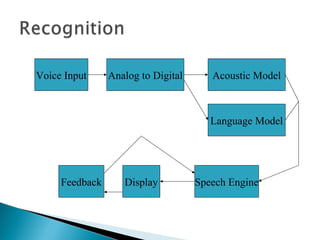
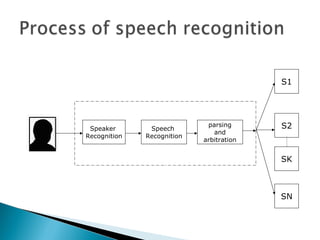
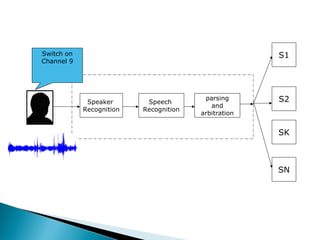
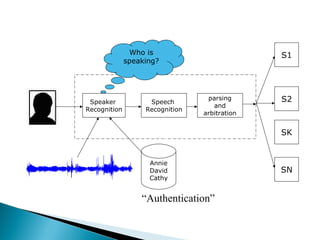
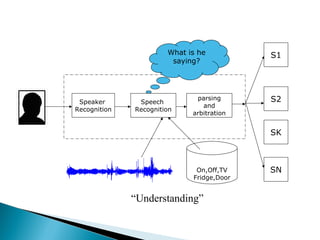
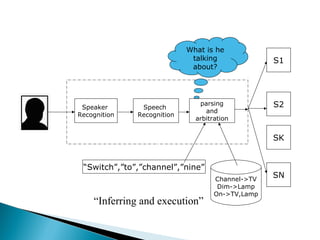
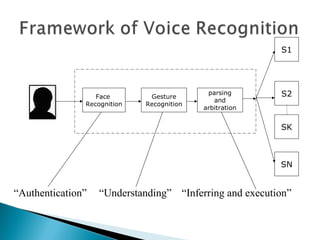
Speech recognition, also known as automatic speech recognition, allows a computer to understand human voice commands. It works by converting analog audio to digital signals, separating speech from background noise, and analyzing phonetic patterns to recognize words. There are two main types - speaker-dependent software requires training a user's voice, while speaker-independent software can recognize any voice without training but is generally less accurate. Speech recognition has applications in fields like military operations, navigation systems, radiology, and call centers. It offers advantages for people with disabilities but also faces challenges from variations in human speech and filtering noise. The technology continues to improve with advances in processing power and algorithms.