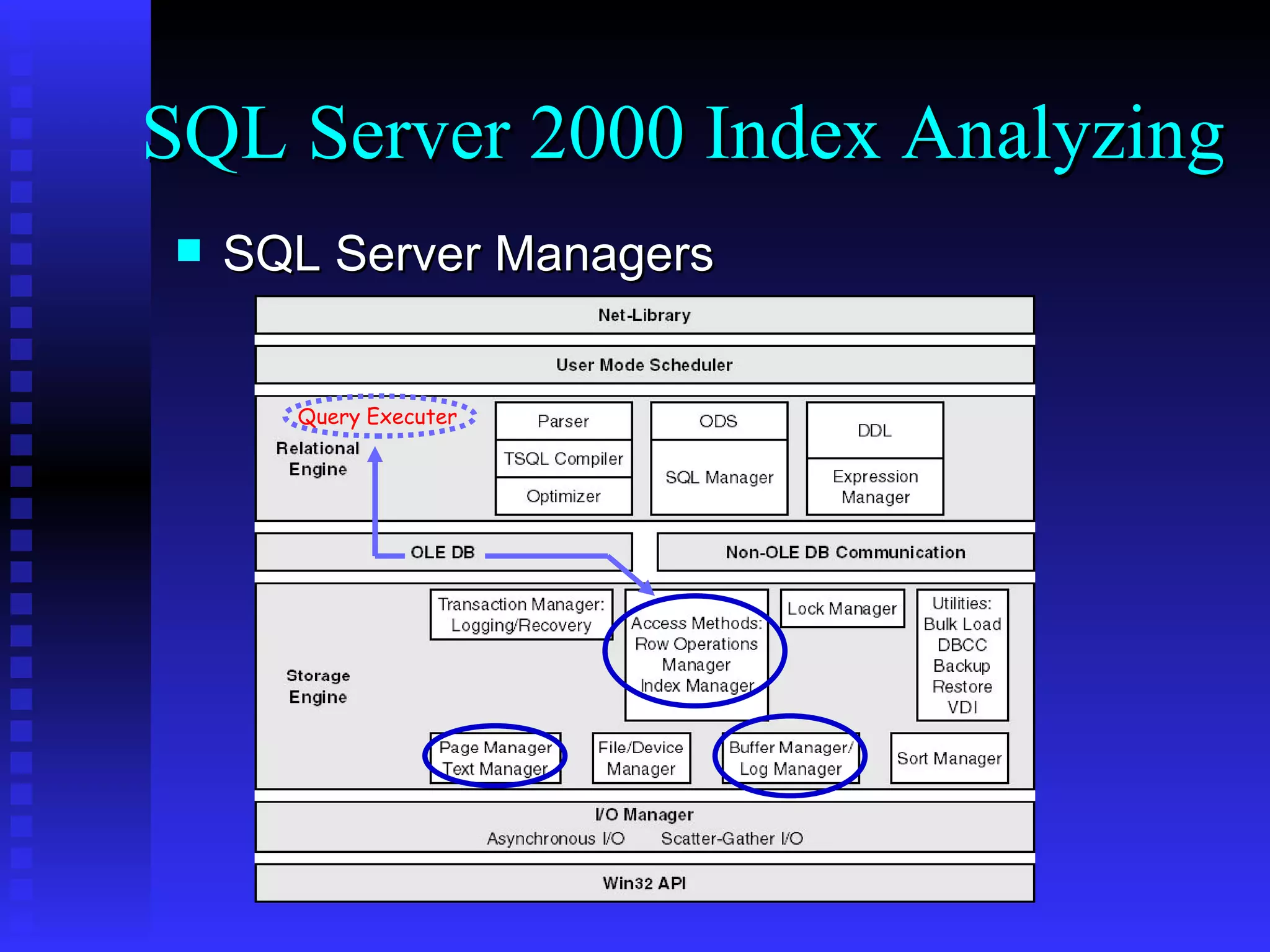
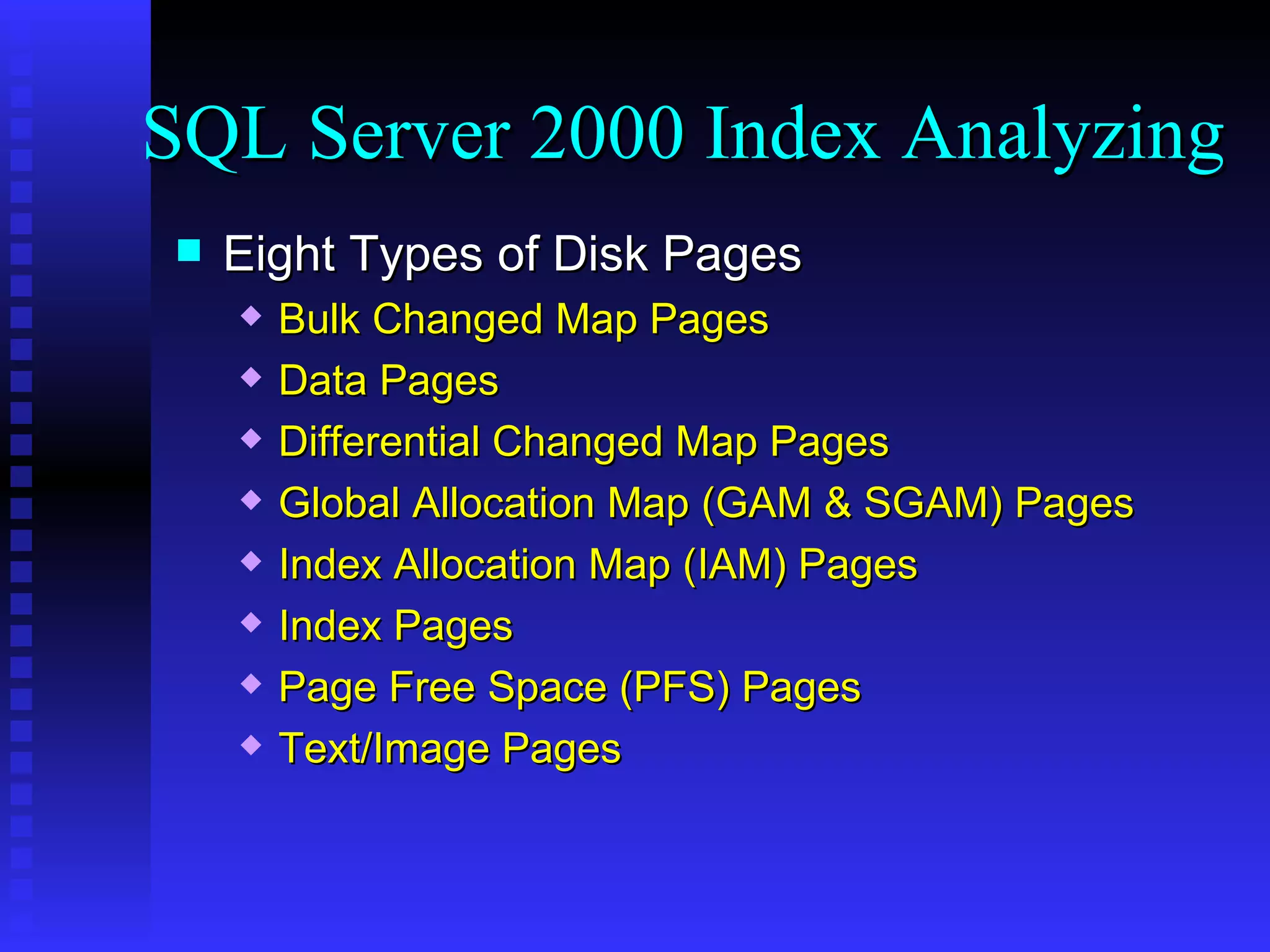
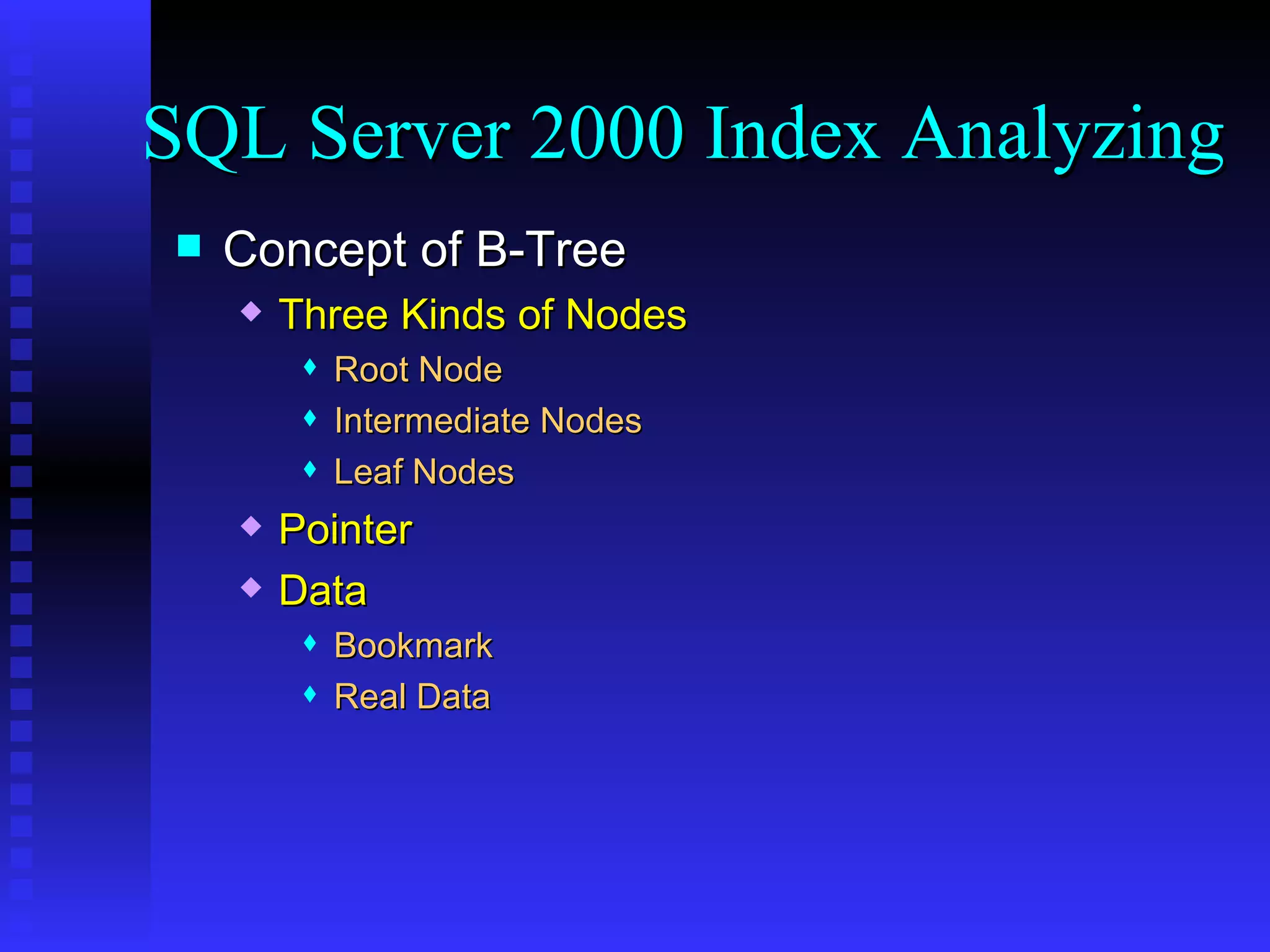
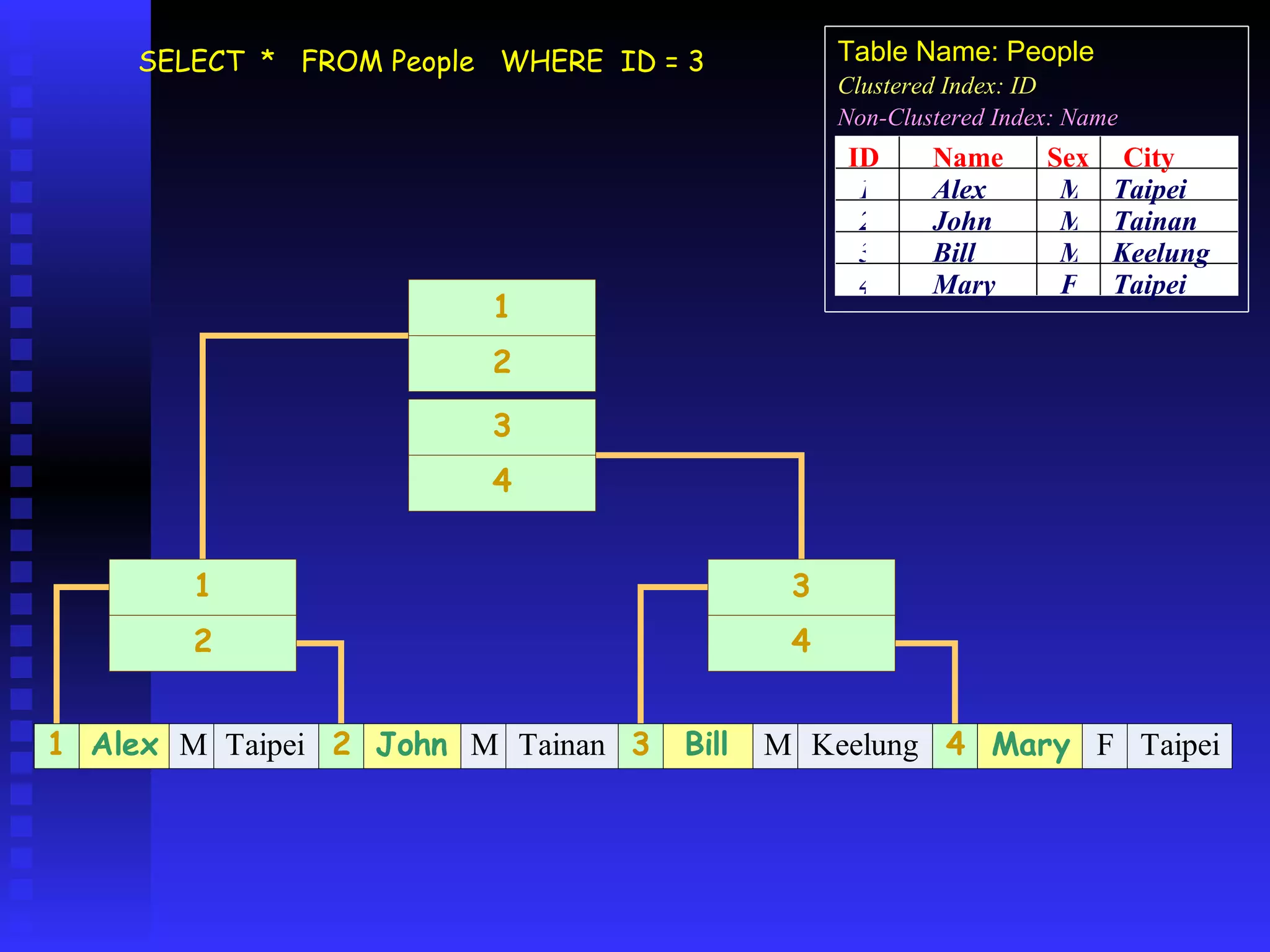
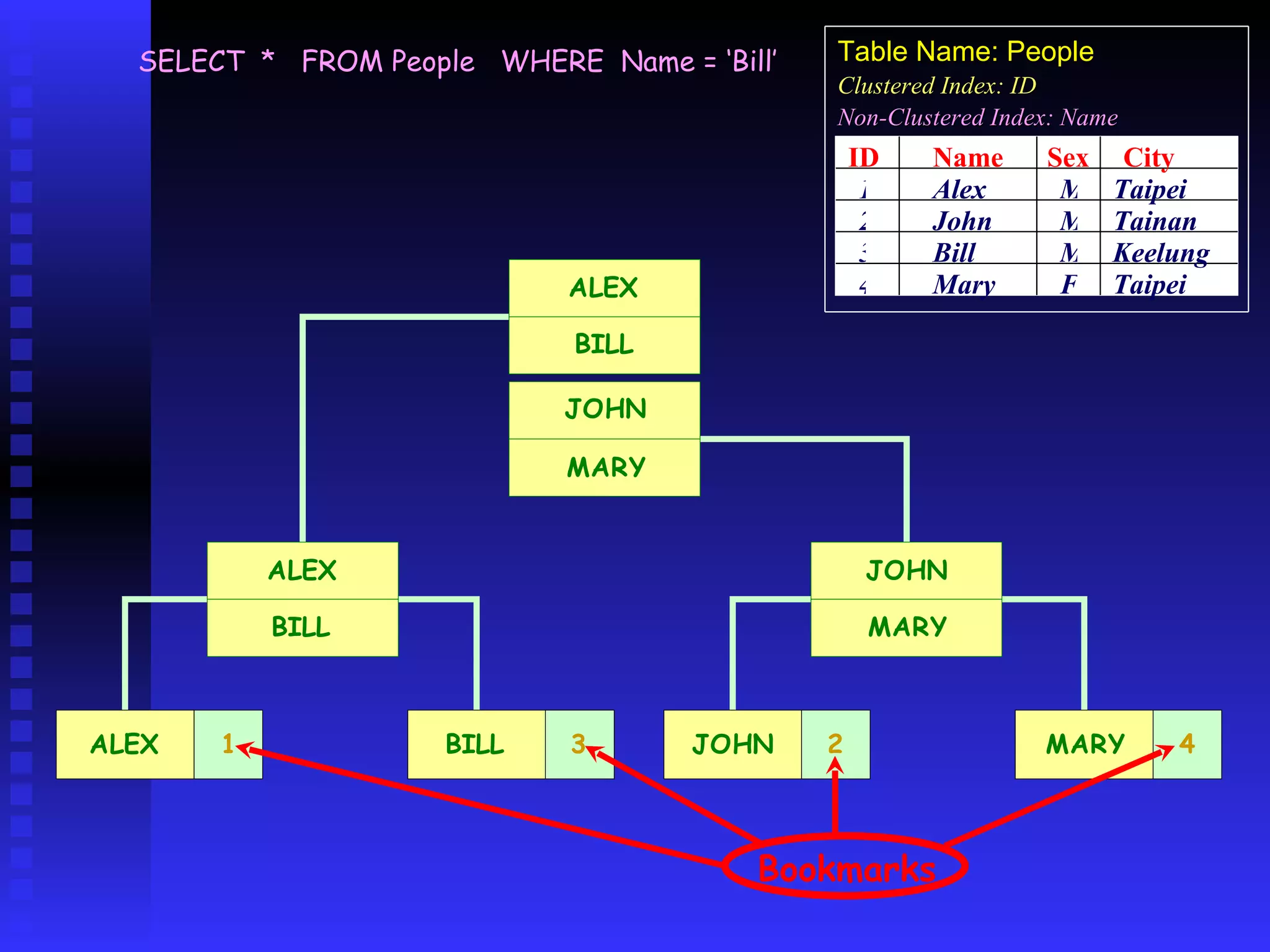
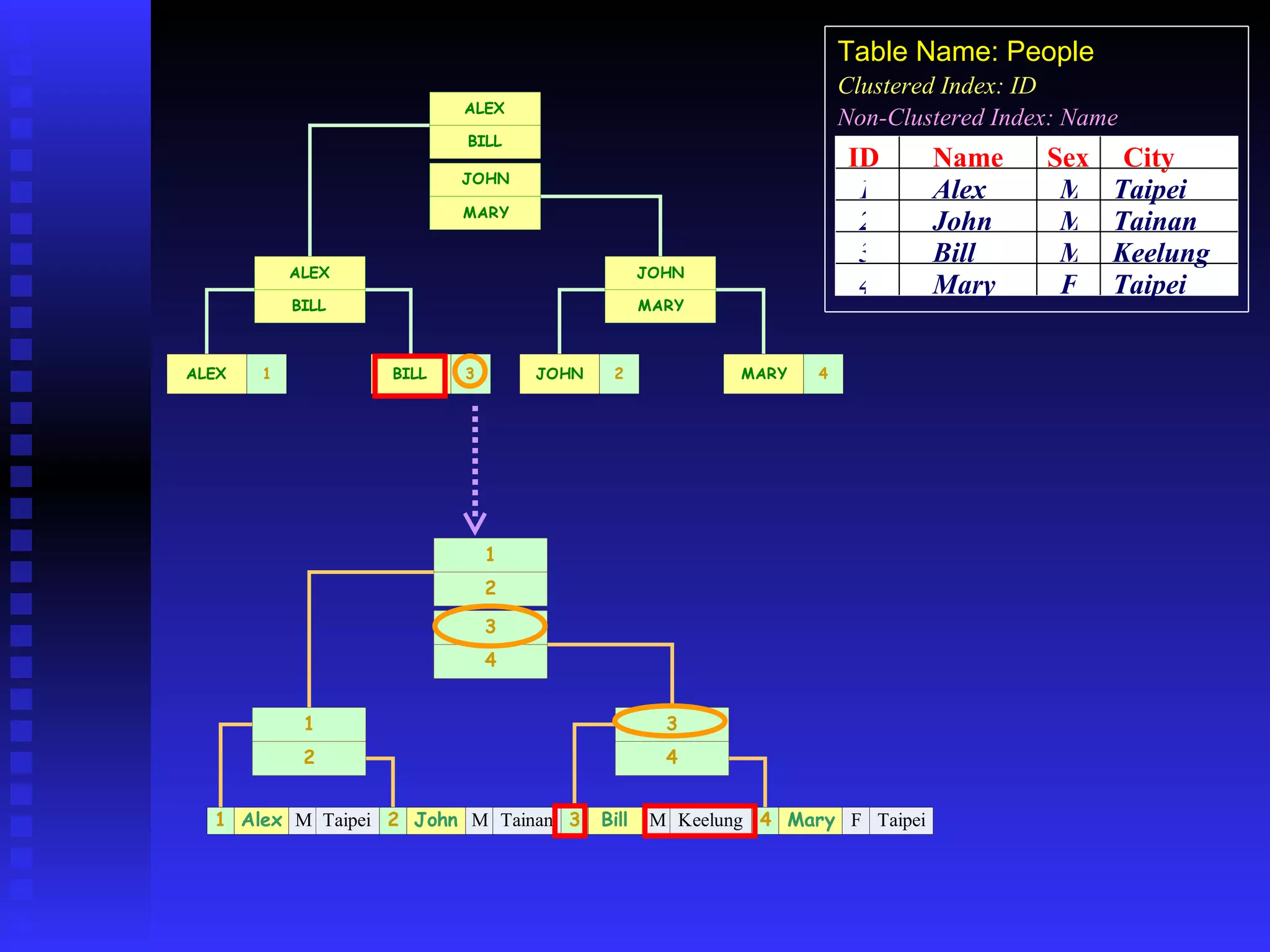
The document discusses performance tuning in SQL Server 2000. It covers index analyzing, the different types of disk pages and indexes in SQL Server 2000. It provides tips for index creation and query design to improve performance, such as using indexes to filter queries and avoiding functions in WHERE clauses. The overall goal is to help optimize queries and tune database performance.