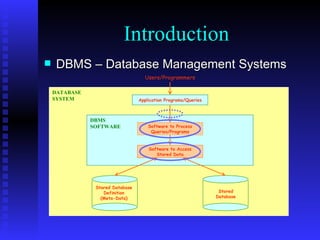
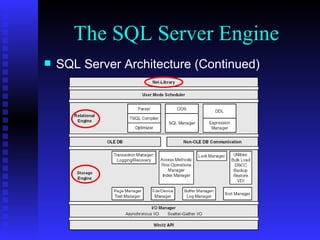
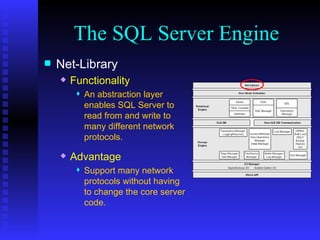
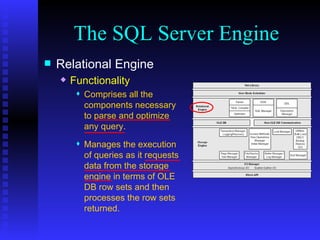
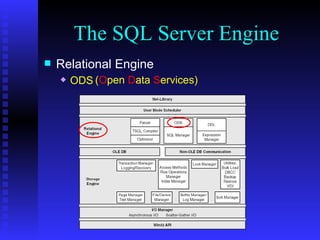
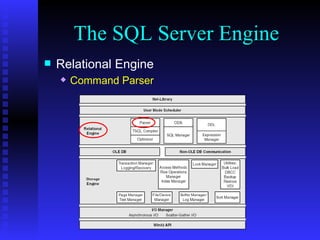
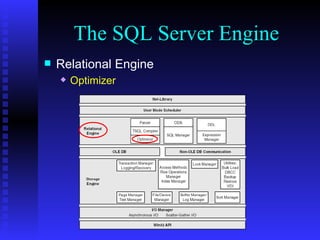
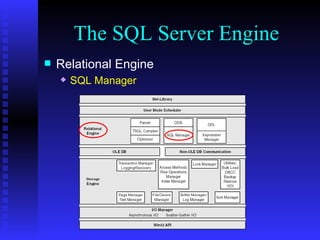
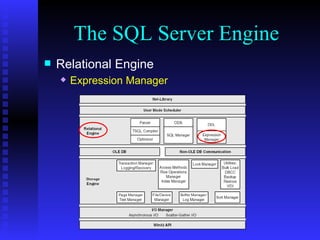
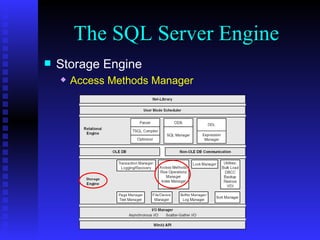
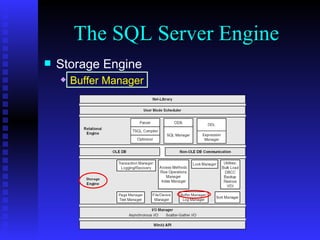
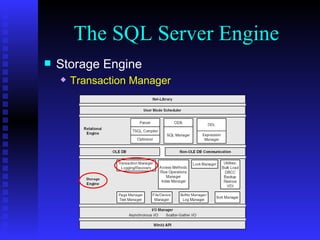
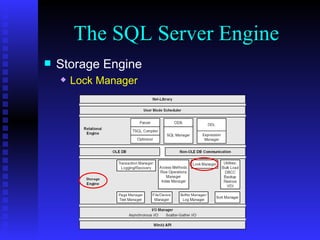
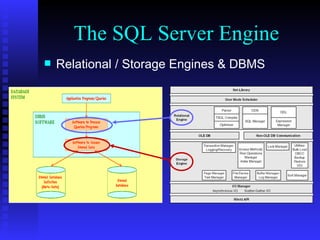
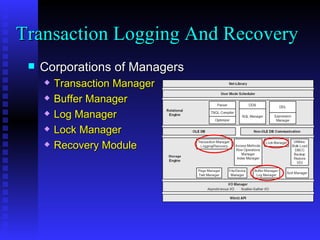
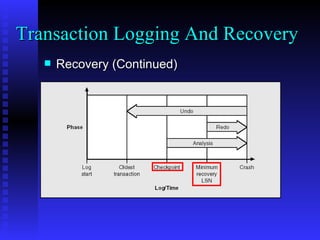
The document provides an overview of the architecture of Microsoft SQL Server 2000. It describes the main components of SQL Server including the SQL Server engine, memory management, and transaction logging and recovery. The SQL Server engine consists of a relational engine and storage engine. The relational engine handles query parsing, optimization, and execution while interacting with the storage engine to access and modify data. The storage engine manages disk pages, buffers, and transactions through components like the buffer manager, lock manager, and transaction manager.