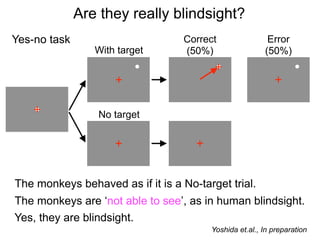
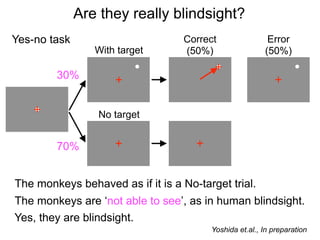
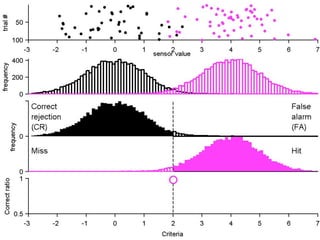
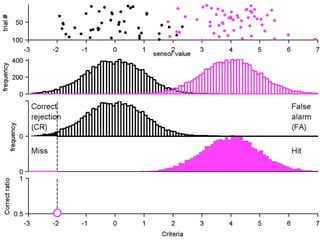
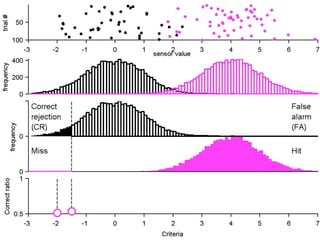
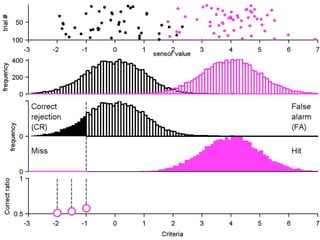
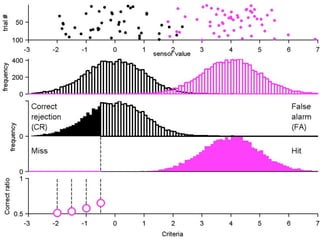
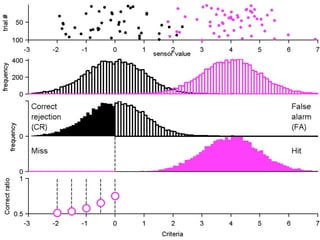
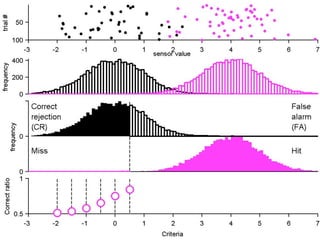
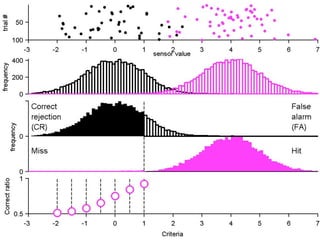
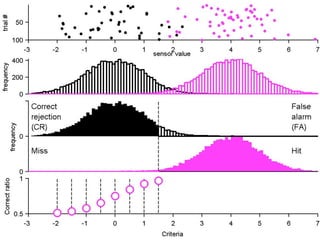
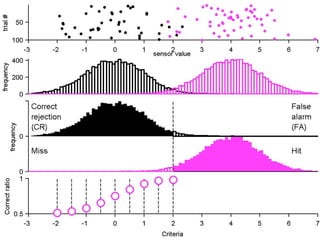
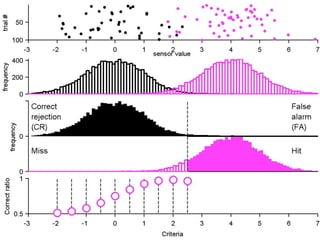
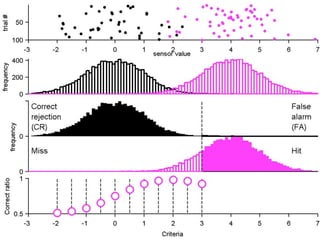
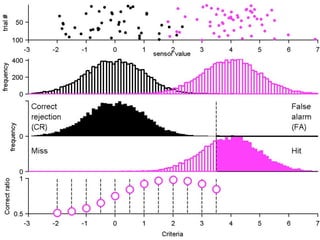
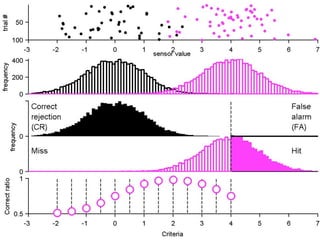
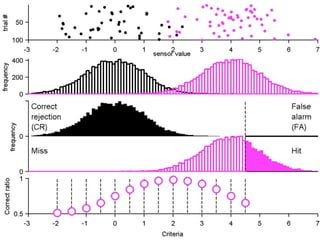
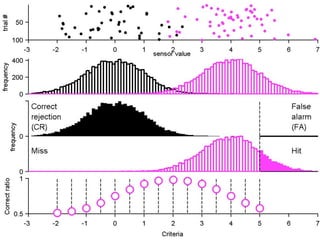
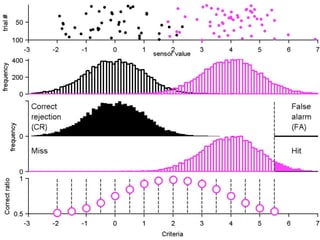
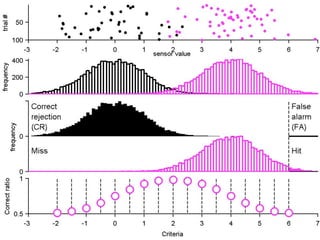
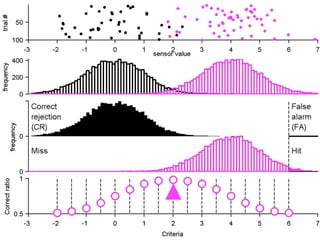
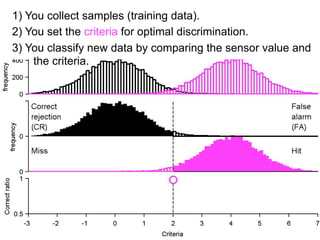
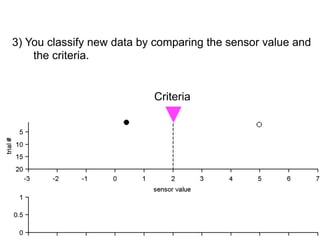
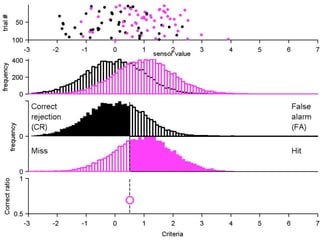
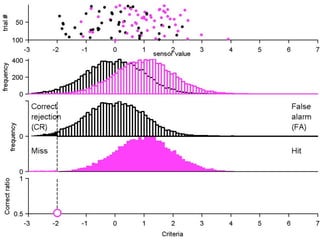
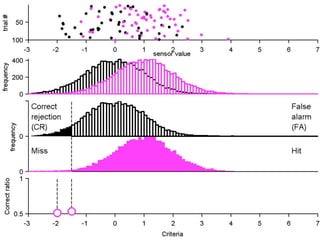
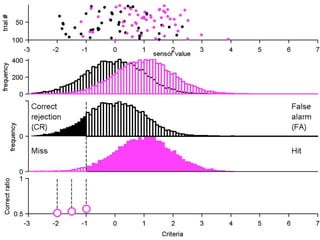
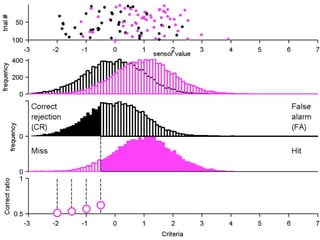
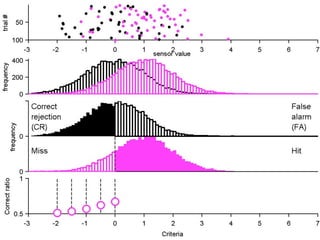
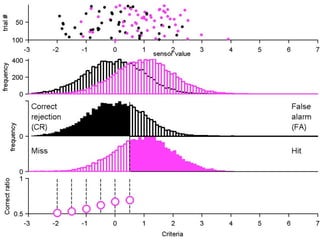
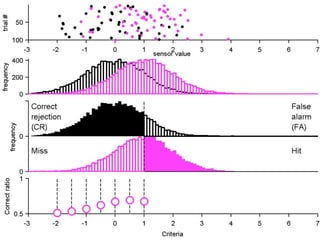
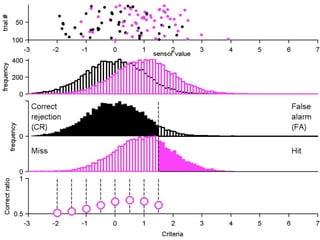
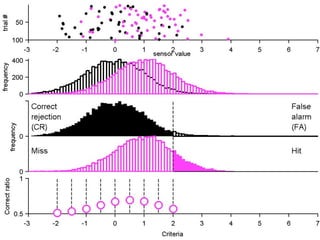
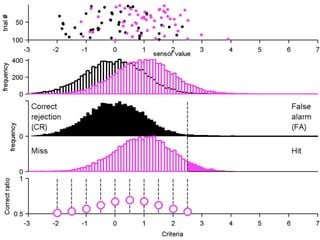
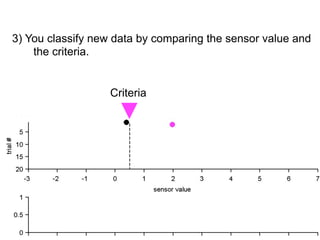
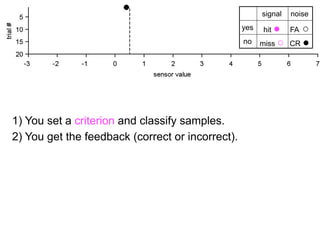
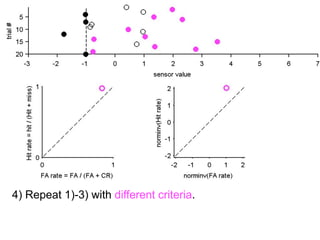
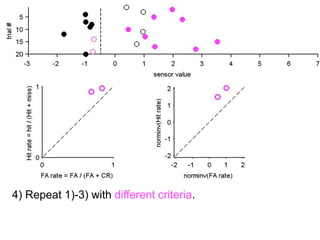
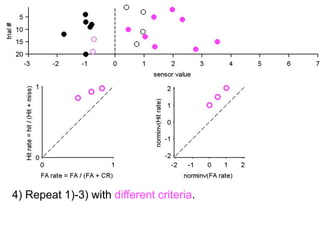
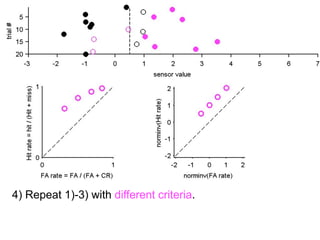
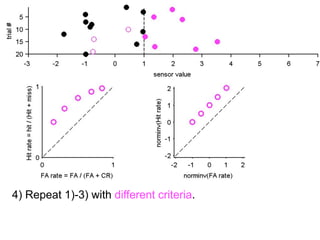
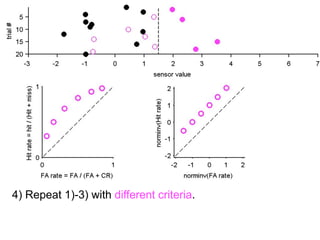
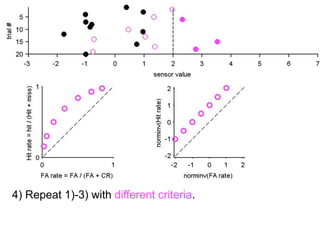
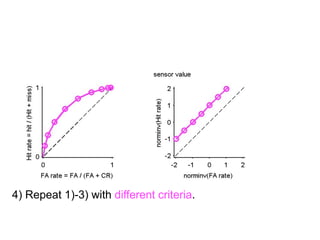
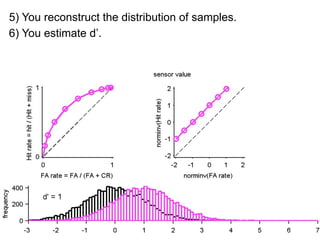
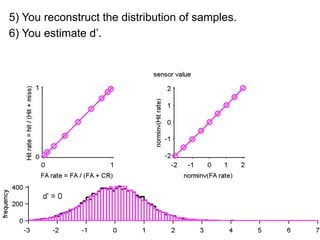
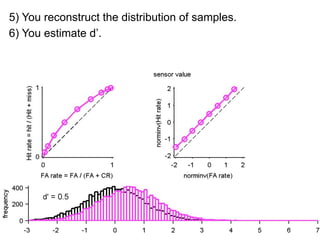
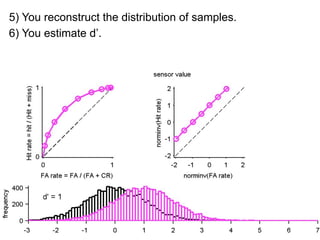
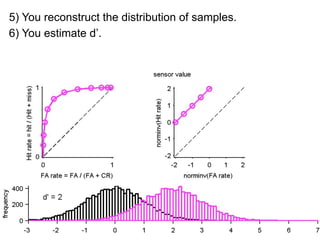
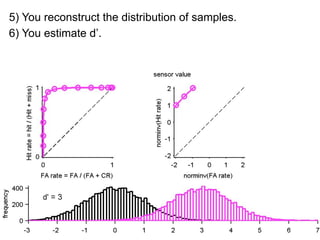
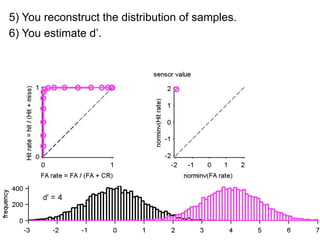
FA
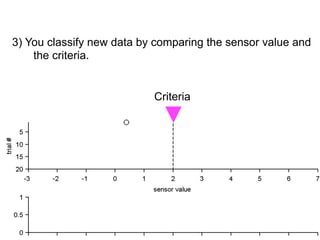
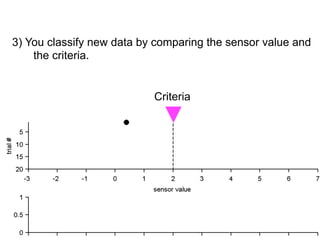
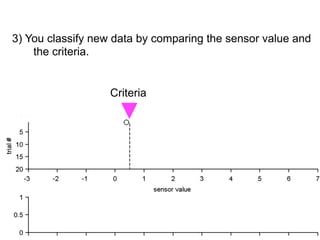
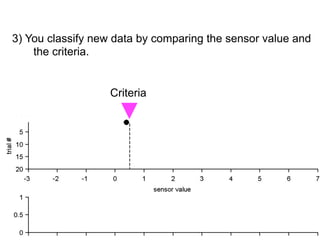
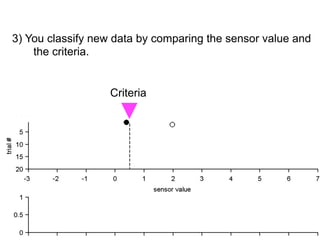
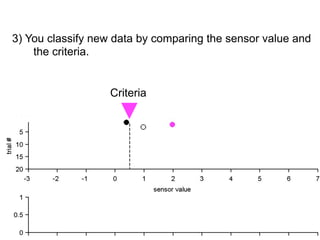
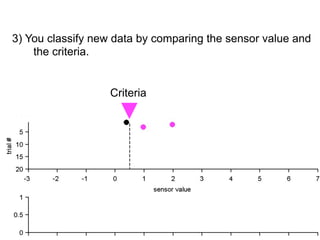
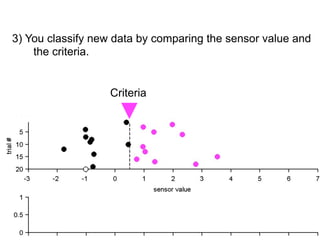
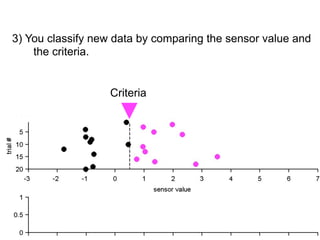
no miss ○ CR ●
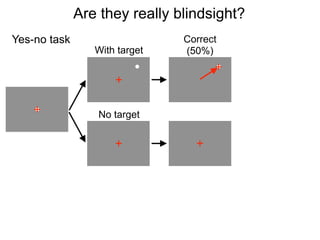
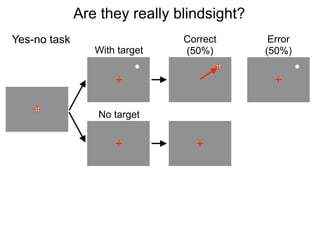
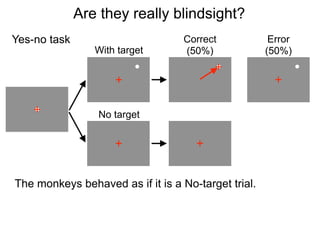
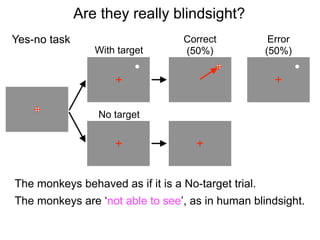
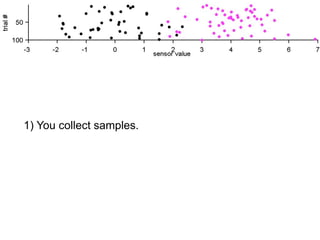
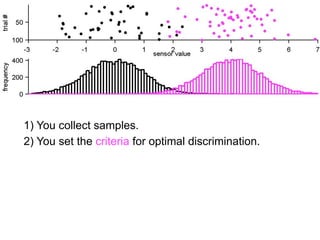
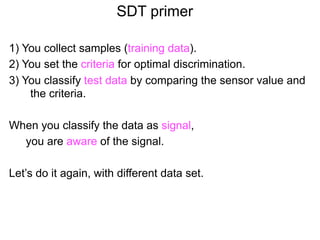
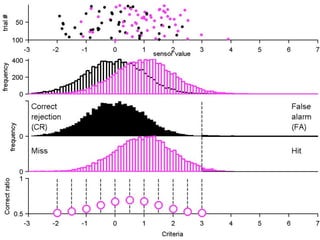
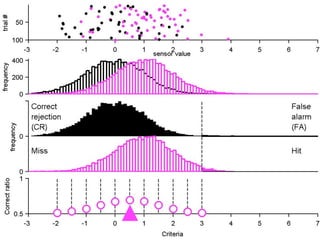
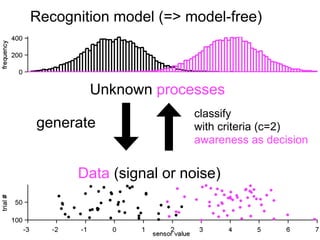
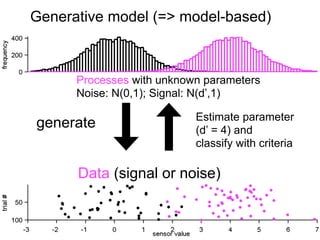
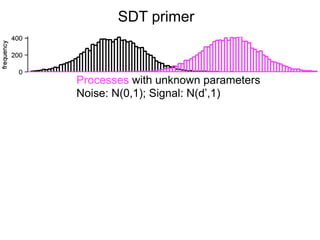
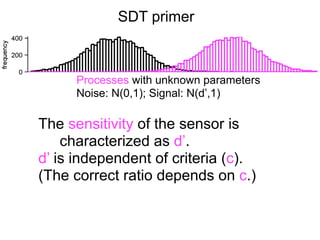
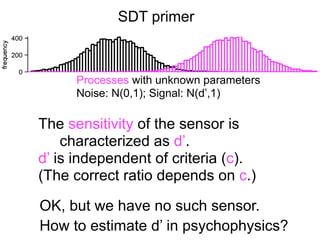
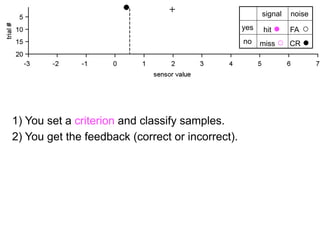
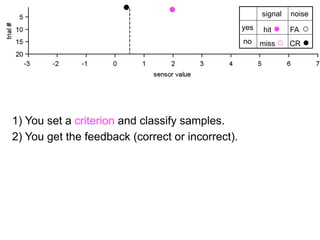
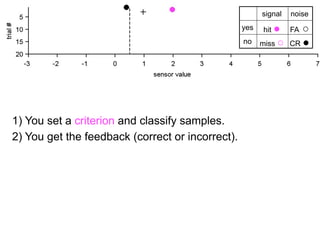
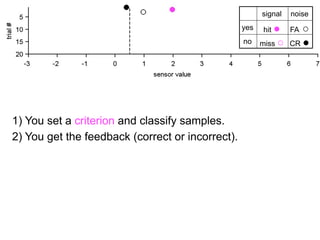
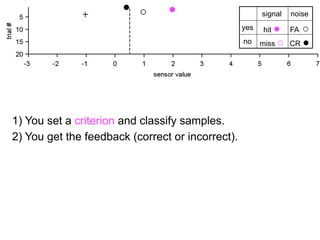
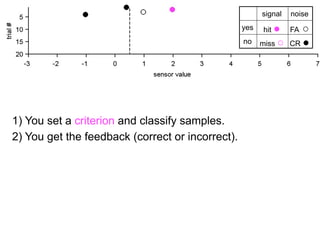
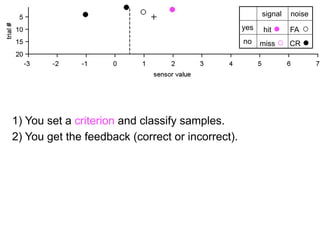
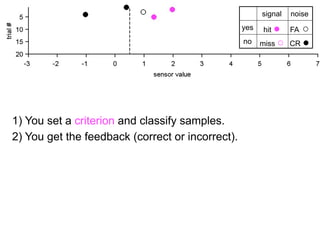
The document describes the process of signal detection theory (SDT). It involves:
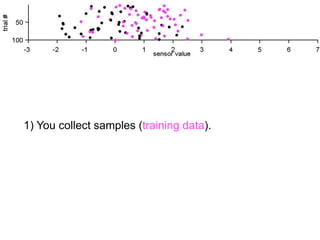
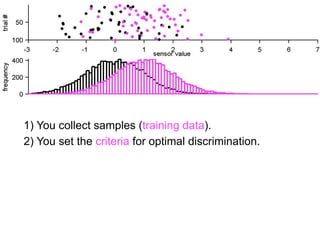
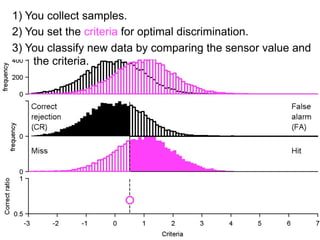
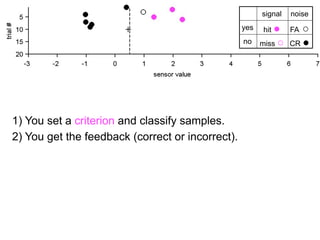
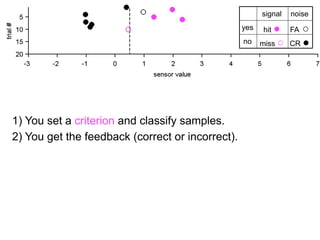
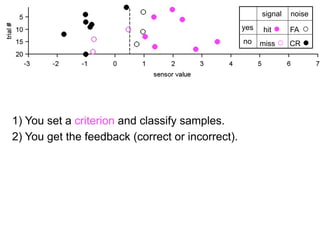
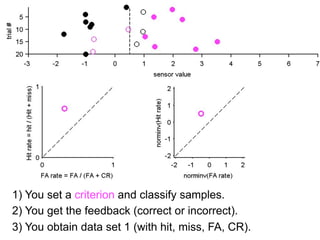
1) Collecting training data samples from known signals and noises.
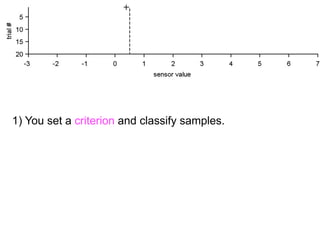
2) Setting criteria for optimal discrimination between signals and noises.
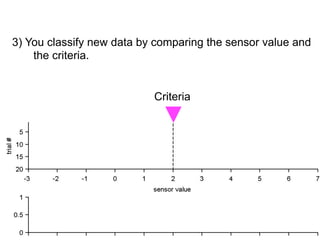
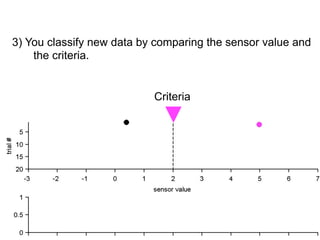
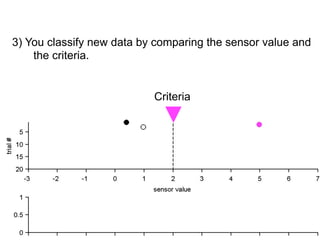
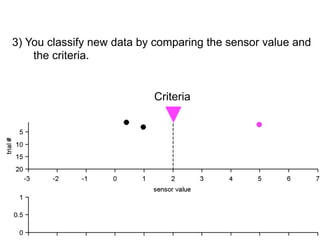
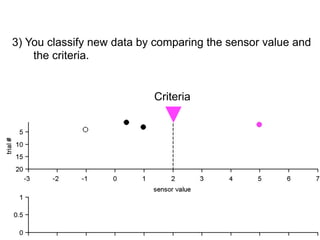
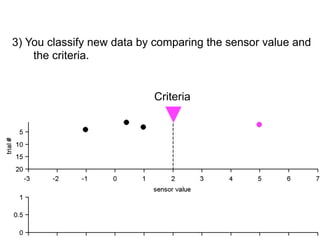
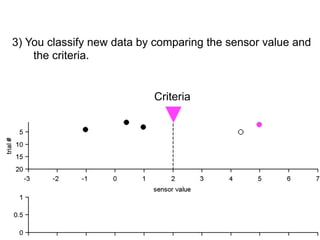
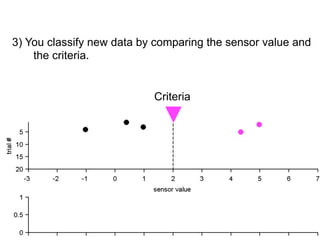
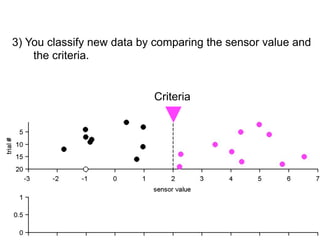
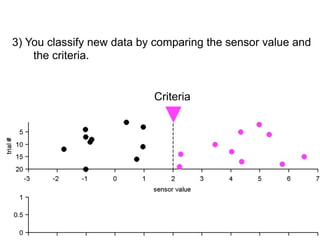
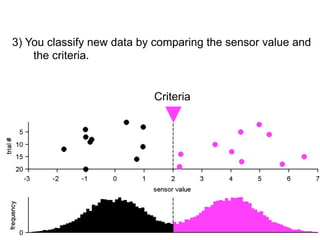
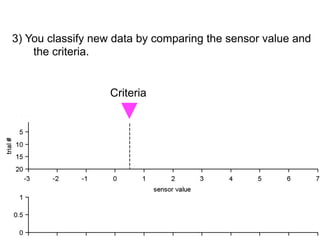
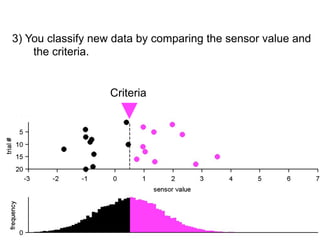
3) Classifying new test data by comparing the sensor values to the discrimination criteria.
The goal is to accurately detect signals while minimizing incorrect classifications of noise as signals.