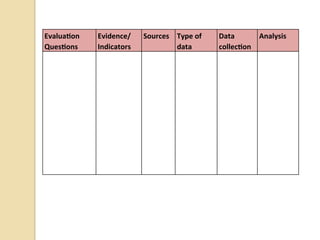
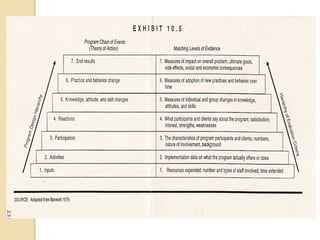
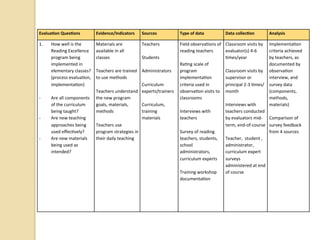
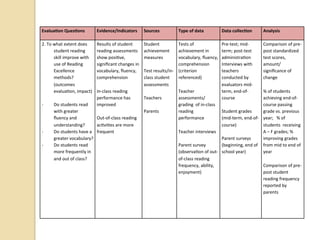
The document summarizes a workshop on designing curriculum evaluations. It provides templates and examples for developing evaluation plans with key components: evaluation questions, indicators of success, data sources, data collection methods, and data analysis strategies. Participants will use the templates to design an evaluation plan for assessing the implementation and impact of a reading program in their schools. The workshop covers qualitative and quantitative evaluation approaches to determine if program elements are being delivered as intended, whether teaching and student outcomes have improved, and the degree to which program goals are being met.