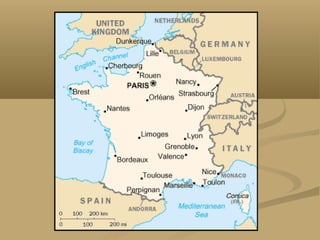
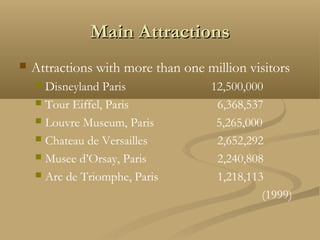
This document provides a detailed overview of France, including its geography, history, culture, and major cities and attractions. It discusses France's location in Western Europe and bordering countries. It then summarizes key facts about France's government, population, languages, religions, economy, and currency. The document proceeds to describe major attractions in different regions of France, including Paris, Normandy, the Loire Valley, Provence, the French Riviera, and others. It highlights famous landmarks, museums, cathedrals, and other cultural sites throughout the country.