Embed presentation
Downloaded 28 times







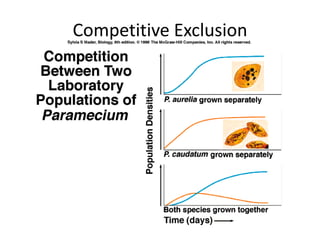
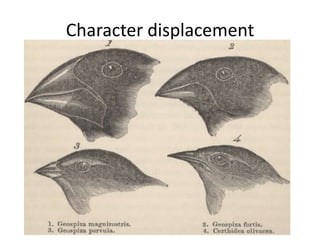
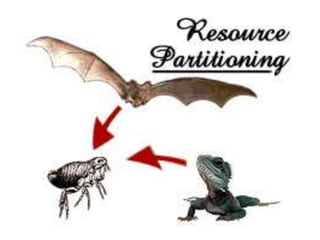

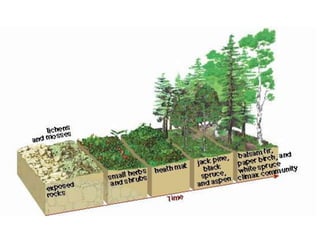

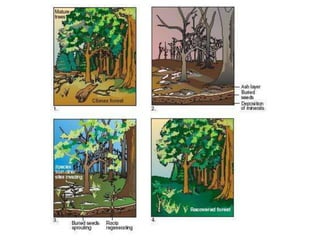

The document discusses 5 major types of species interactions: predation, mimicry, parasitism, mutualism, and commensalism. It also discusses competition between species for limited resources, which can lead to competitive exclusion or evolution of differences to reduce competition through character displacement or resource partitioning. Ecological succession is described as the gradual replacement of species over time in an area, beginning with pioneer species and progressing to a climax community.















