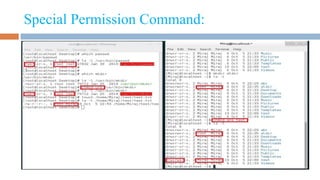
The document discusses special permissions in Linux, including setuid, setgid, and the sticky bit. It explains how these permissions affect the execution of files and directories, detailing commands to set and remove these bits. The document also outlines standard file permissions such as read, write, and execute.