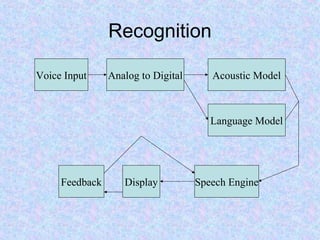
Speech recognition, also known as automatic speech recognition, allows computers to understand human speech by converting analog audio to digital text using acoustic and language models to recognize sounds and predict words. It can be used for dictation, navigation, commercial applications, and more, and comes in speaker-dependent and speaker-independent varieties, with the former being more accurate but requiring voice training. The technology continues to improve in accuracy through advances like better modeling of speech, filtering of noise, and systems that can interpret intended meaning despite errors.