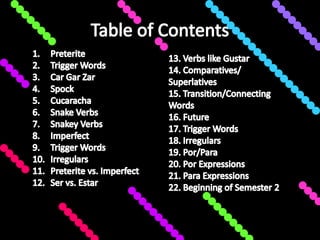
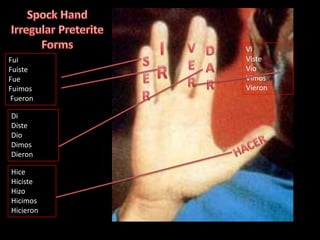
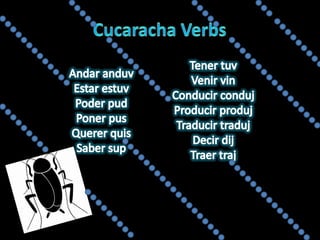
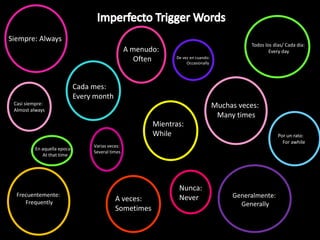
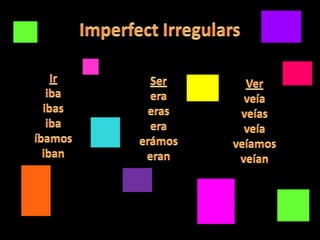
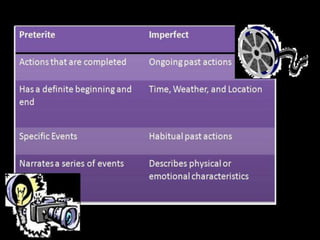
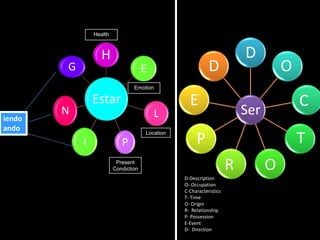
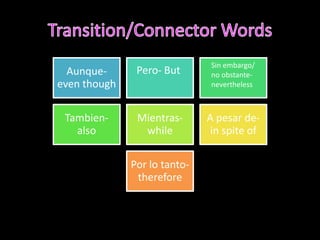
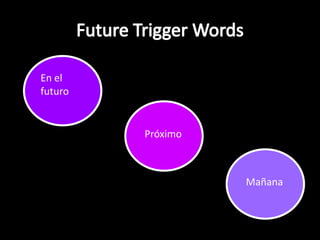
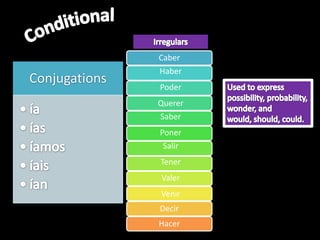
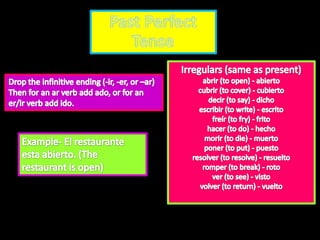
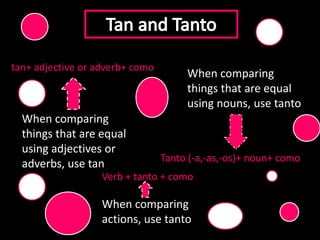
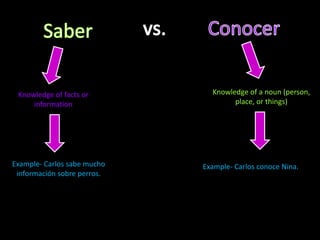
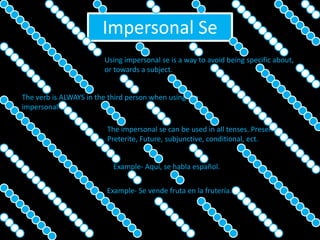
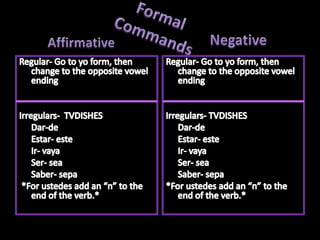
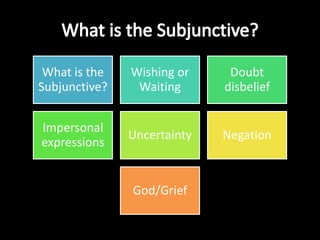
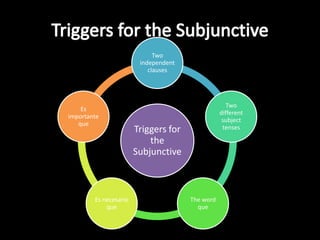
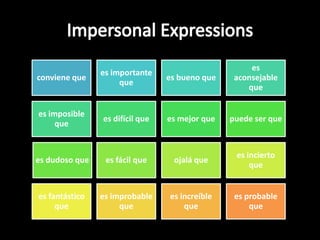
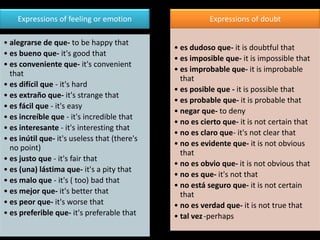
This document provides an outline for a grammar book covering various Spanish grammar topics across two semesters. The first semester covers topics such as preterite and imperfect tenses, irregular verbs, por/para expressions, the future tense, and ser vs. estar. The second semester continues with additional tenses and topics including the conditional, present perfect, past perfect, subjunctive, commands, and the subjunctive mood. For each topic, there are brief explanations, examples, and lists of irregular verbs.