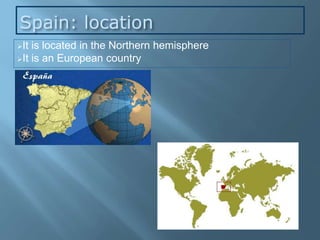
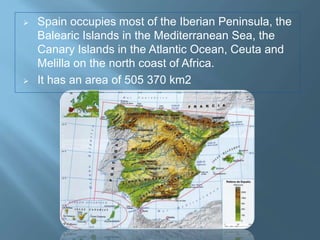
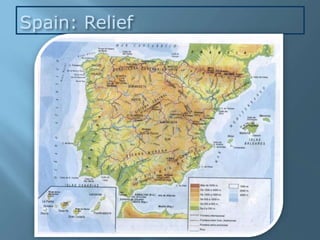
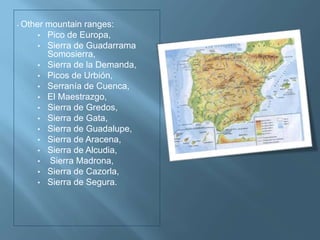
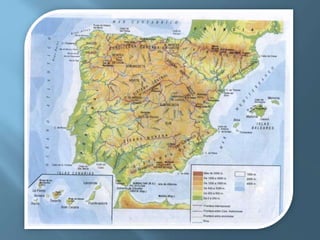
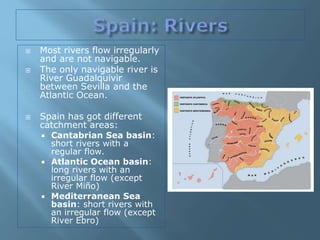
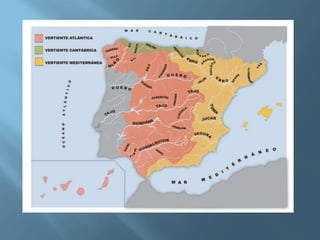
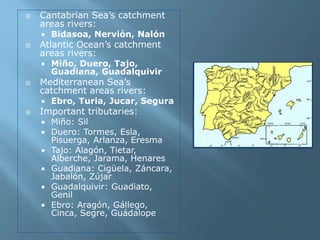
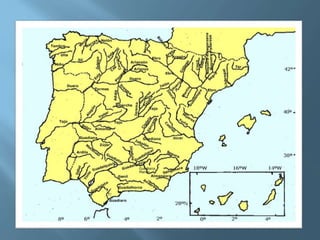
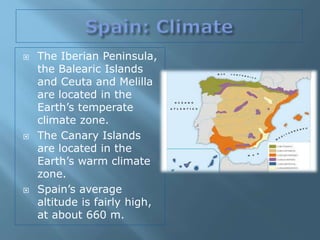
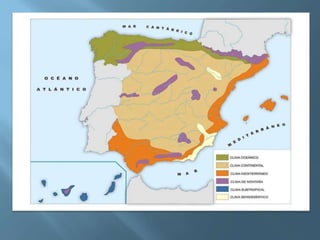
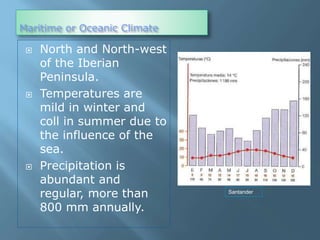
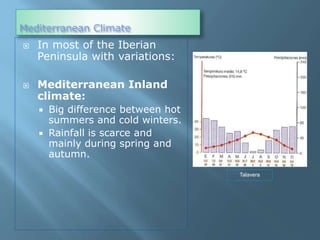
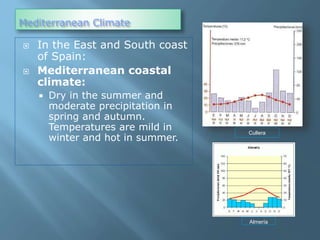
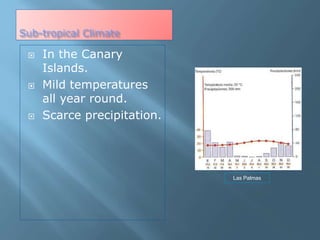
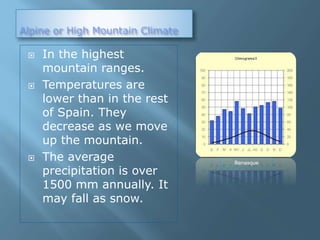
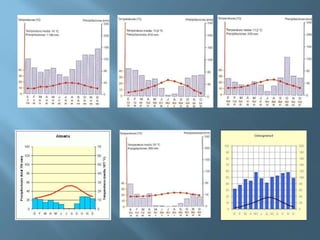
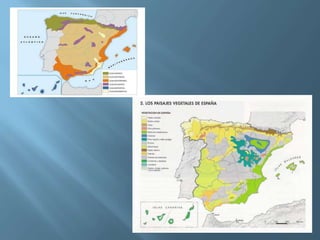
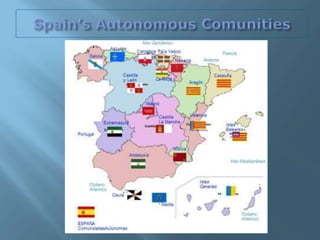
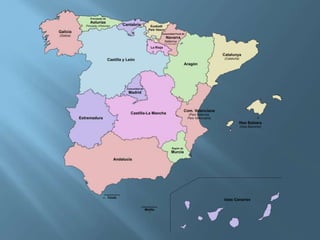
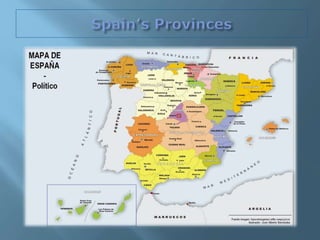
The document provides an extensive overview of Spain's geography, including its location, relief features, climates, and ecological systems. It details the country's diverse landscapes, significant mountains, rivers, and distinct climatic zones while also discussing environmental issues such as deforestation and pollution. Furthermore, it suggests strategies for protecting and improving Spain's natural environment.