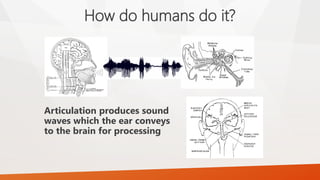
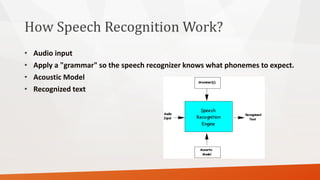
Speech recognition systems translate spoken words to text. They have evolved from discrete dictation to continuous dictation and have gotten smarter with grammar rules. Accuracy can be measured to examine a recognizer's ability. Some systems require training to a specific speaker while others are speaker independent. Computers do speech recognition by digitizing the audio, analyzing it acoustically and linguistically, and interpreting it based on phonemes and a grammar. Speech recognition has applications in navigation, mobile phones, home automation, education, security, and wearable computers. Generators are programs that create other programs, such as password generators, code generators, and random number generators used for licensing keys or testing.