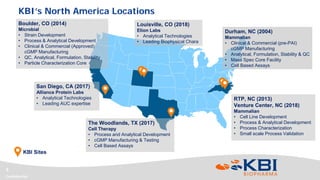
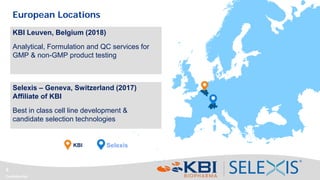
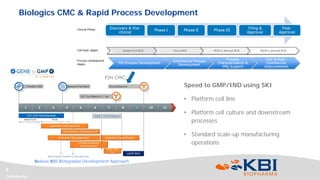
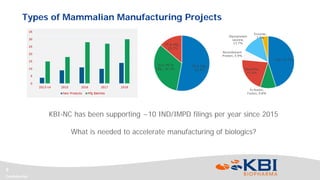
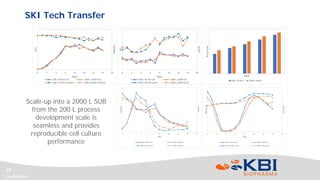
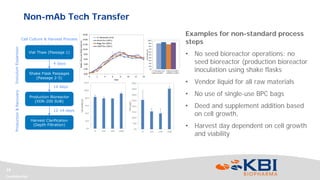
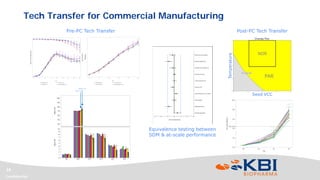
This document discusses strategies for rapidly transferring biologics manufacturing processes from development to commercial production. It provides examples of how KBI Biopharma employs standardized platform processes and integrated development approaches to minimize changes between scales. For antibody processes, extensive use of platform cell lines, media, and unit operations allows seamless transfer. Non-antibody processes require more customization but subsequent products can still leverage a base platform. Tech transfer timelines are established early and deliverables like batch records are reviewed. This enables timely preparation for cGMP manufacturing and regulatory filings.