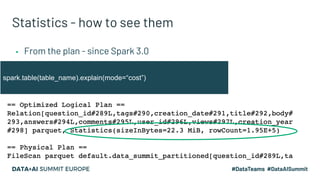
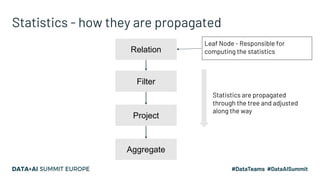
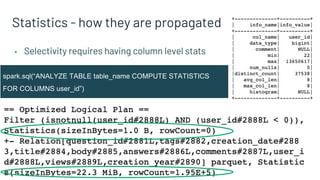
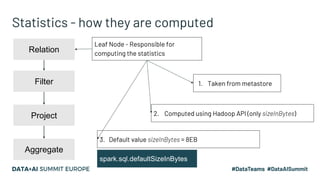
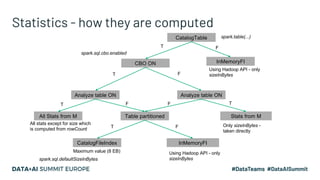
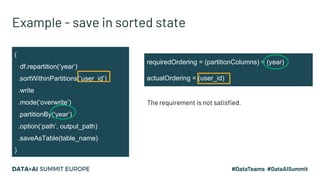
The document presents advanced concepts in Spark SQL, focusing on the use of statistics, data sorting, and performance optimization techniques. It covers how to compute and propagate statistics, the importance of enabling cost-based optimization, and methods for saving data in sorted states. The author emphasizes best practices for improving join performance and ensuring proper table analysis in partitioned datasets.