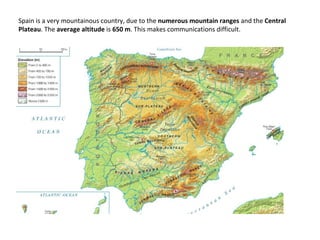
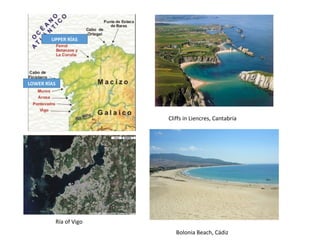
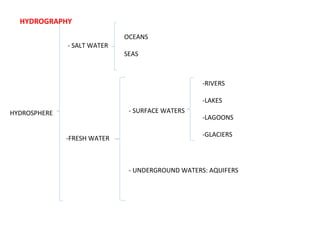
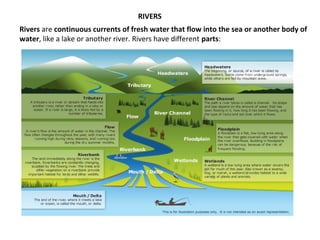
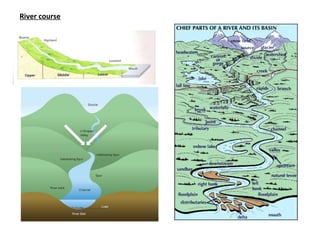
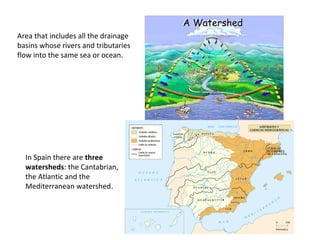
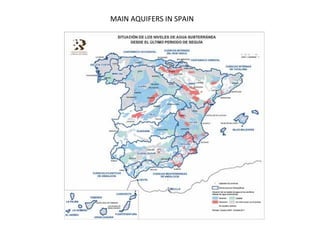
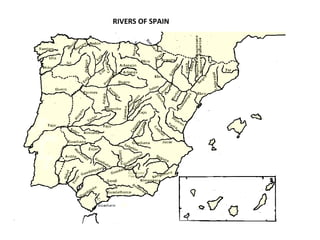
Spain has a very mountainous landscape with numerous mountain ranges that make travel difficult. It has three main watersheds that drain into the Atlantic Ocean, Cantabrian Sea, and Mediterranean Sea. Spain also hosts over half of Europe's biodiversity and has many protected natural areas, including 15 national parks, that help preserve the country's rich wildlife.