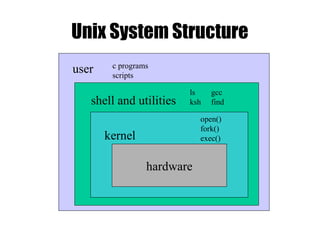
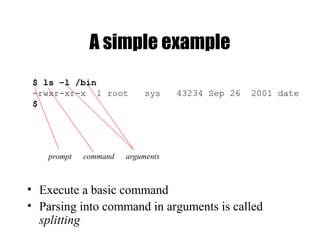
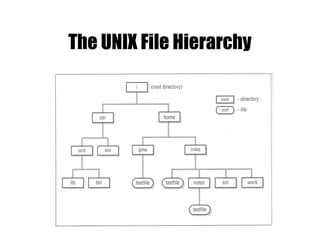
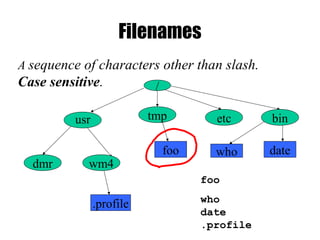
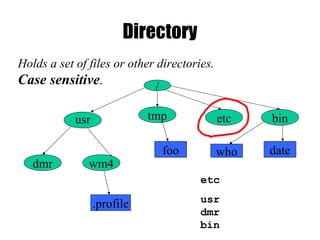
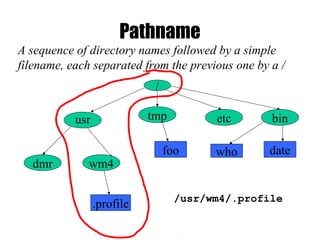
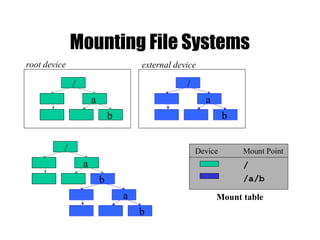
The document provides an overview of Unix basics, including the structure of the Unix file system, user shells, and essential utilities. It explains the functionality of shells, file hierarchy, common commands for managing files and directories, and file permissions. The summary emphasizes the similarity of Unix file systems and the use of special device files for communication with devices.