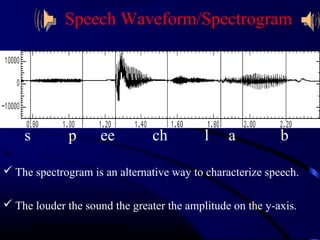
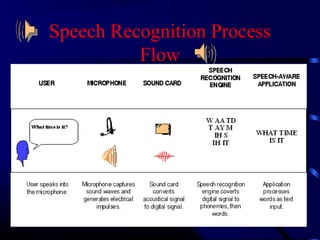
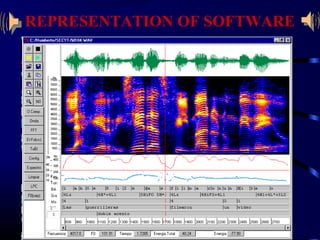
Speech recognition technology allows users to communicate through spoken commands. It works by converting acoustic speech signals captured by a microphone into text. There are two main types of speech models - speaker independent models that can recognize many people, and speaker dependent models customized for a single person. The speech recognition process involves an audio input being digitized, then broken down into phonemes which are statistically modeled and matched to words in a grammar according to a dictionary to output recognized text.