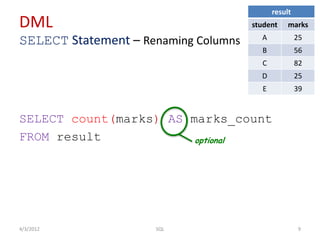
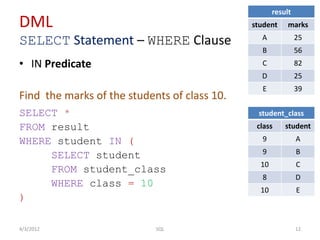
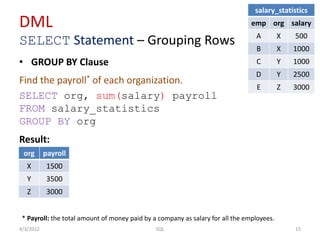
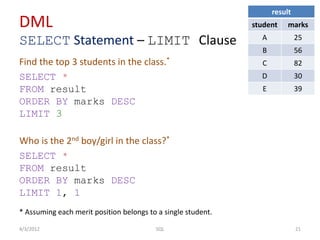
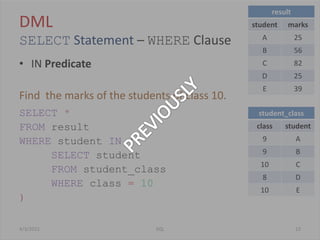
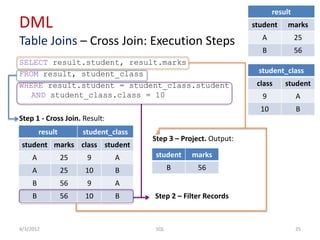
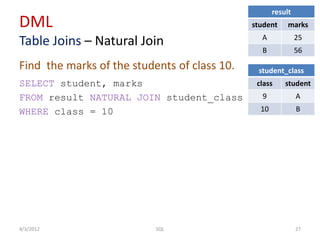
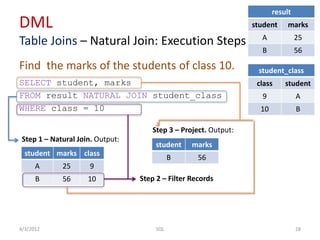
The document provides an overview of SQL, focusing on Data Definition Language (DDL) and Data Manipulation Language (DML) concepts, including commands for creating, altering, and managing tables, as well as querying data. It covers various SQL operations such as selecting data, using aggregate functions, applying where clauses, grouping and sorting results, and performing table joins. Key concepts include the distinction between DDL and DML, the use of projections, and the specifics of SQL syntax for different operations.