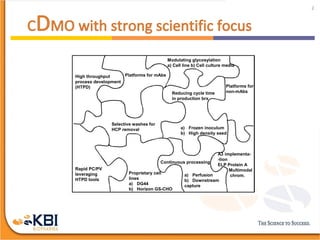
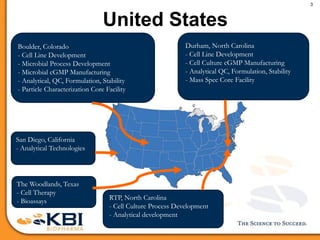
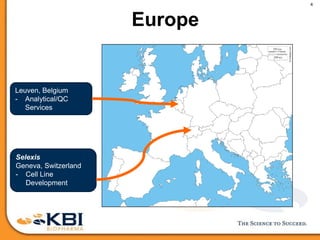
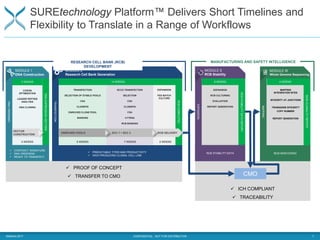
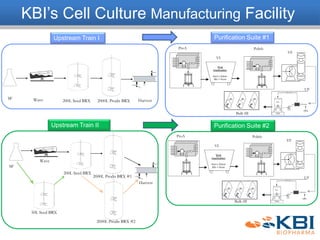
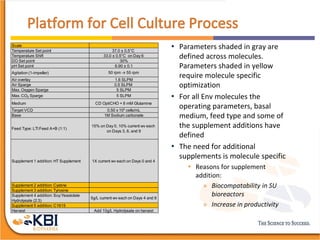
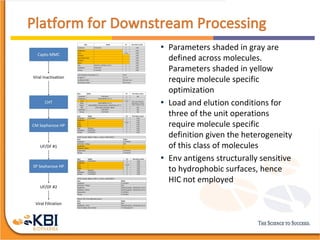
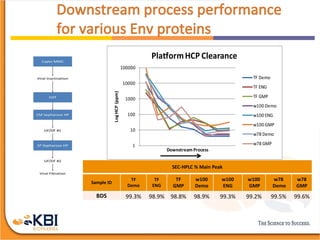
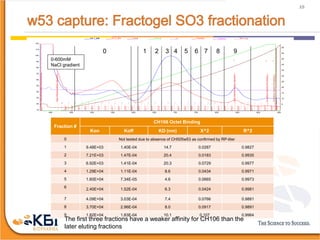
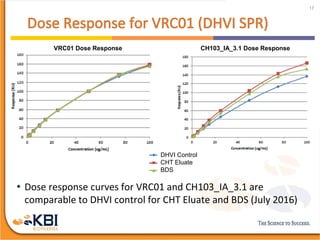
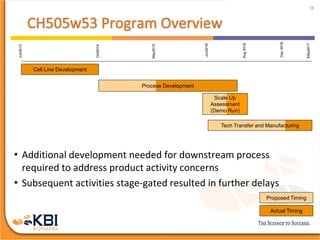
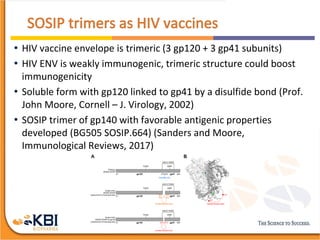
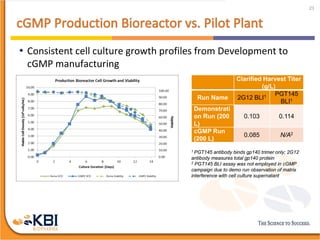
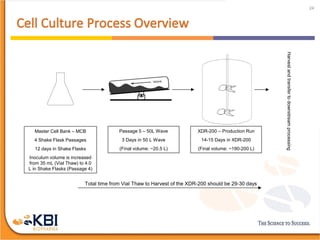
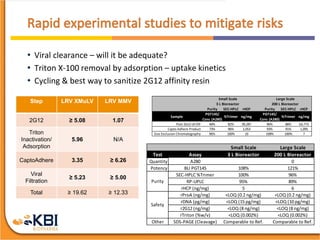
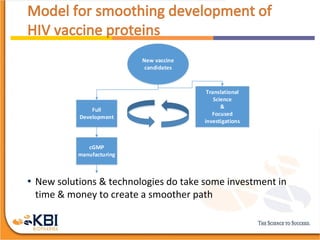
The document outlines the development and manufacturing processes for HIV vaccines, focusing on high throughput process development (HTPD) and innovative cell line technologies. It discusses the production cycle, challenges in glycosylation, and the integration of various processes to enhance manufacturing efficiency, capacity, and product quality. Additionally, it highlights advancements in technology and methodologies to improve both upstream and downstream processes in the vaccine development lifecycle.