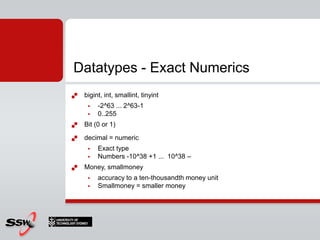
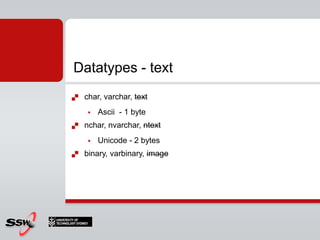
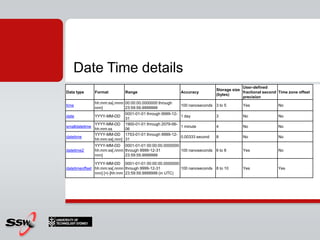
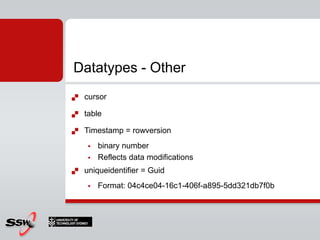
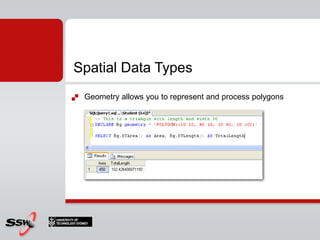
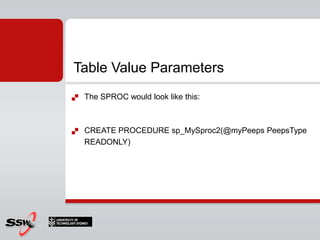
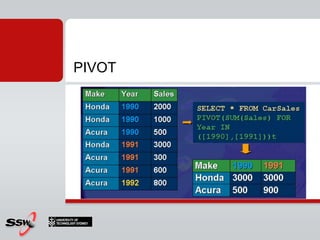
This document provides an overview and agenda for a SQL Server 2008 for Developers course. The course will cover new data types in SQL Server 2008, inline variable assignment, table value parameters, DDL triggers, common table expressions, XML queries, PIVOT/UNPIVOT, and ADO.NET. It includes links to course materials and information about the instructor's background in C#/.NET and agile methodologies.



































![Working with XML - ExplicitSELECT TOP 3 1 AS TAG, NULL AS PARENT,BusinessEntityID AS [Person!1!BusinessEntityID],FirstName AS [Person!1!FirstName!ELEMENT]FROM AdventureWorks.Person.PersonFOR XML EXPLICIT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02tsql-100811002300-phpapp02/85/SQL-Server-Introduction-to-TSQL-55-320.jpg)





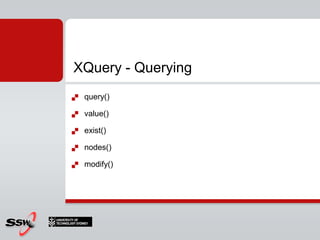
![XQuery - QueryingSELECT @x.exist('/christmaslist/person[@gift="socks"]')SELECT @x.exist('/christmaslist/person[@gift="lump of coal"]')SELECT @x.exist('/christmaslist/person[@gift="Socks"]‘)SELECT @x.value('/christmaslist[1]/person[1]/@name', 'VARCHAR(20)‘)SELECT @x.query('/christmaslist/person')](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02tsql-100811002300-phpapp02/85/SQL-Server-Introduction-to-TSQL-61-320.jpg)