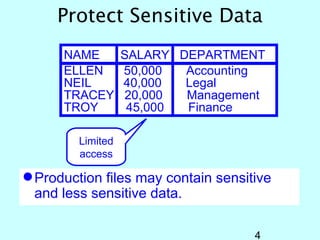
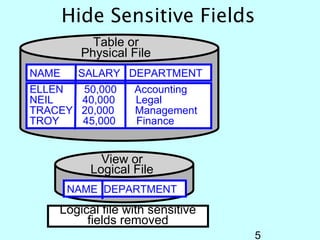
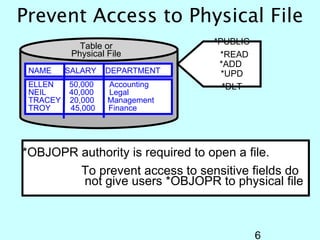
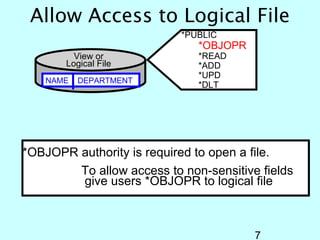
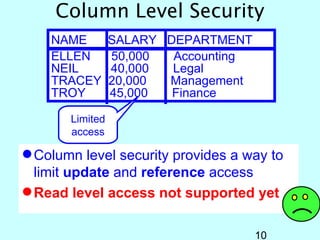
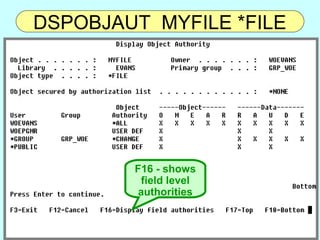
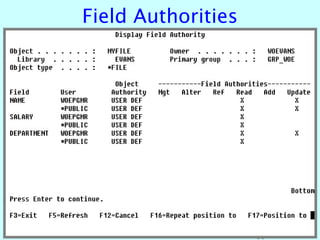
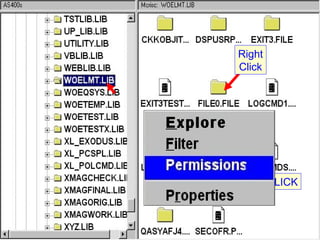
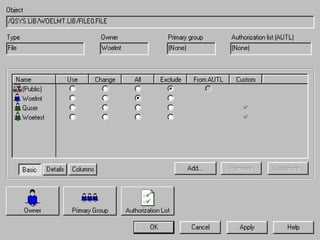
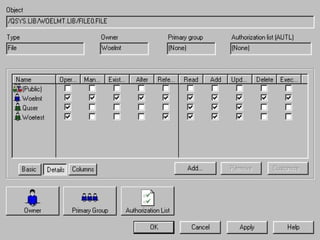
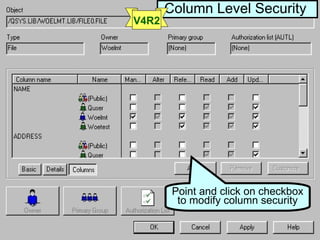
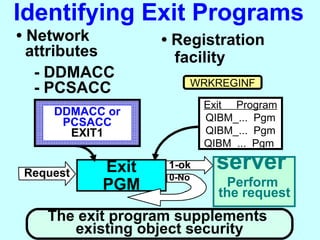
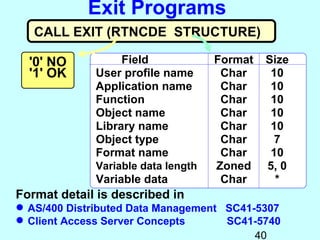
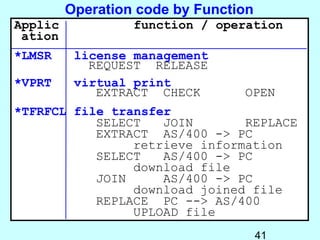
- OS/400 security allows logical files and column-level security to protect sensitive data in databases. Exit programs can also supplement object-level security by restricting specific operations and monitoring user activity.
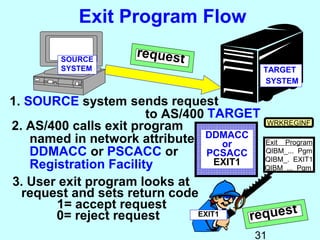
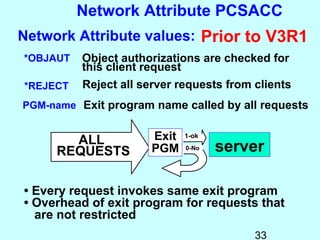
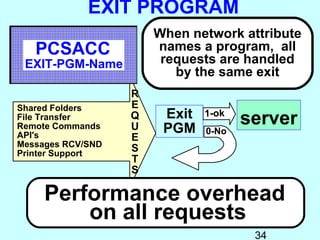
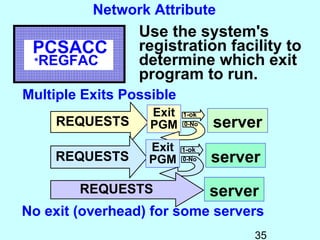
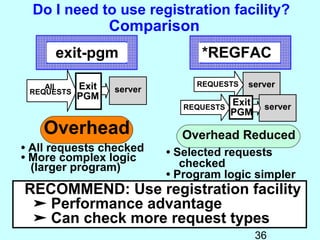
- Exit programs identify requests using network attributes and can reject or allow requests by returning codes to the system. The registration facility determines the appropriate exit program to run for different request types. This avoids performance overhead of running an exit program for all requests.