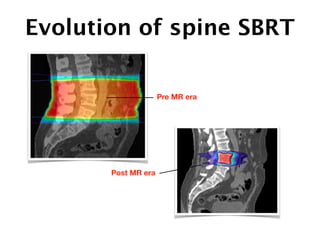
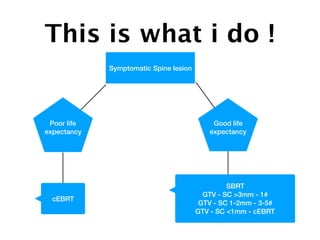
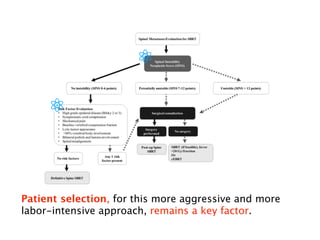
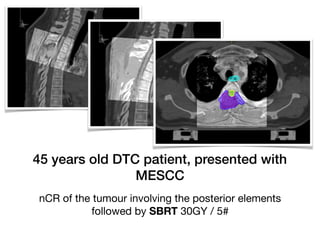
1) SBRT for spinal metastases requires careful patient selection and treatment planning to balance pain/local control and toxicity risks. Fractionation and dose constraints must consider organs at risk like the spinal cord.
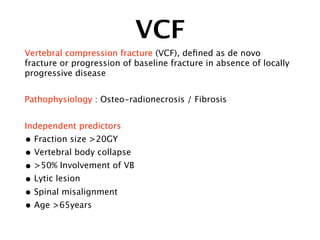
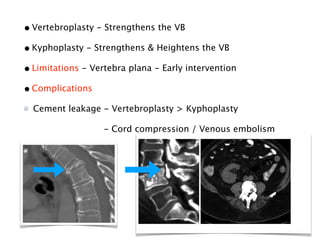
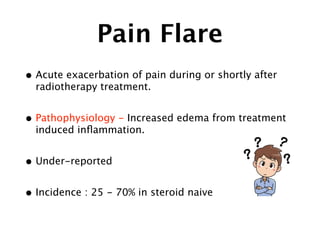
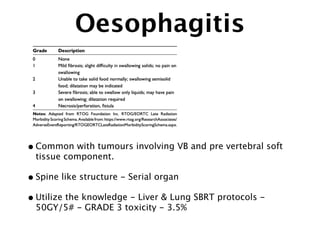
2) Common toxicities include vertebral compression fractures, pain flares, radiation myelopathy, and myositis. Mitigation strategies include pre-treatment stabilization, fractionation, steroids, and immobilization.
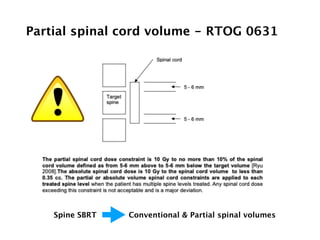
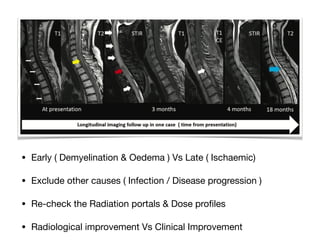
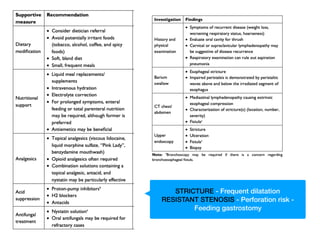
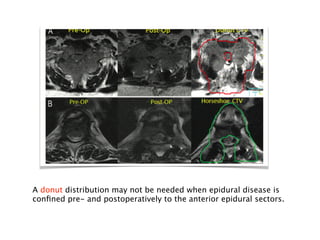
3) Dose constraints from trials not reporting toxicity may be too high. Partial spinal cord volumes, cauda equina differences, and serial organ considerations like the esophagus require attention.