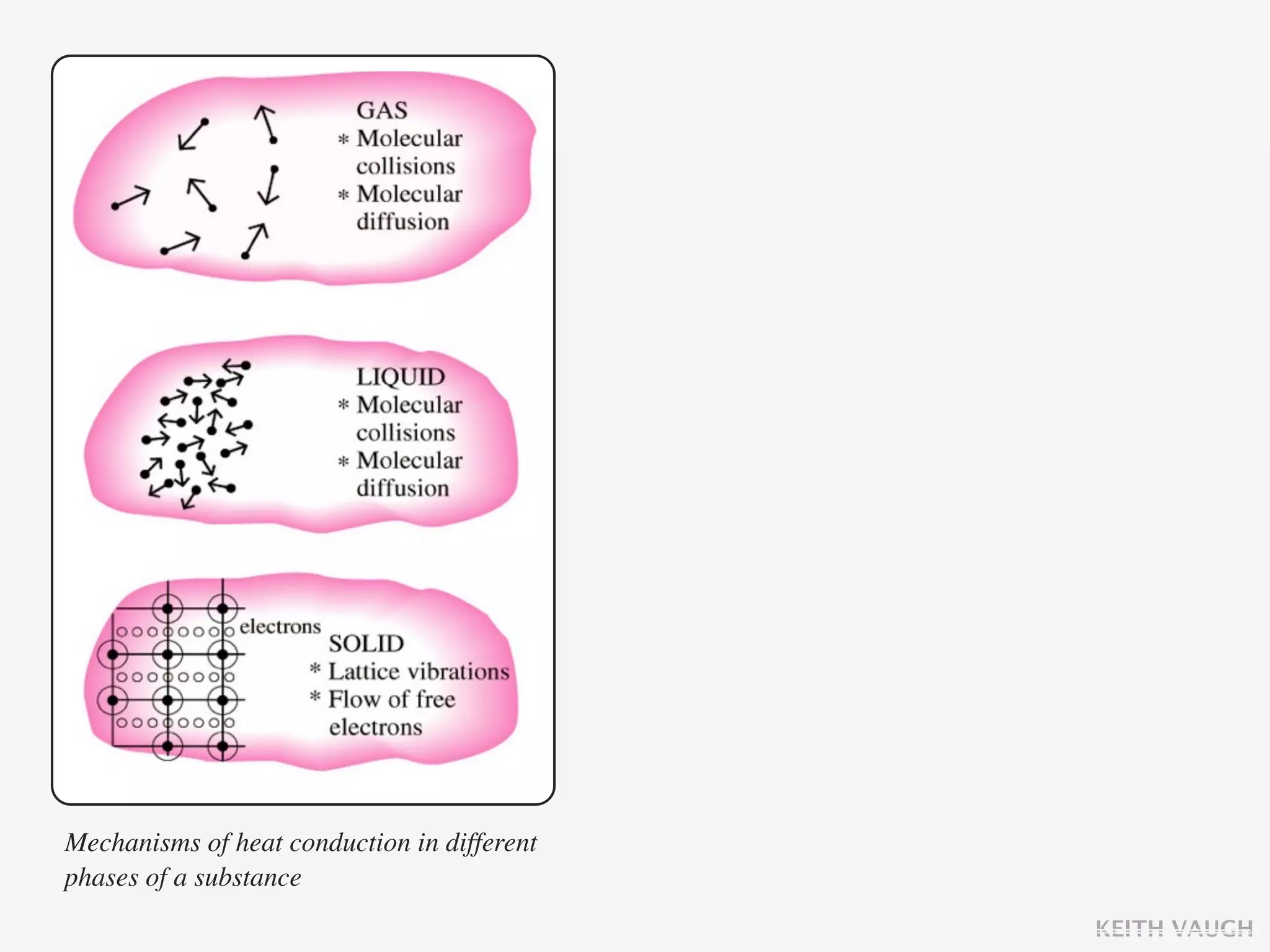
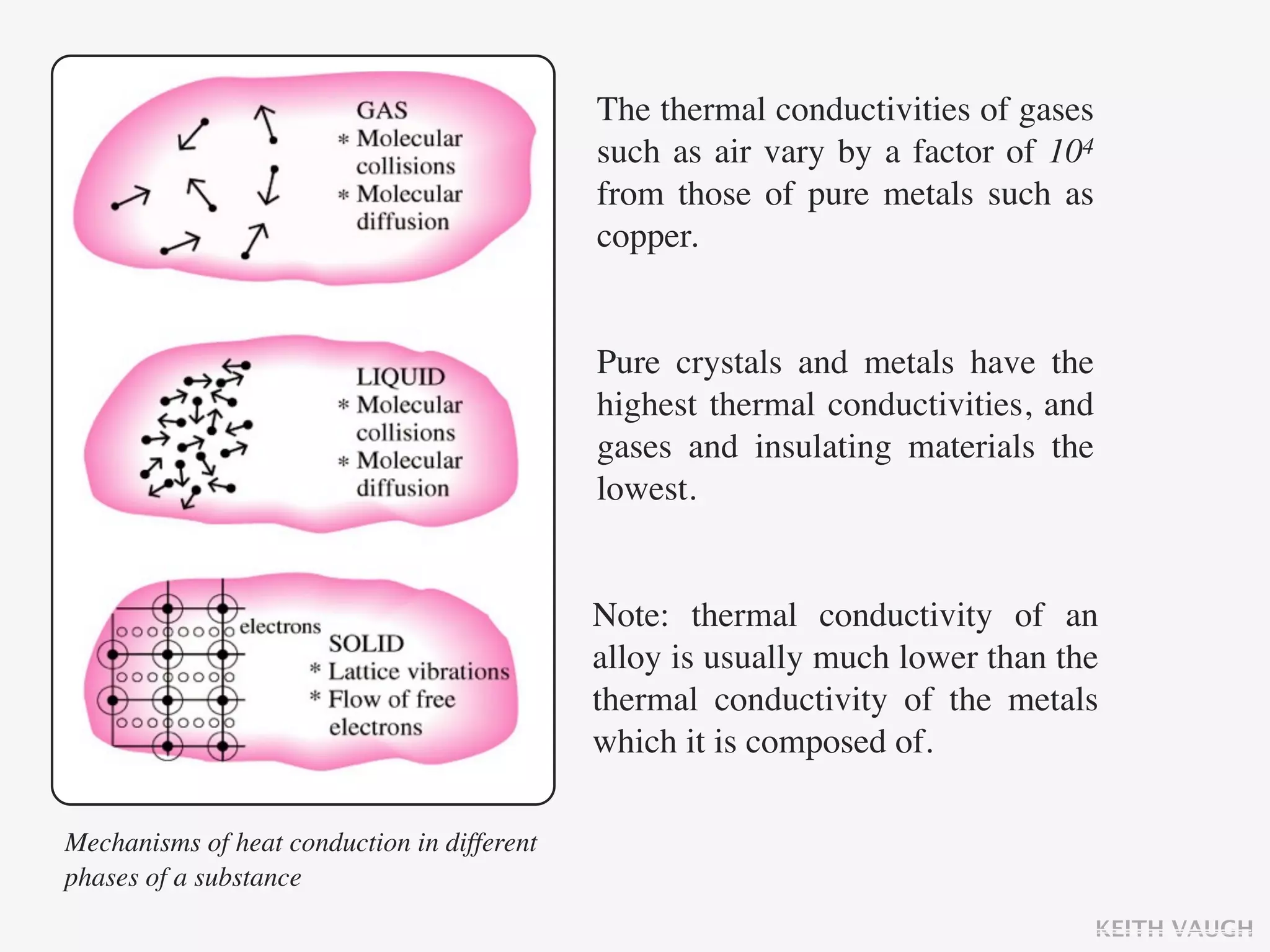
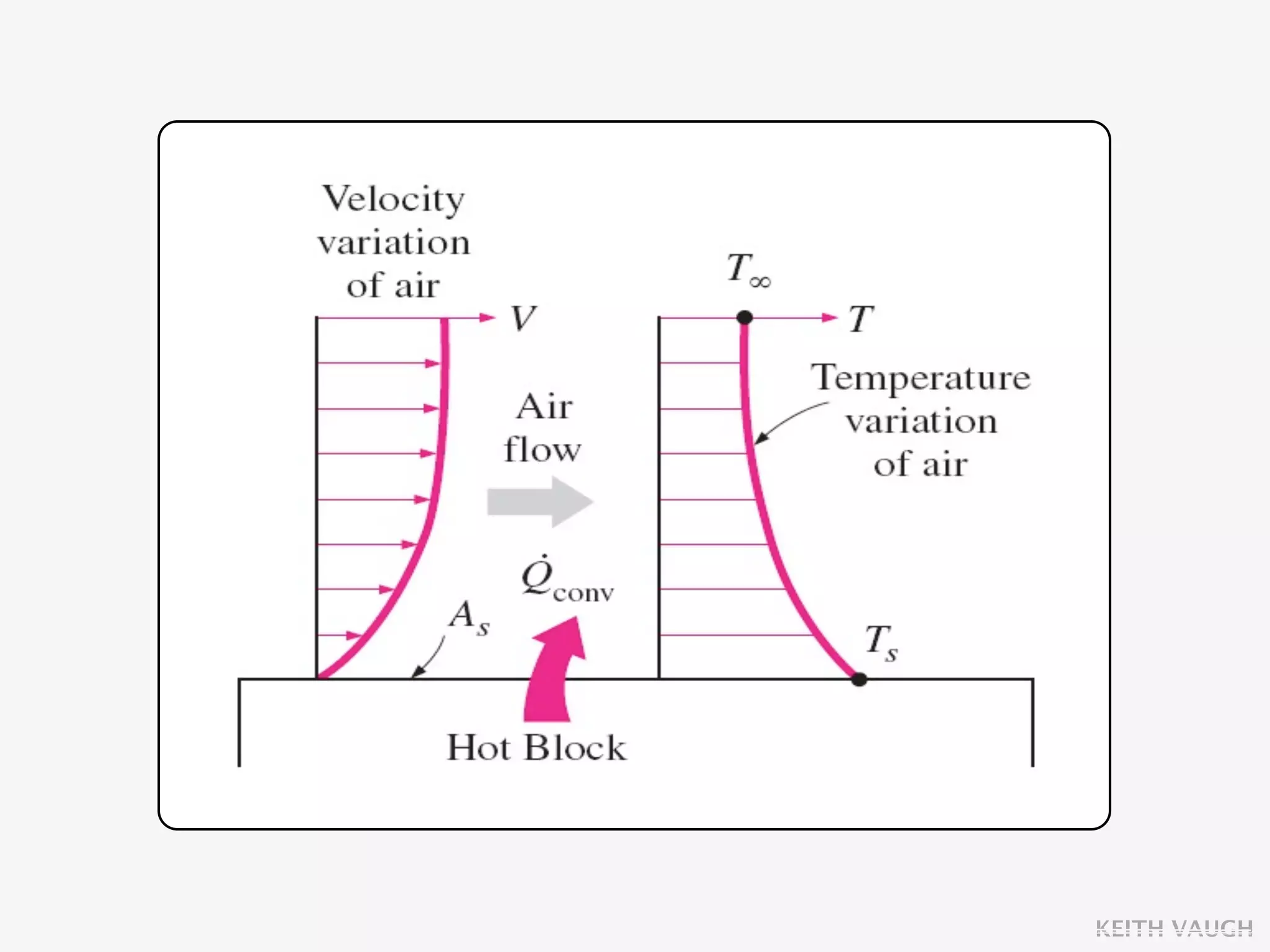
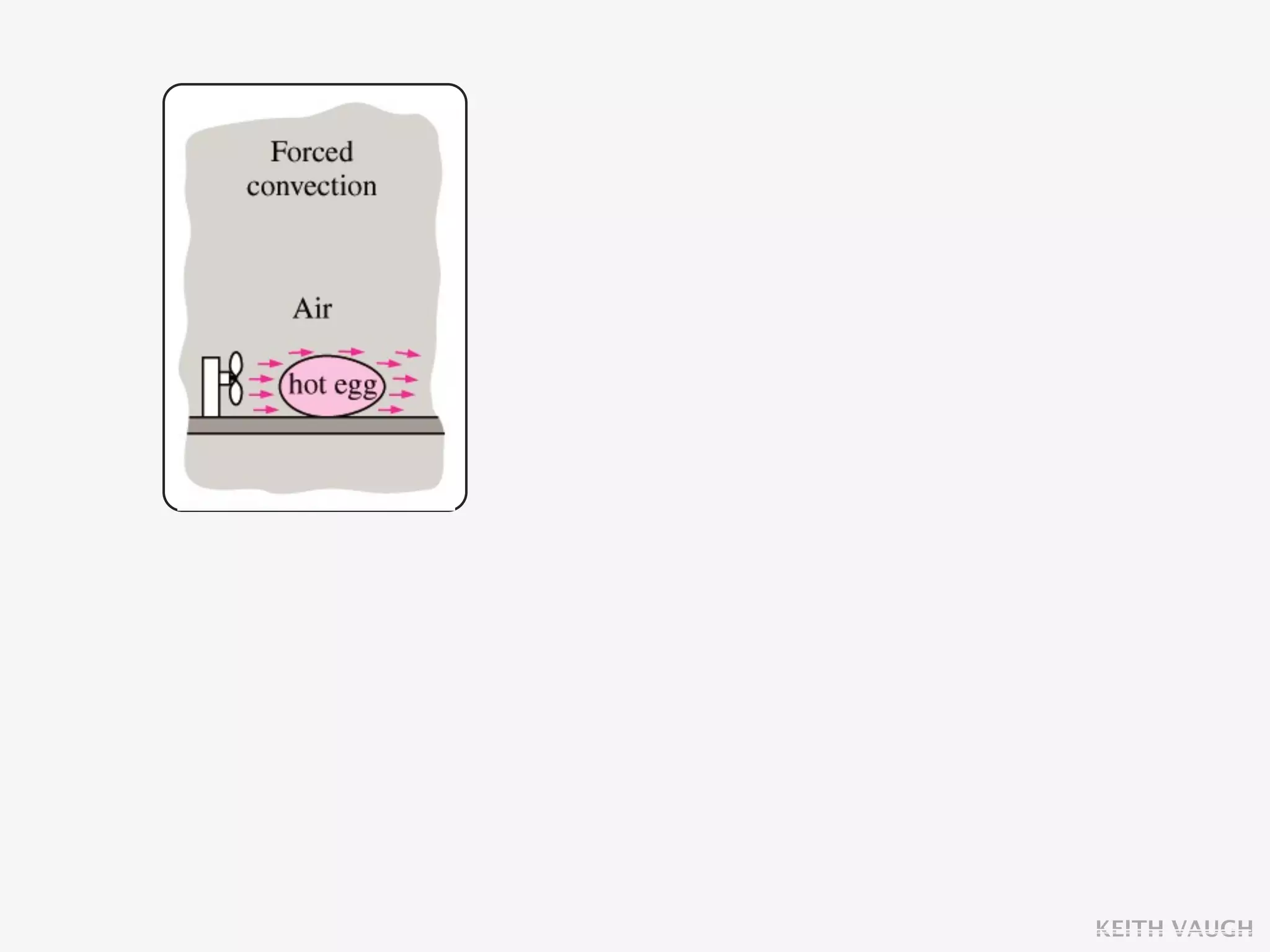
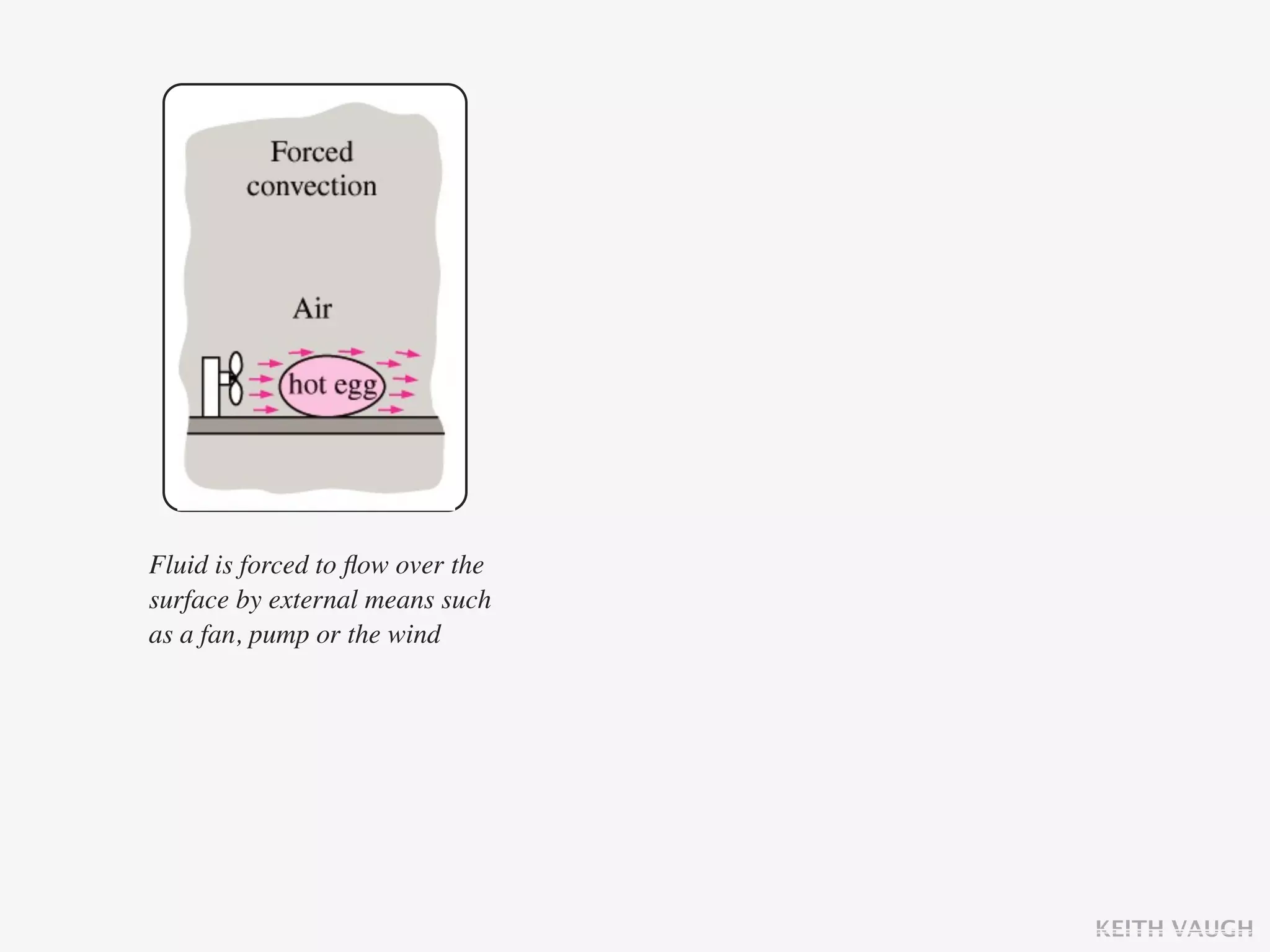
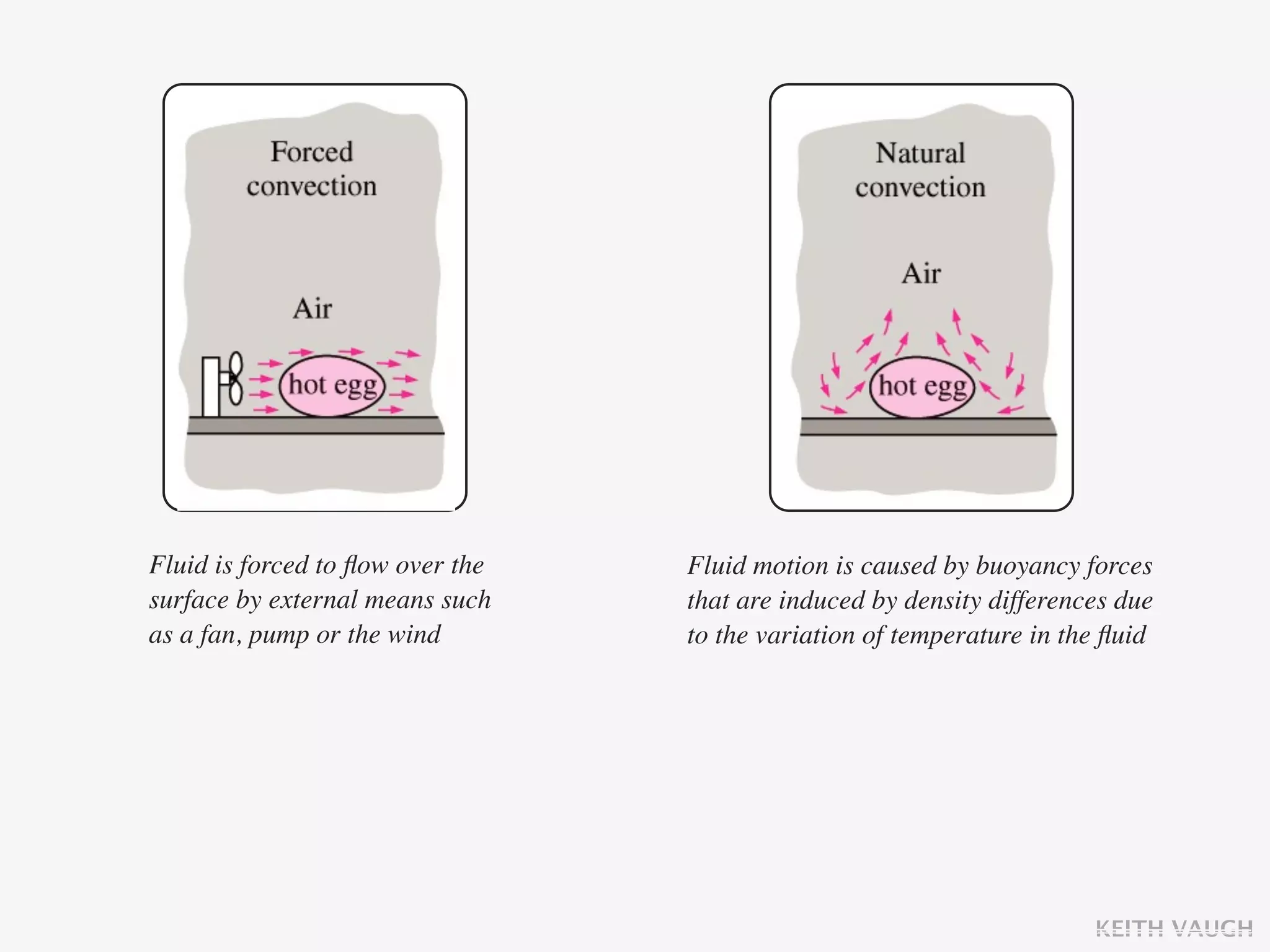
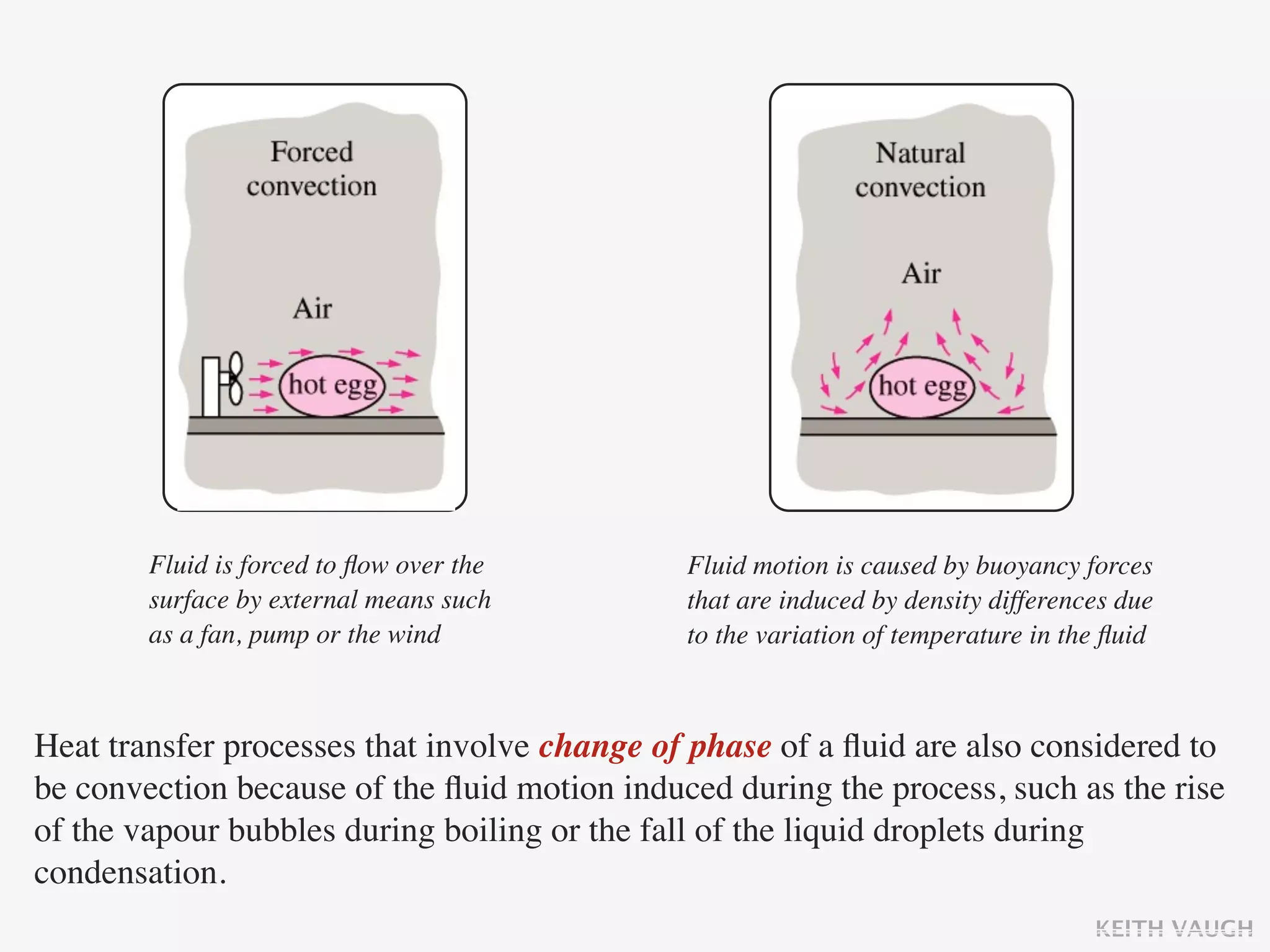
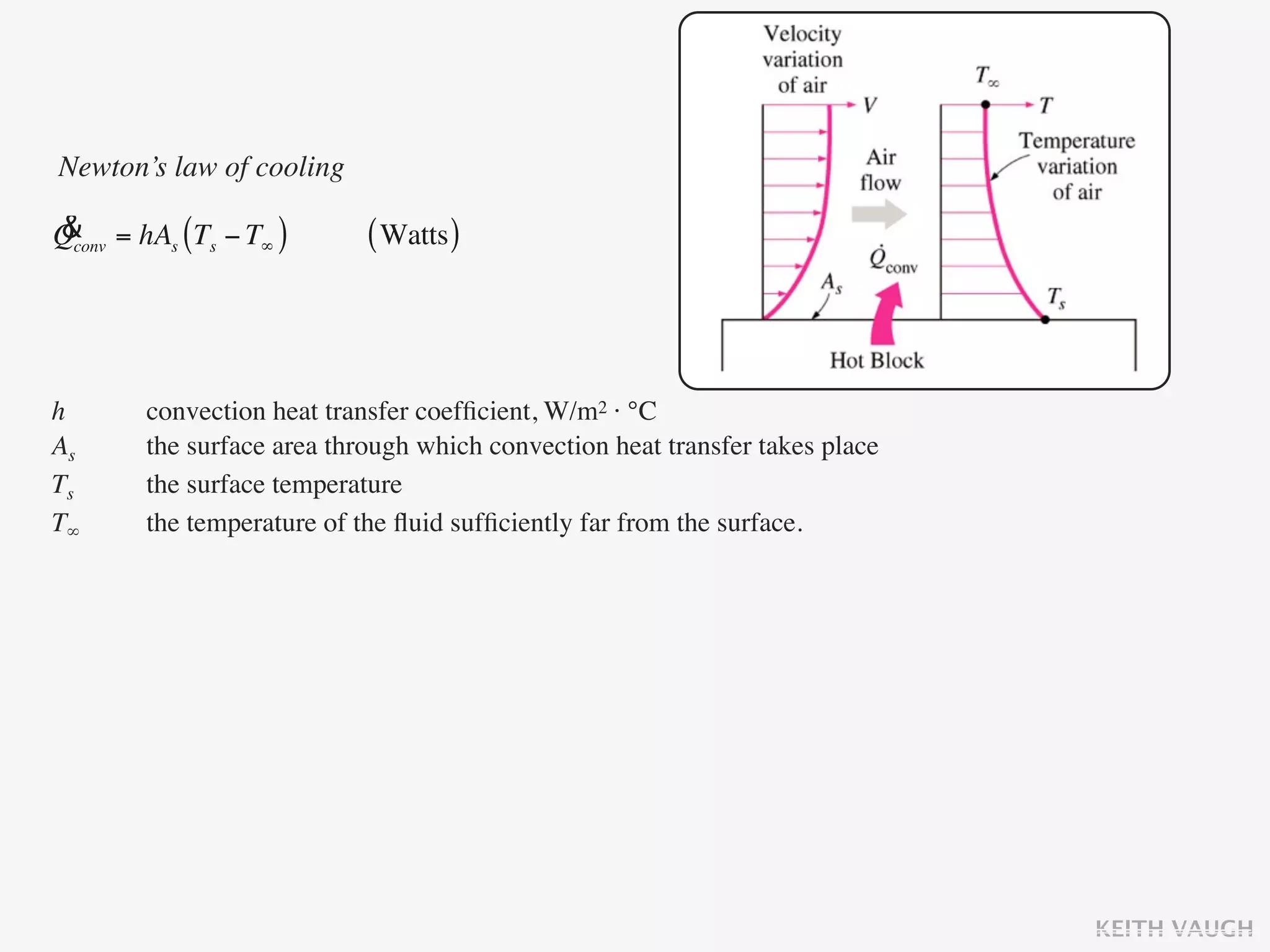
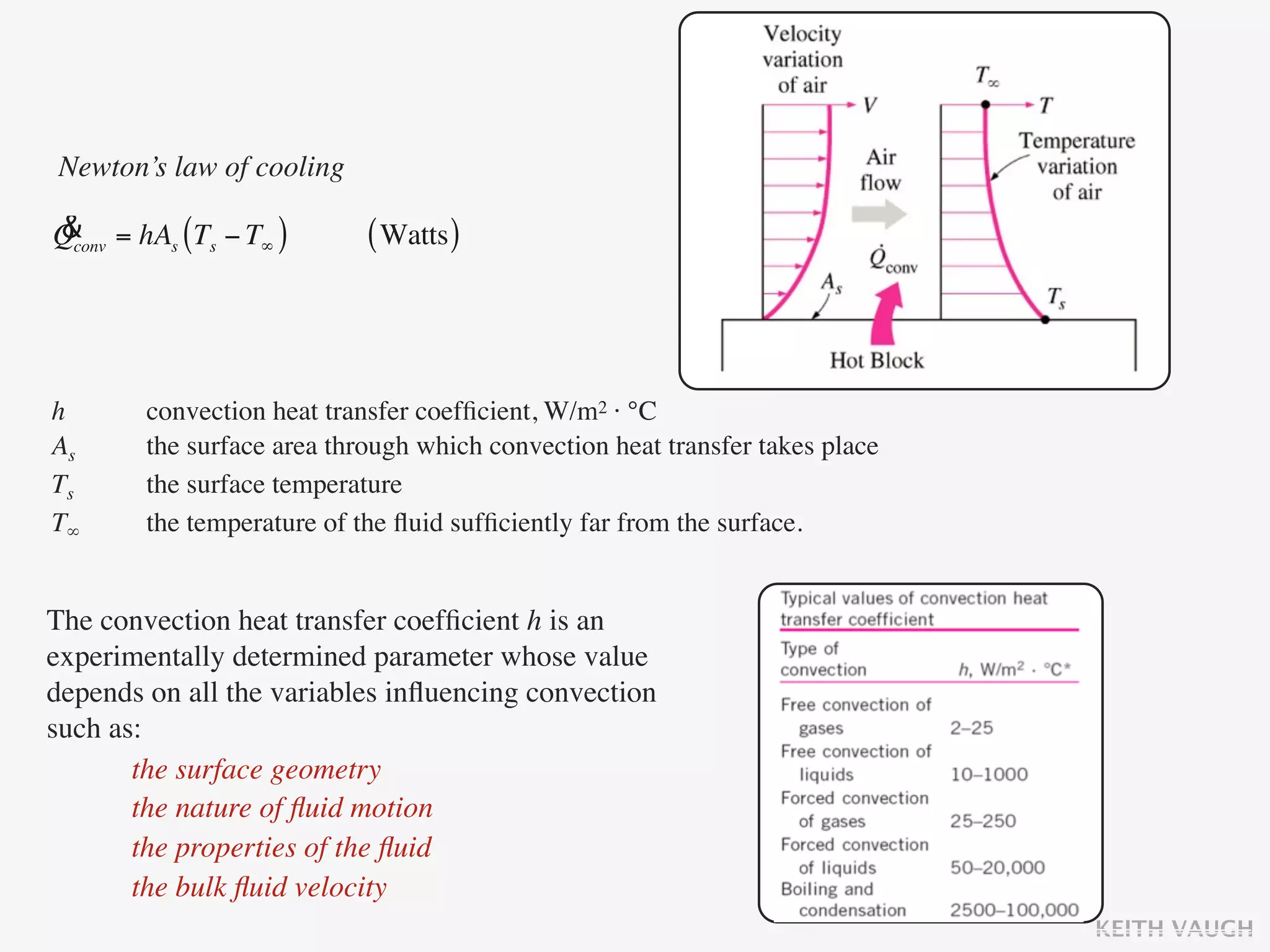
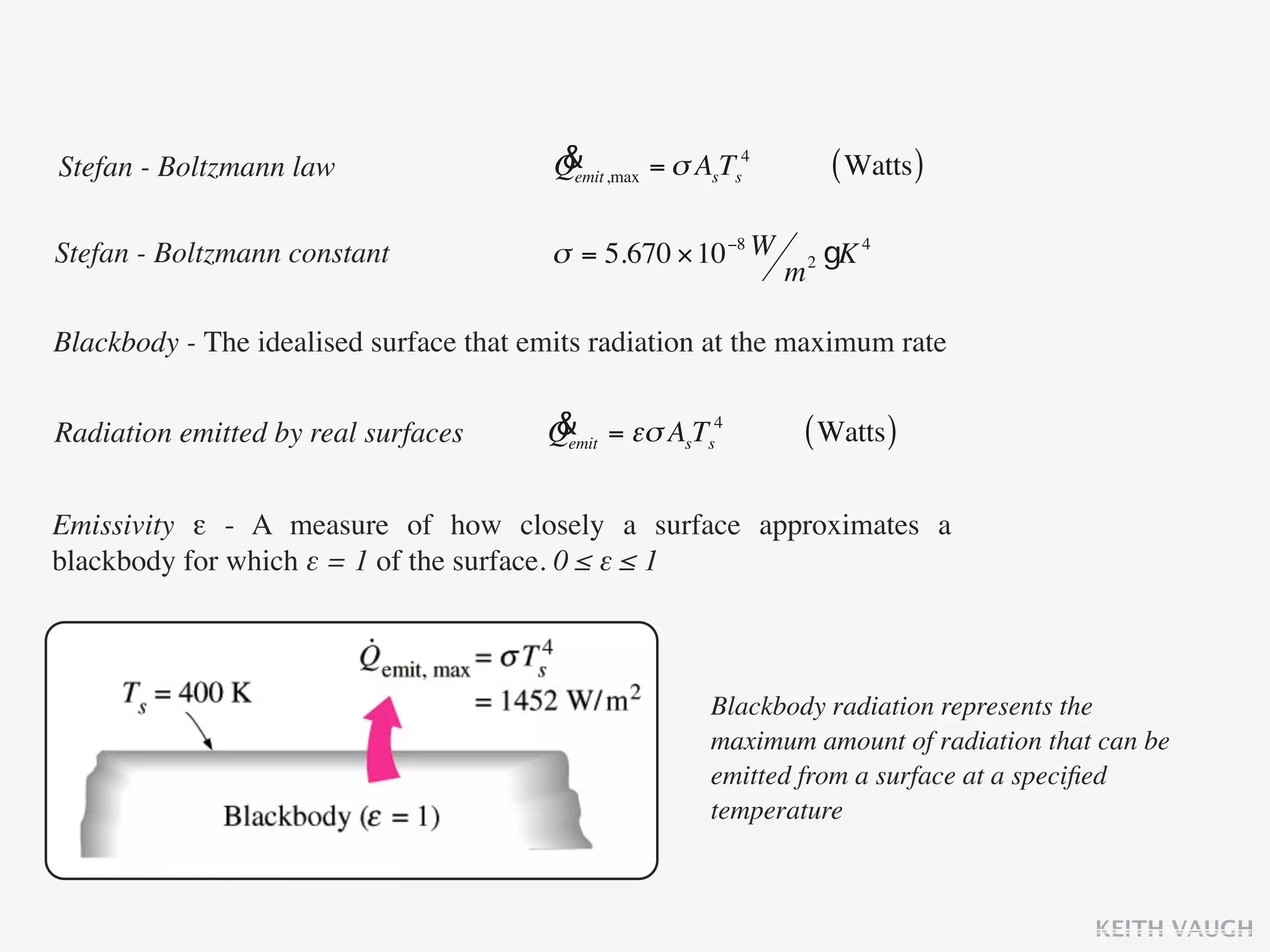
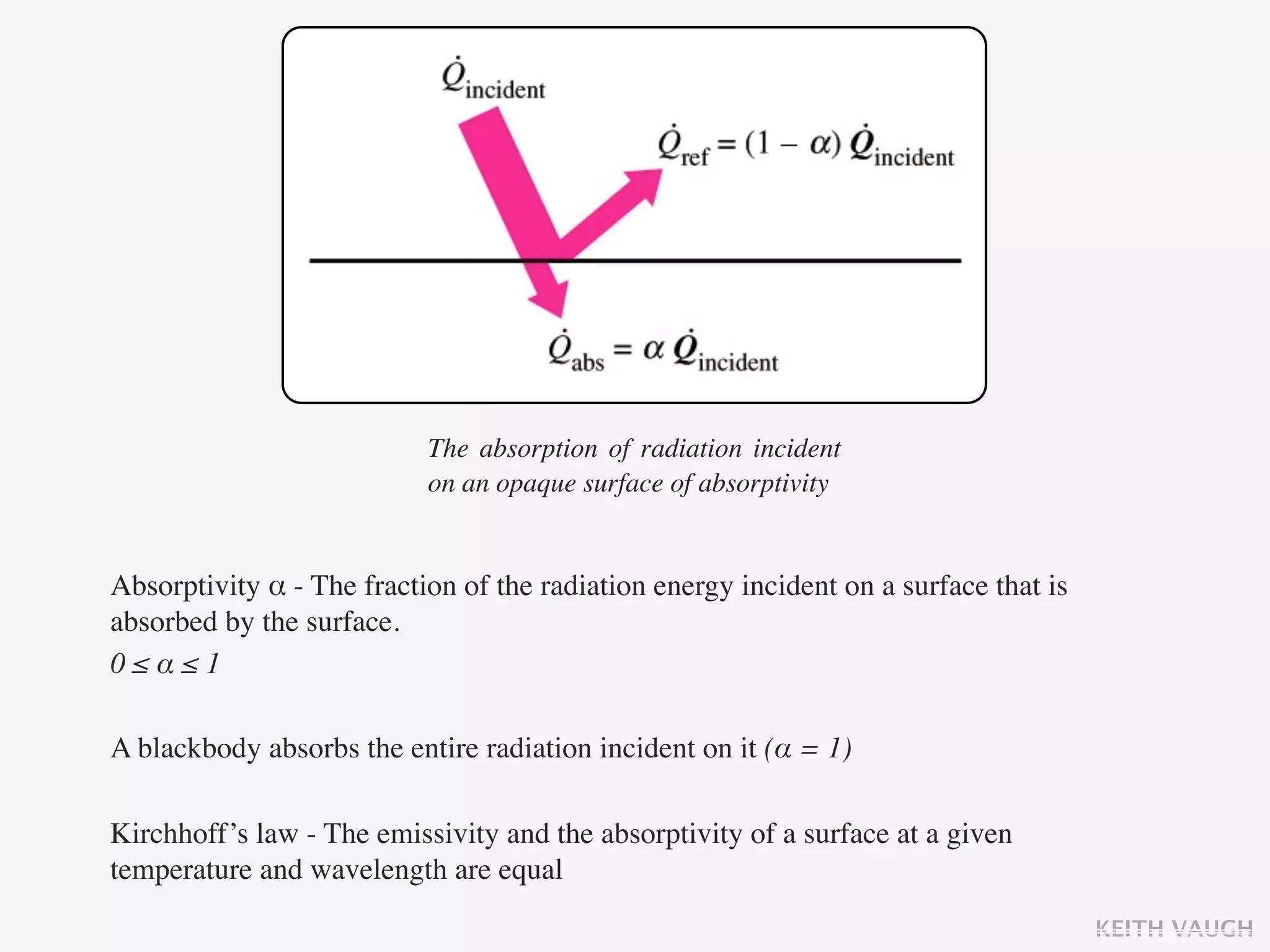
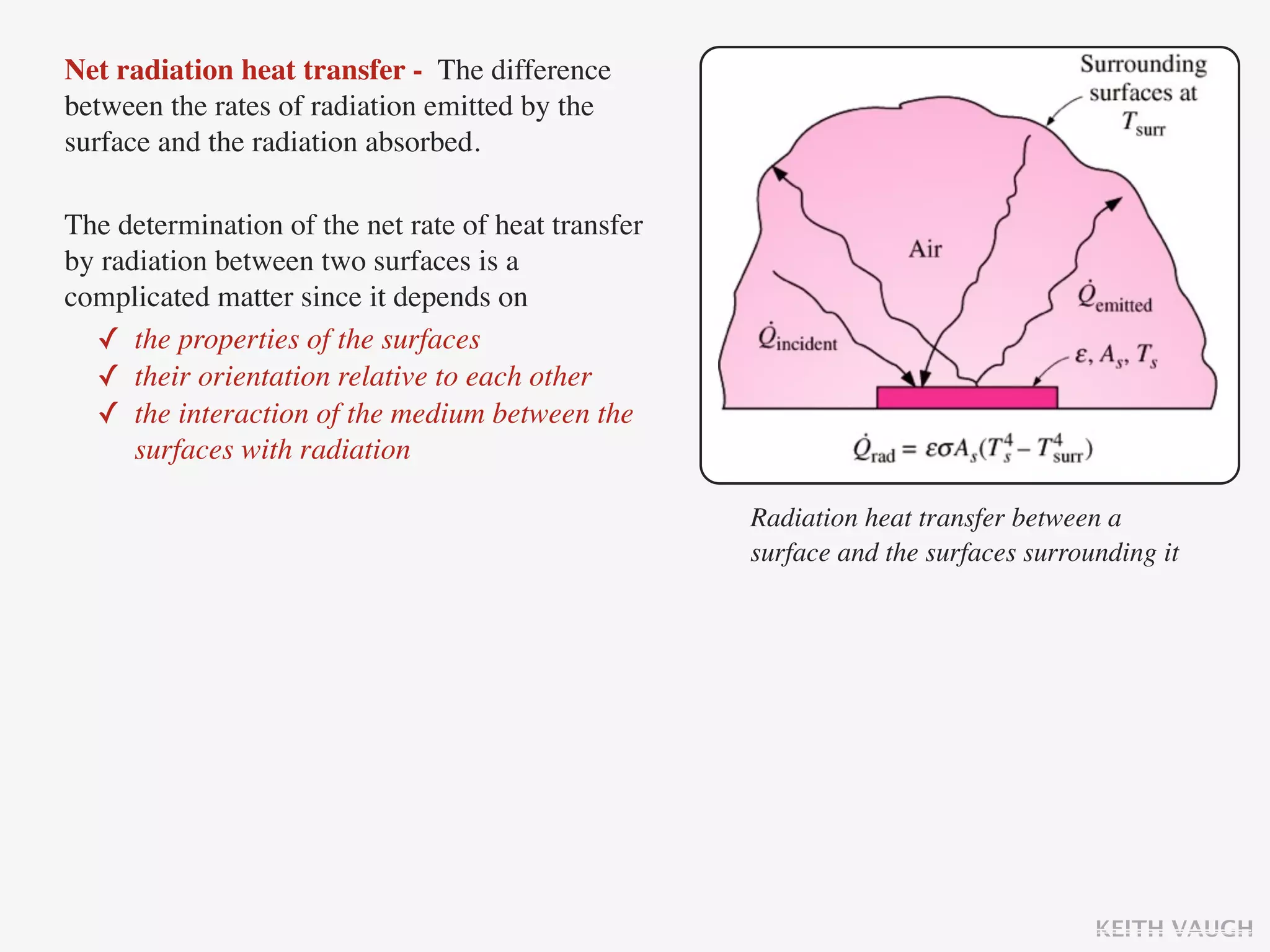
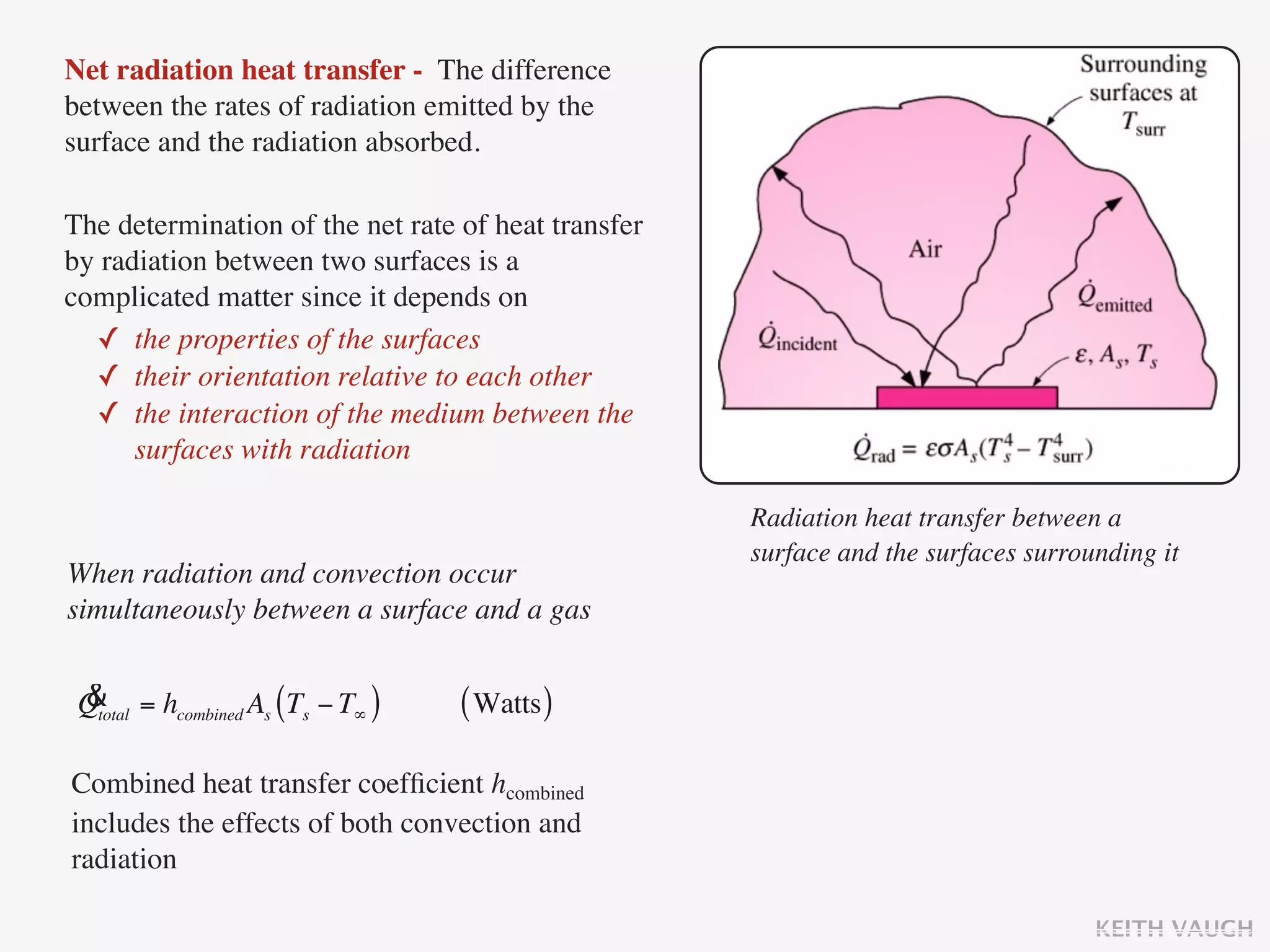
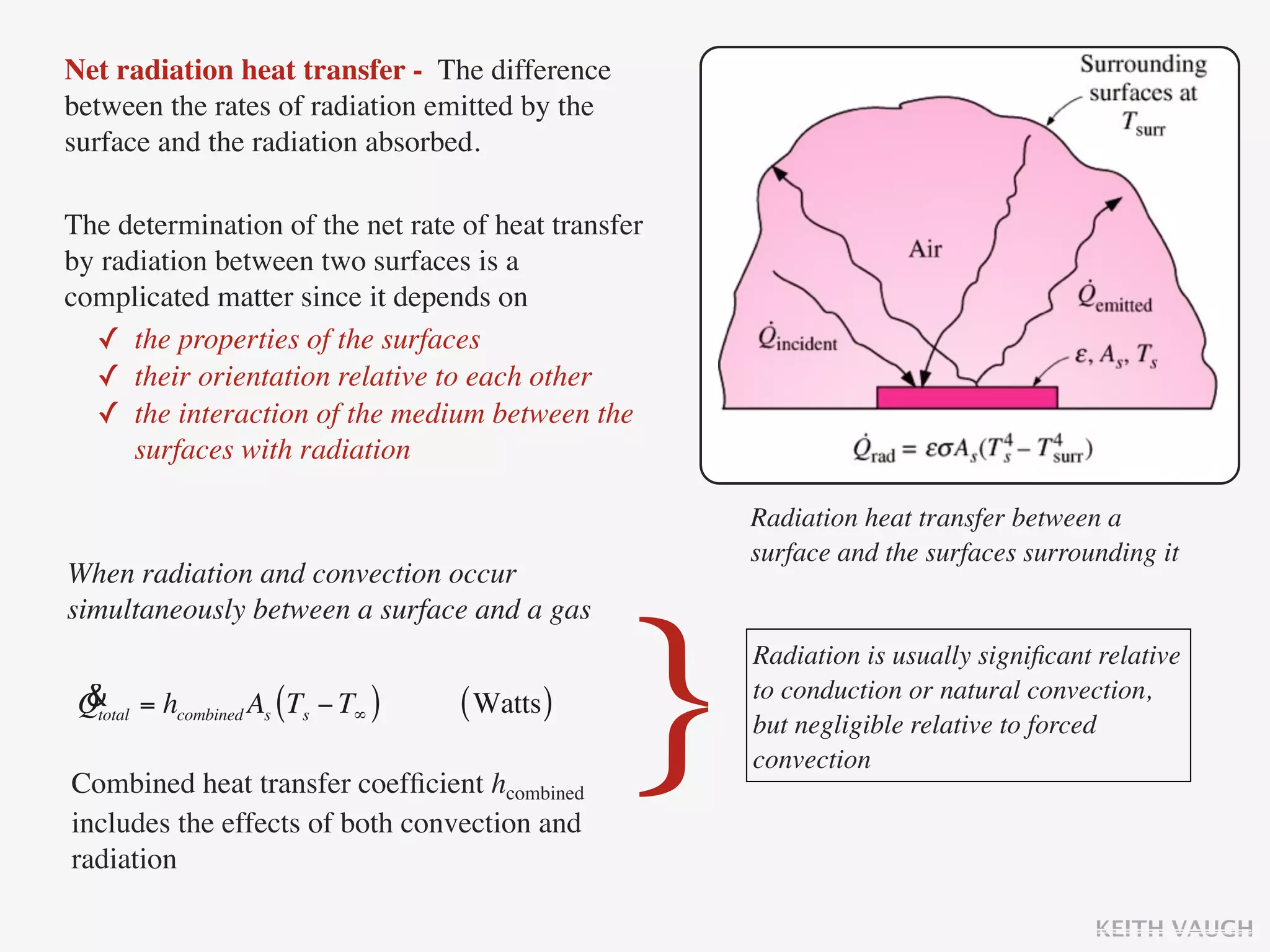
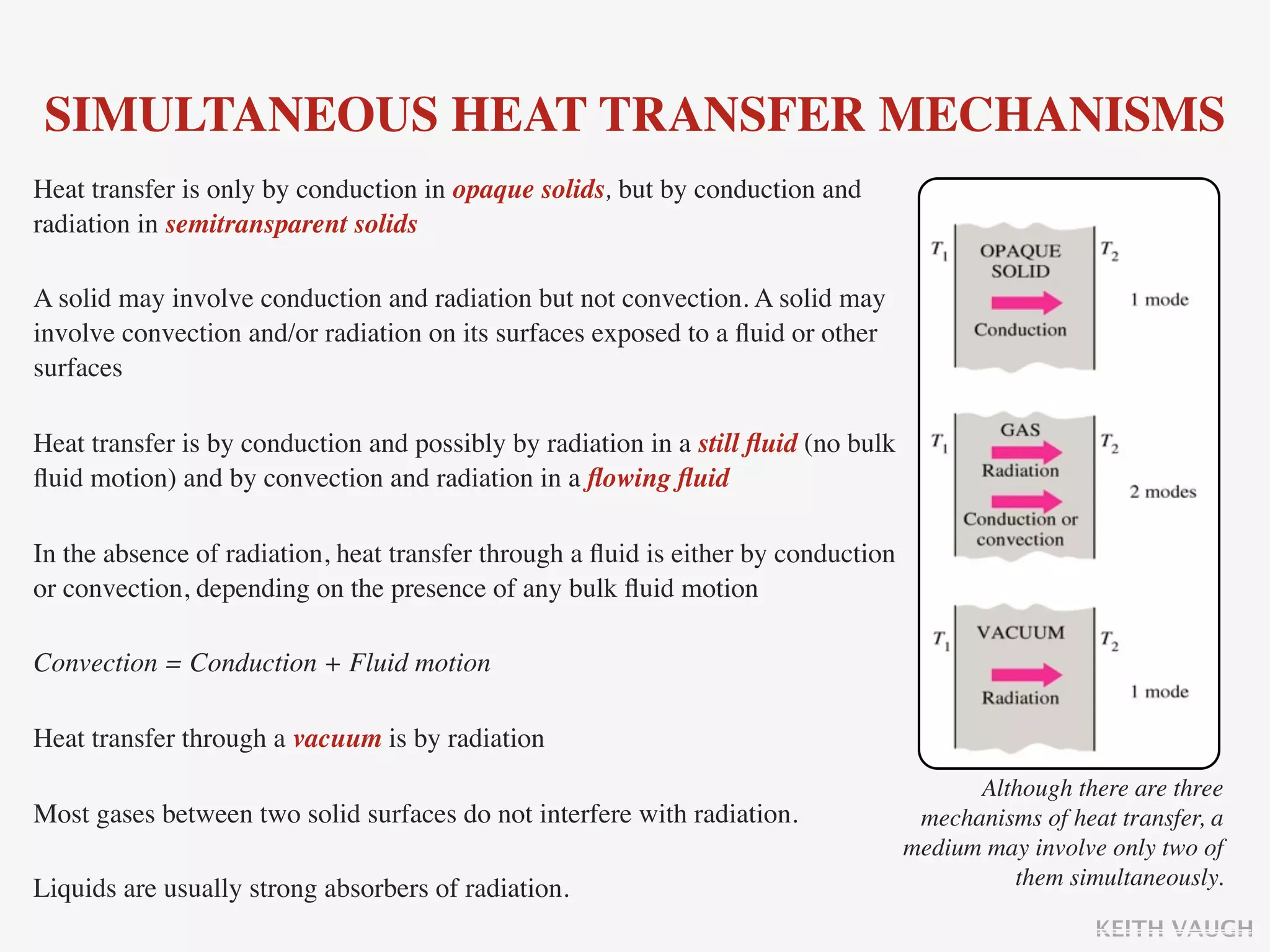
The document discusses the basic mechanisms of heat transfer, which are conduction, convection, and radiation. It describes conduction as the transfer of energy between particles through interactions and collisions. Conduction in solids is explained to occur through molecular vibrations and electron transport. Fourier's law of heat conduction establishes that the rate of heat conduction through a material is proportional to the thermal conductivity, temperature gradient, and area, while being inversely proportional to thickness. Thermal conductivity is introduced as a measure of a material's ability to conduct heat.