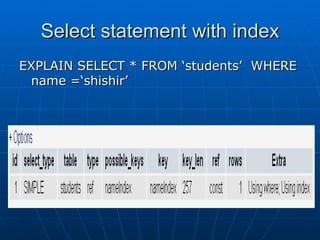
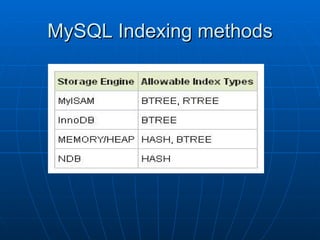
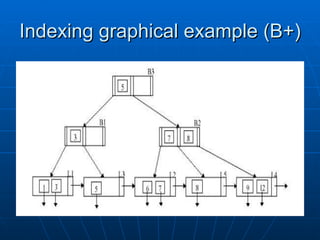
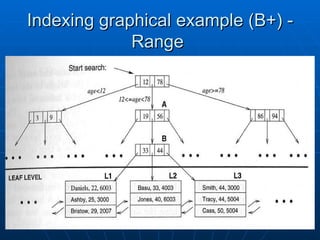
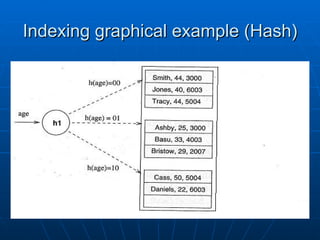
The document discusses indexing in MySQL databases. It defines indexing as adding metadata like page numbers to data to allow for faster retrieval. Indexes provide advantages like faster queries but also disadvantages like using extra storage space. Indexes are most useful for operations that retrieve data, not add or modify it. The document provides examples of using CREATE INDEX and DROP INDEX statements to add and remove indexes. It also discusses when indexes are appropriate to apply, such as to fields used in WHERE clauses, and when they are not needed, like on usually unchanging fields. Finally, it covers index types like single column, multi-column, and range indexes as well as indexing methods like B+ trees and hashing.