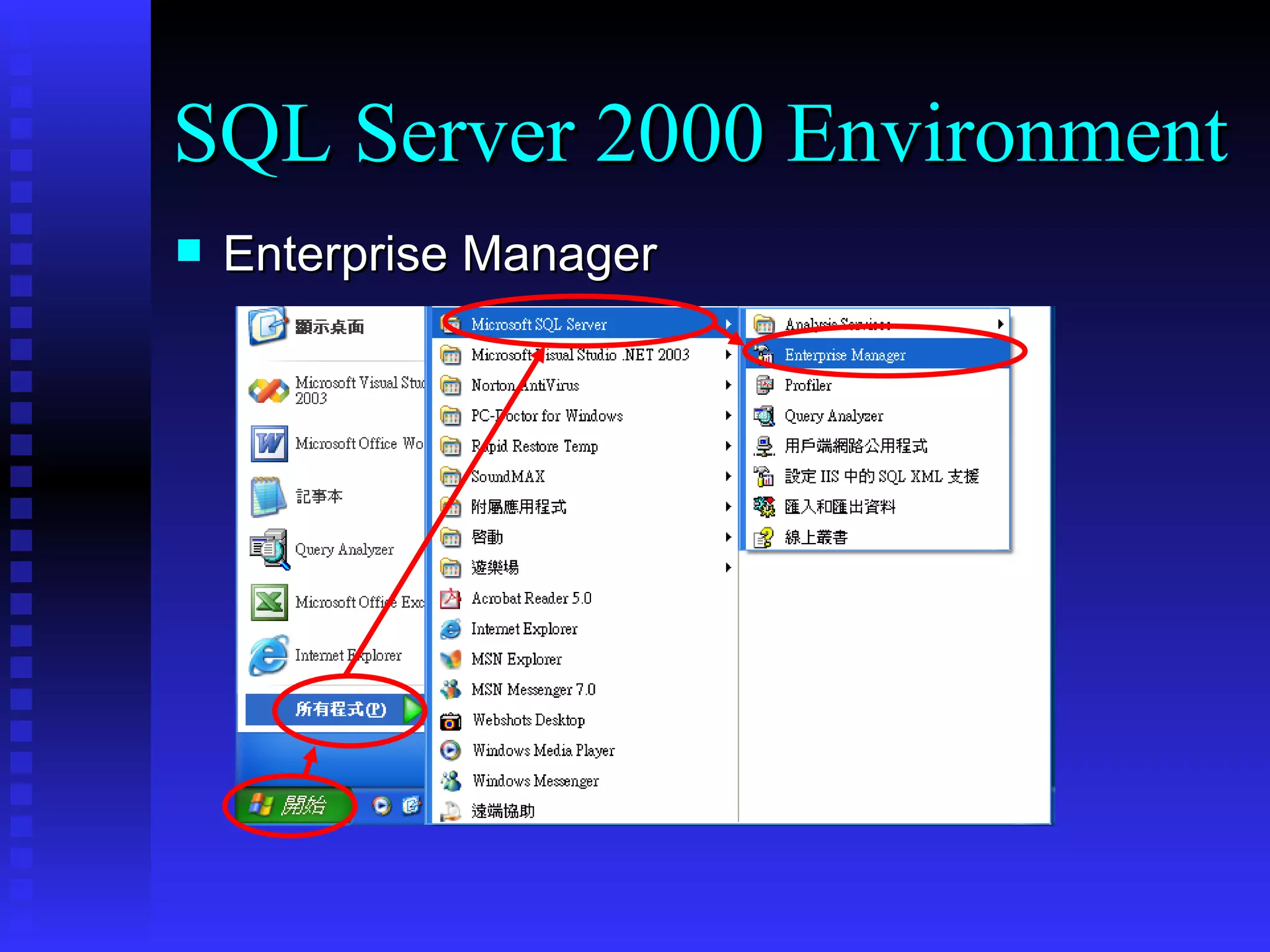
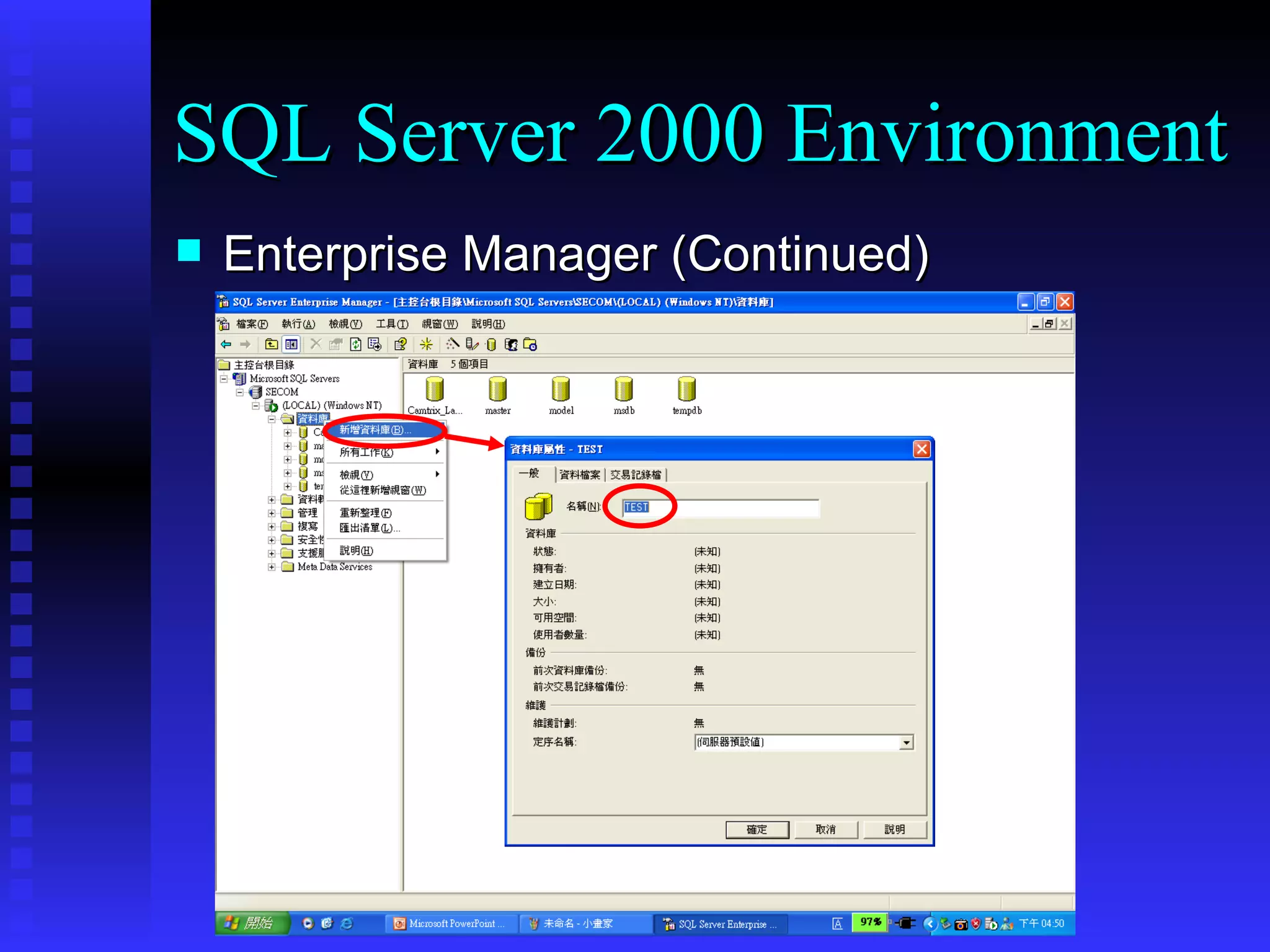
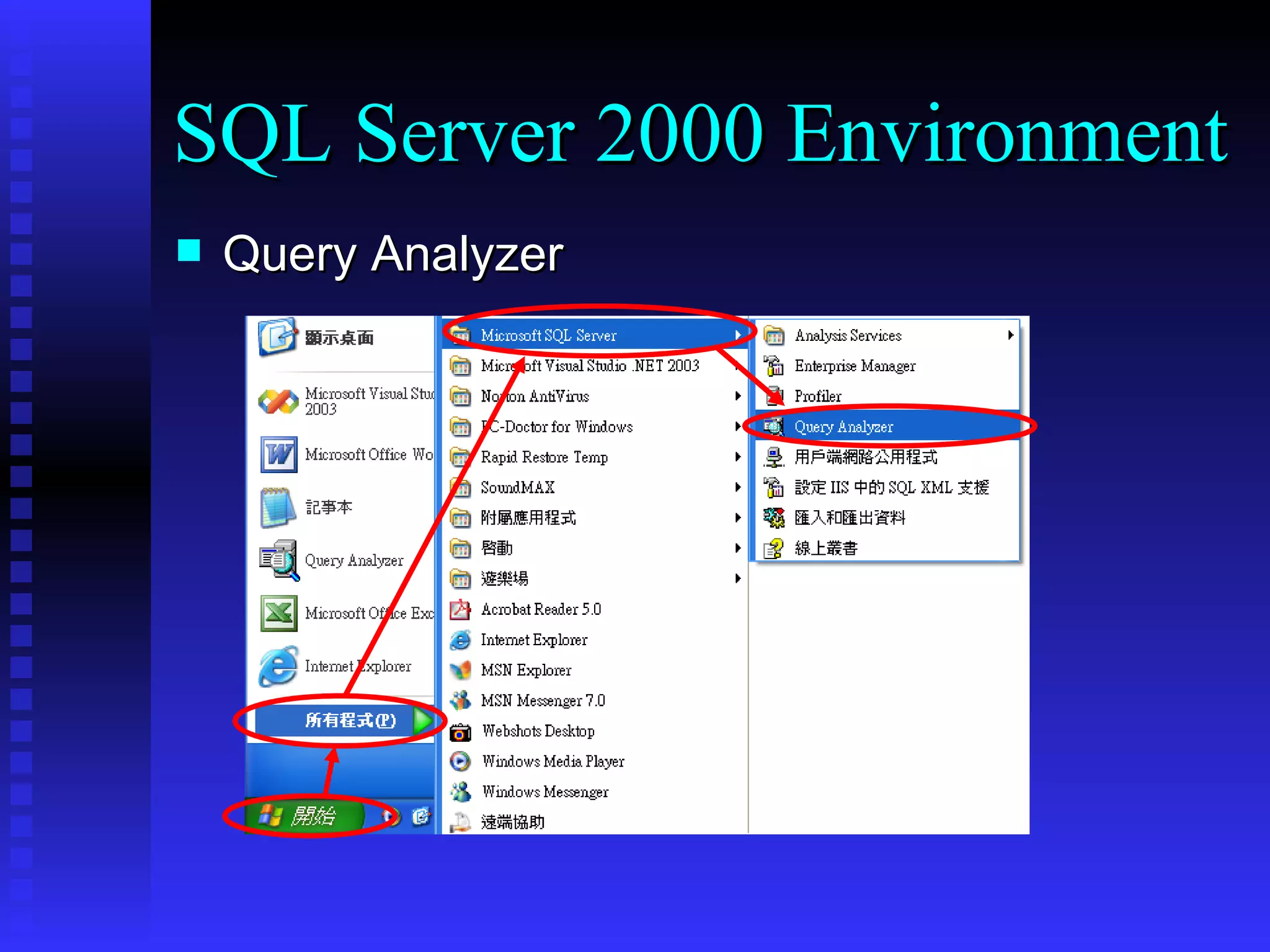
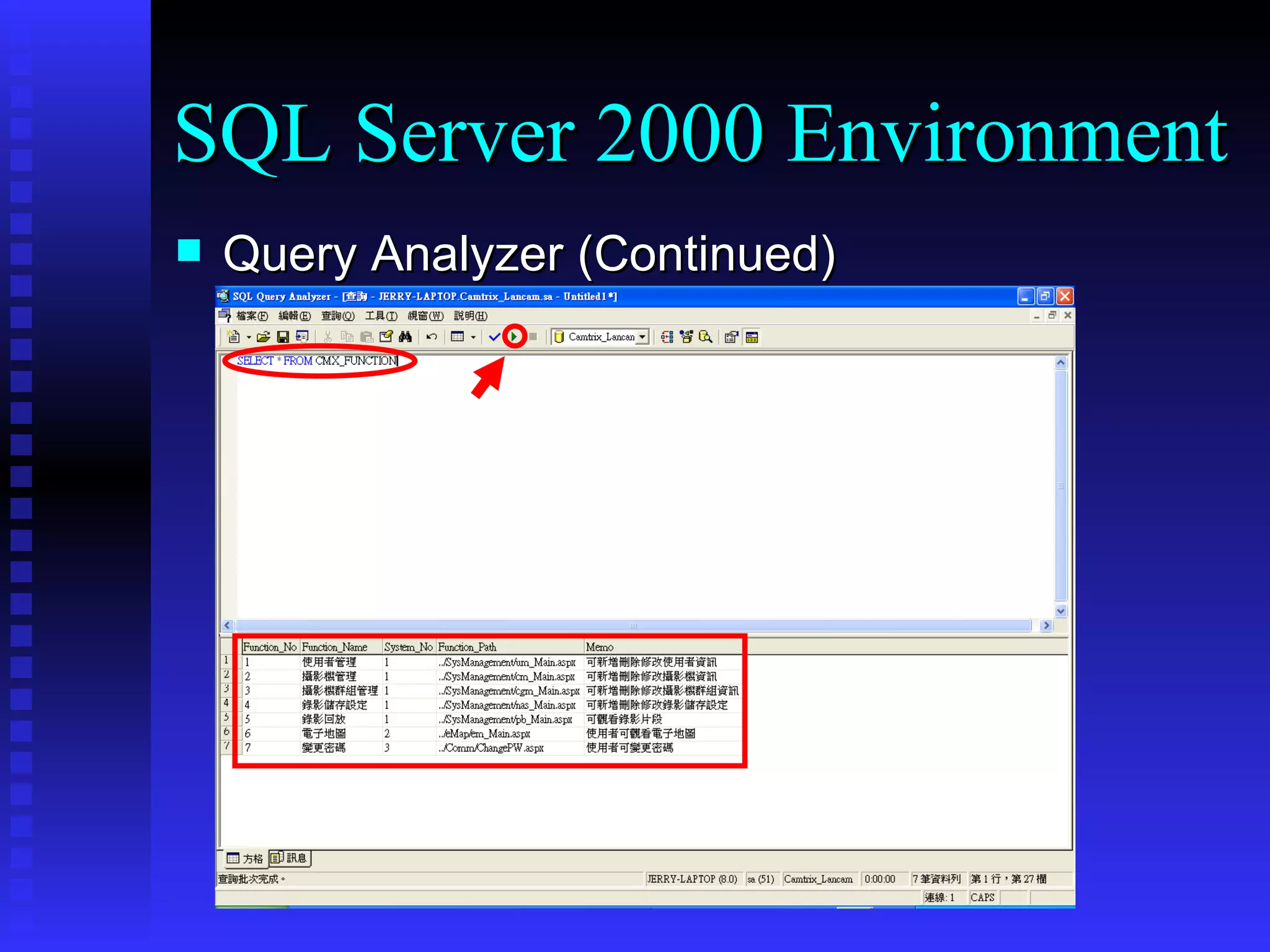
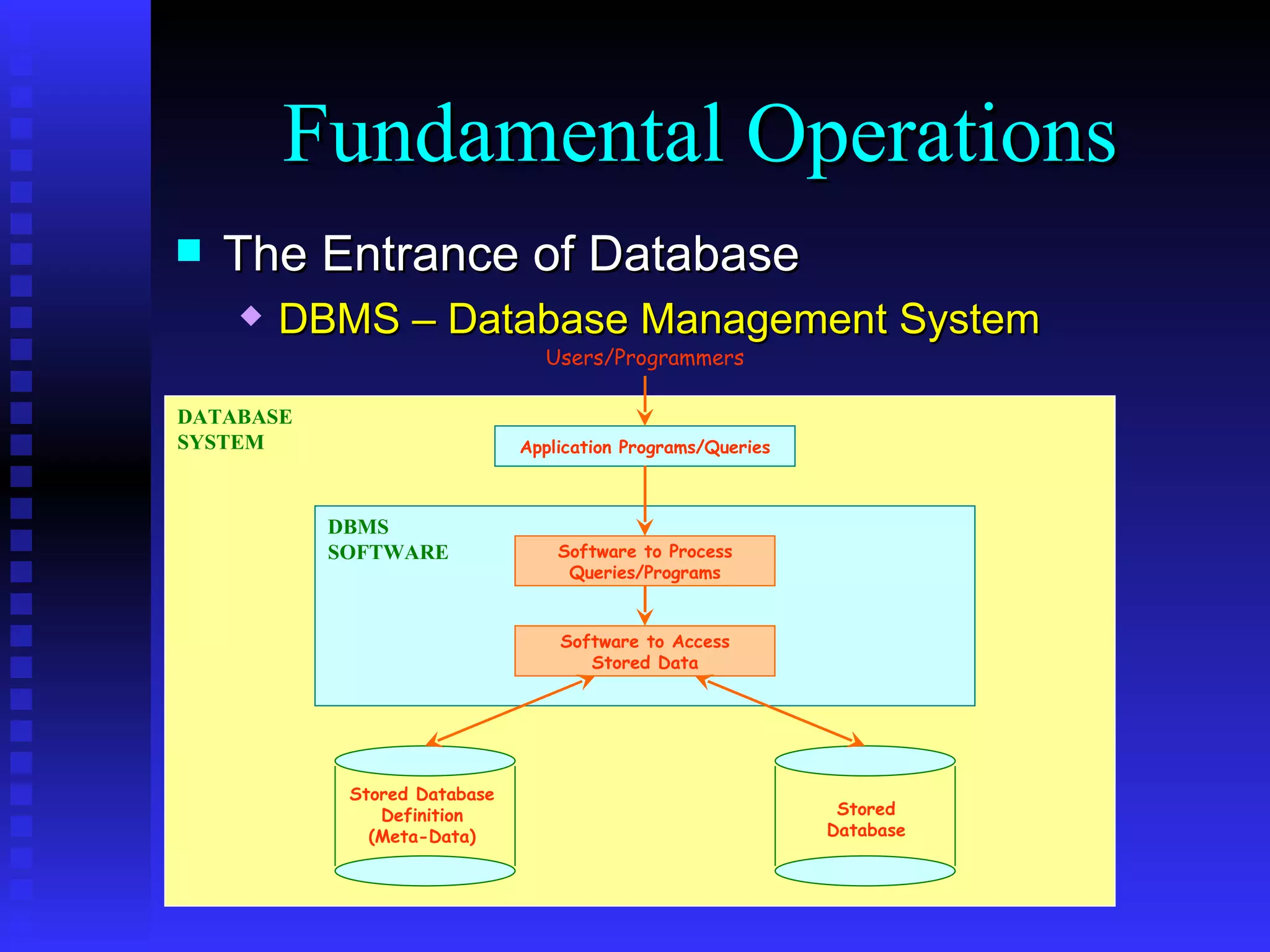
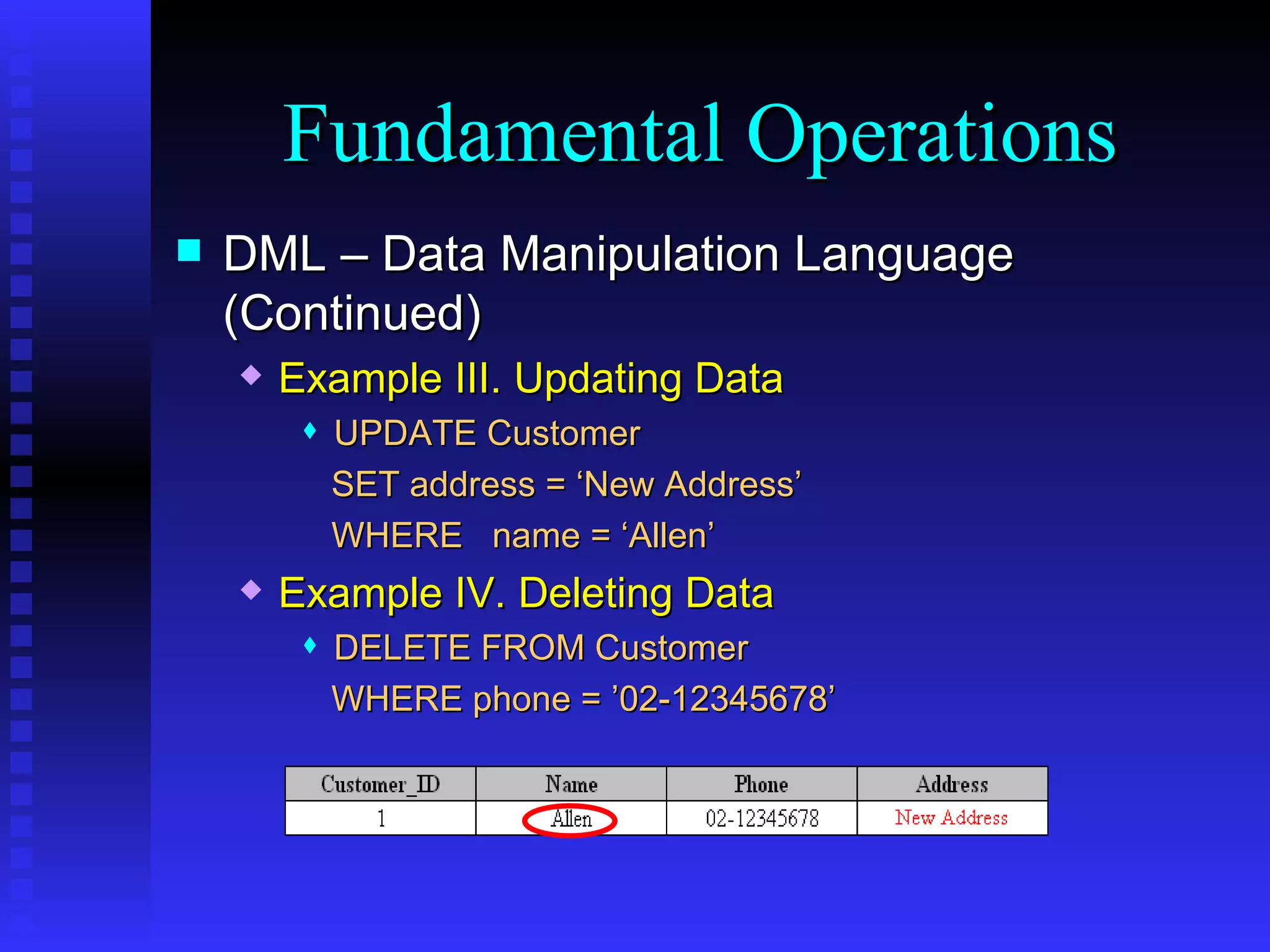
This document provides an agenda for a training on SQL Server 2000, covering the SQL Server 2000 environment including tools like Service Manager and Enterprise Manager, fundamental database operations including tables, indexes and DDL/DML/DCL commands, and recommended references for further reading on SQL Server and database fundamentals.