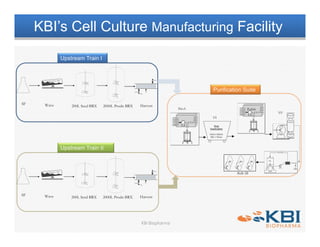
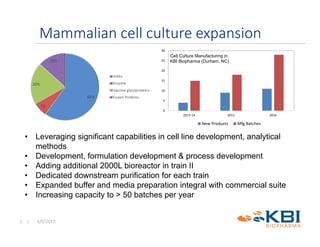
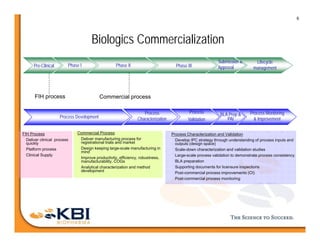
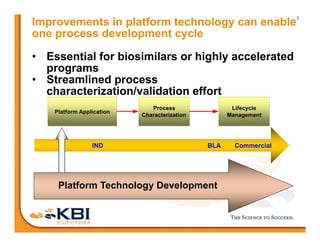
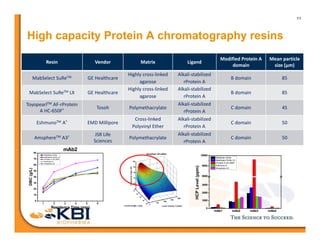
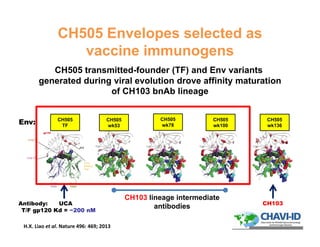
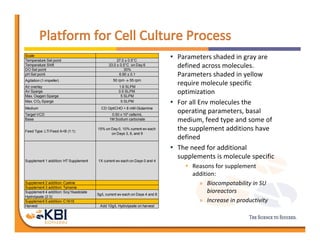
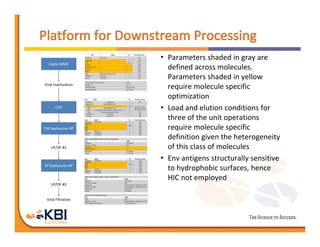
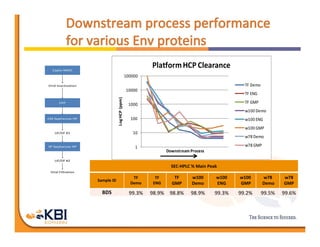
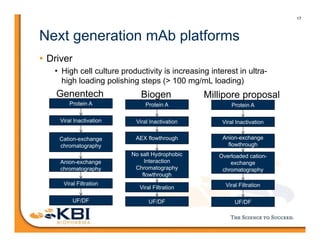
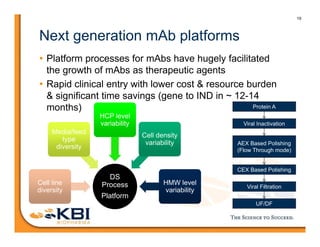
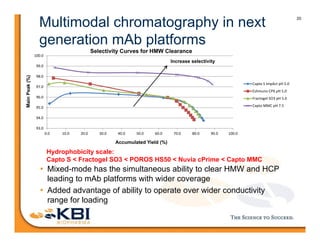
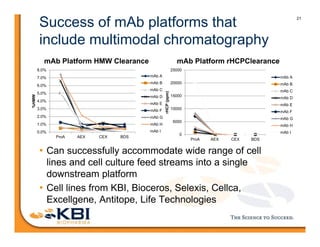
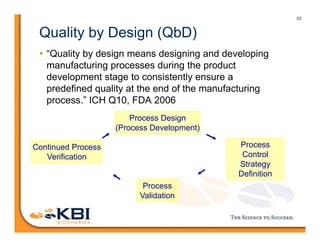
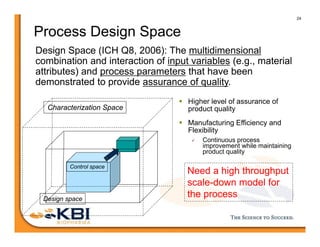
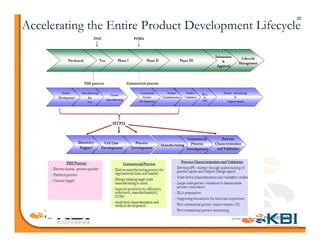
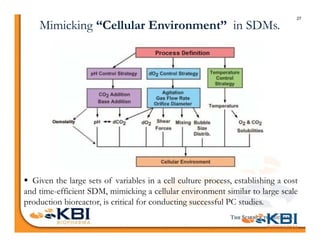
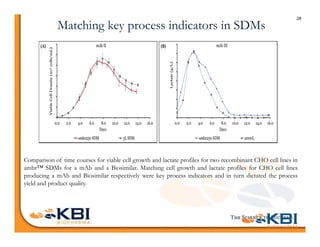
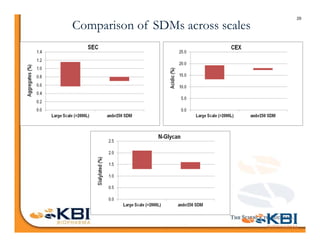
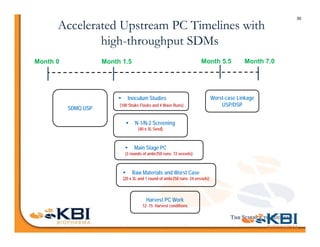
The document discusses advancements in mammalian antibody (mAb) commercialization, highlighting KBI Biopharma's capabilities in cell line development, manufacturing, and analytical services. It emphasizes the shift from clinical to commercial process development and the integration of high-throughput systems for efficient product development cycles. Additionally, it outlines the importance of robust scientific understanding and innovative chromatography techniques in optimizing mAb processes for scalability and productivity.