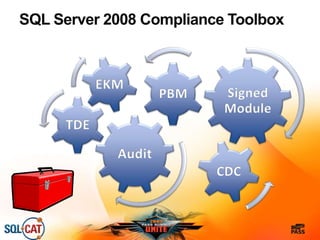
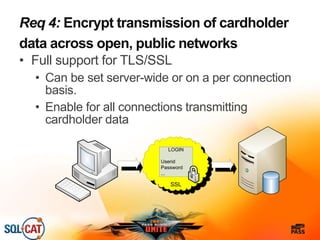
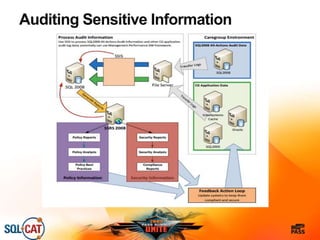
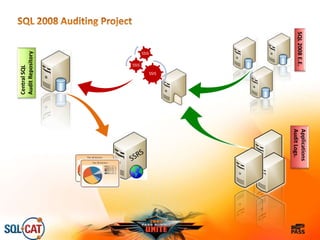
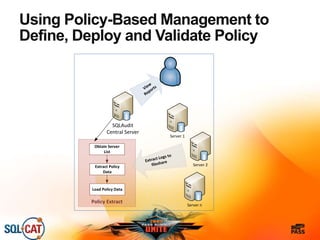
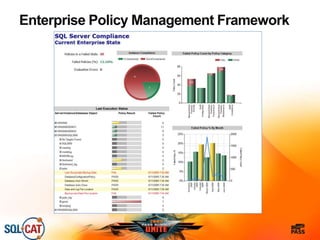
The document outlines security and compliance challenges faced by organizations, specifically focusing on SQL Server and related regulations such as PCI and HIPAA. It emphasizes the importance of robust security features, proper database management practices, and the role of the SQL Server Customer Advisory Team in assisting with complex projects. Various case studies showcase successful implementations and best practices in achieving compliance and enhancing data security.