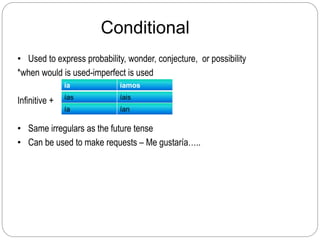
This document contains the table of contents for a Spanish 3 grammar book. It lists 18 topics that will be covered, including the conditional tense, present perfect tense, subjunctive mood, commands, and differences between saber and conocer. For each topic, there is a brief introductory explanation of 1-3 sentences. The document also includes lists of irregular verb forms for certain tenses.