The document provides an overview of the Common Technical Document (CTD) format, established by the ICH for drug registration submissions in the U.S., EU, and Japan. It outlines the CTD's history, structure, benefits, and the introduction of the electronic version (eCTD) to enhance submission efficiency, accuracy, and communication. The CTD format includes detailed modules covering administrative information, summaries, quality data, non-clinical and clinical study reports, and emphasizes harmonization across international regulatory bodies.

![CTD
Common Technical Document [CTD]: It is an format set by ICH which was agreed by the
Regulatory Agencies of Europe , Japan & the U.S.
The FDA characterized the CTD as “An information package of clinical, non clinical,
manufacturing, technical data in the same content that would be submitted for registering
new drugs in all 3 ICH regions i.e. U.S,European Union and Japan.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ctdandectdbynikhil-191213093418/85/CTD-and-eCTD-Format-2-320.jpg)



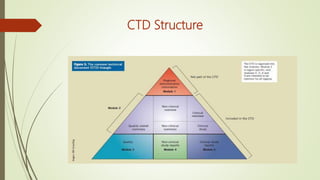
![Module 1
Administrative Information [Region specific]
This module should contain documents specific to each region
The content & format of this module can be specified by the relevant regulatory
authorities.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ctdandectdbynikhil-191213093418/85/CTD-and-eCTD-Format-7-320.jpg)
![Module 2
CTD Summaries [QOS]
It should begin with a general introduction to the pharmaceutical , including its pharmacological
class , mode of action & proposed clinical use. i.e. information should not exceed one page
It contain 7 sections in the following order:
-2.1 CTD TOC [Module 2 – 5] [Table Of Content]
-2.2 CTD Introduction
- 2.3 Quality Overall Summary
-2.4 Nonclinical overview
- 2.5 Clinical overview
- 2.6 Non clinical summary
- 2.7 Clinical summary](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ctdandectdbynikhil-191213093418/85/CTD-and-eCTD-Format-8-320.jpg)
![ The organization of these summaries is described in 3 separate documents:
A] M4 Q – The CTD quality
B] M4 S – The CTD Safety
C] M4 E – The CTD Efficacy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ctdandectdbynikhil-191213093418/85/CTD-and-eCTD-Format-9-320.jpg)
![Module 3
Quality [CMC]
3.1 TOC of Module 3
3.2 Body of Data
- 3.2. Drug substance
-Generall information
-Manufacture
-Characterisation
-Control of Drug Substance
-Reference Standards or Materials
-Stability](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ctdandectdbynikhil-191213093418/85/CTD-and-eCTD-Format-10-320.jpg)



![Module 5
Clinical Study Reports
TOC of Module 5
5.2 Tabular listing of clinical studies
5.3 Clinical study reports
-5.3.1 Repots of biopharmaceutical study[BA-BE]
-5.3.2 Reports of PK [biomaterial] study
-5.3.3 Reports of PK studies
-5.3.4 Reports of PD studies
-5.3.5 Reports of Efficacy and safety studies
-5.3.6 Reports of Post marketing experience
-5.3.7 Case Report forms & Individual patient listings
5.4 Literature References](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ctdandectdbynikhil-191213093418/85/CTD-and-eCTD-Format-14-320.jpg)
![e CTD
It is electronic version of CTD, so called as electronicc common technical document [e
CTD]
e CTD composed of 2 types of specification
- Content specification – As defined by ICH
- Technical specification- Electronic softwares
CTD (pdf) (Paper)
eCTD XML backbone](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ctdandectdbynikhil-191213093418/85/CTD-and-eCTD-Format-15-320.jpg)

![e CTD Characteristics
All Modules 1 to 5 have granularity options[ level of detail a document has ]
PDF documents linked via XML backbone
Increased document granularity.
Transparency of entire submission
Ease of navigation and review](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ctdandectdbynikhil-191213093418/85/CTD-and-eCTD-Format-17-320.jpg)



