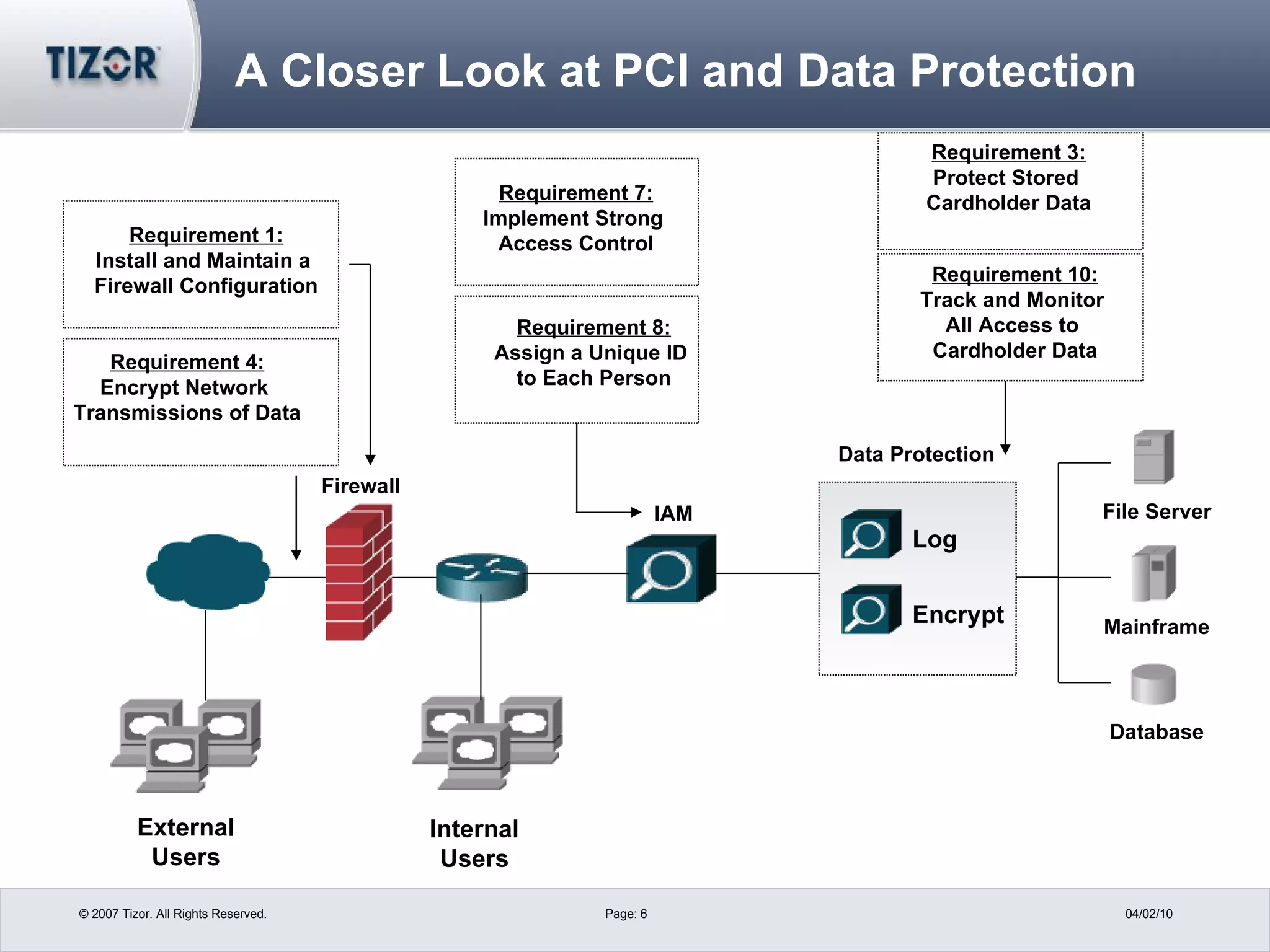
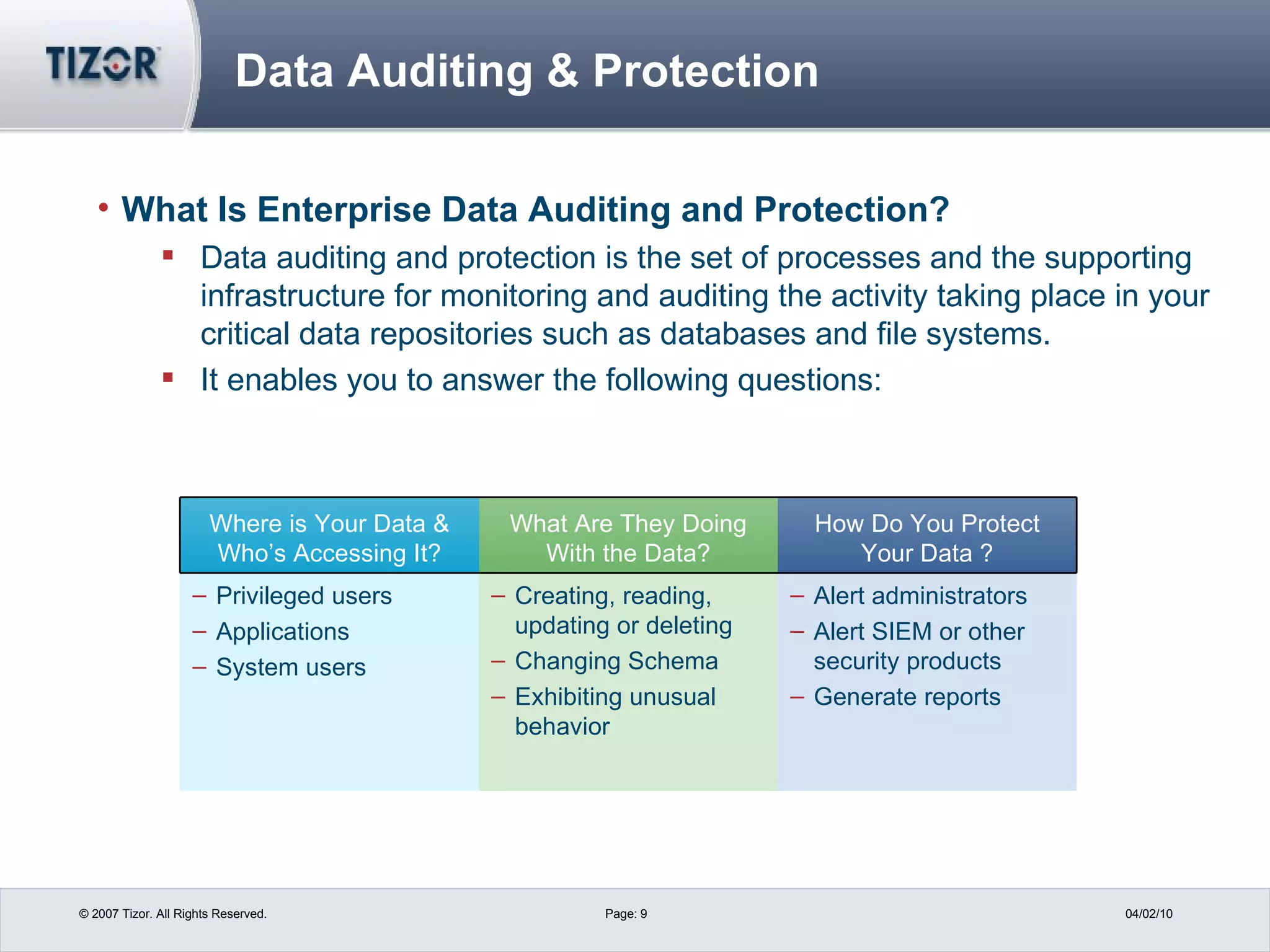
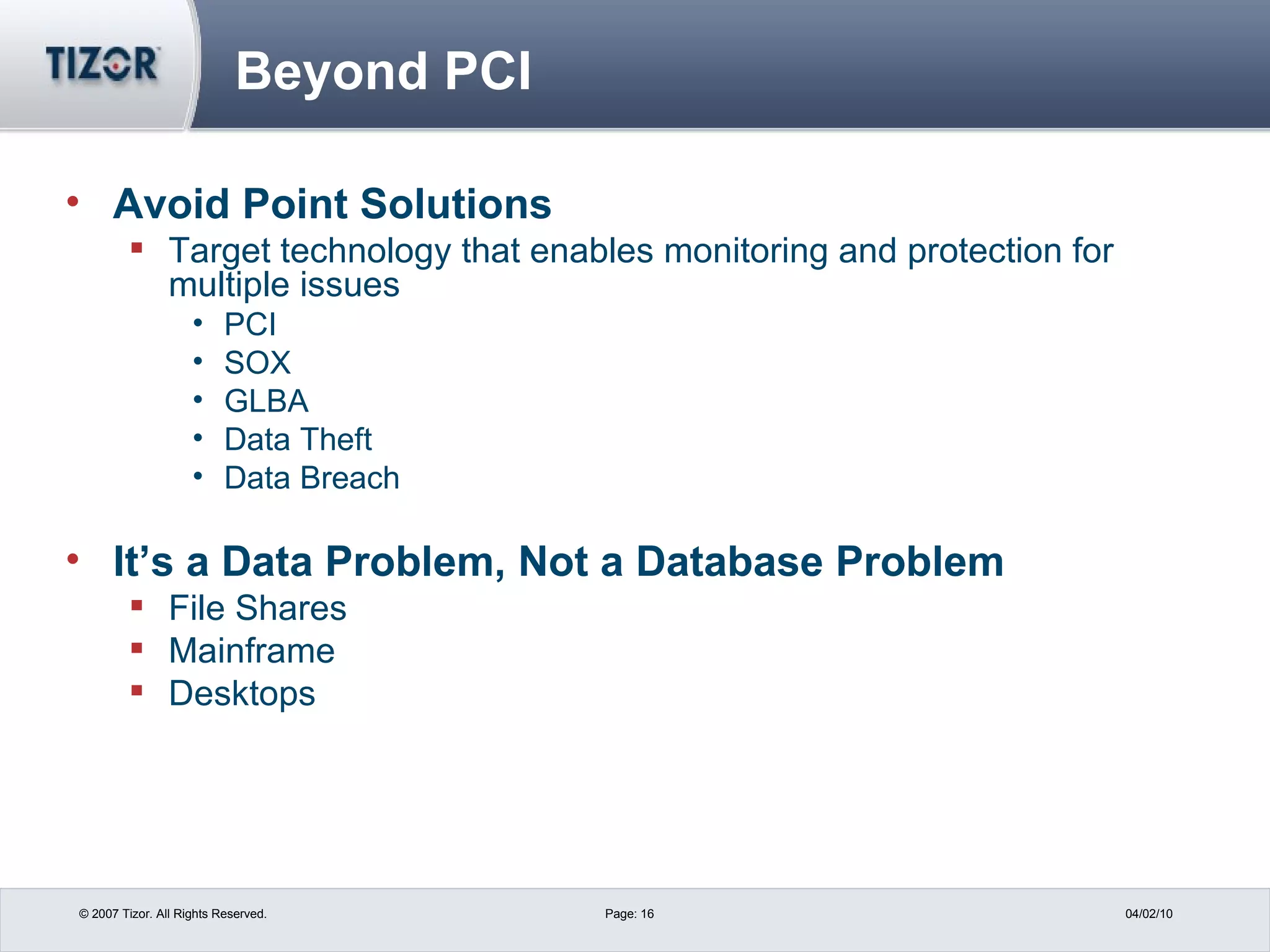
The document discusses best practices for PCI compliance and data protection. It introduces new PCI-DSS requirements and how they apply to merchants, service providers and hosting companies. It emphasizes using data discovery tools, limiting data access and retention, and implementing strong access controls, encryption, monitoring and auditing. The document recommends moving beyond point solutions to a layered data defense approach that protects data from unauthorized access and exfiltration across different systems.













![Questions? Michael Semaniuk 978-243-3212 [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tizordatabestpracticesppt4072/75/Tizor_Data-Best-Practices-ppt-17-2048.jpg)