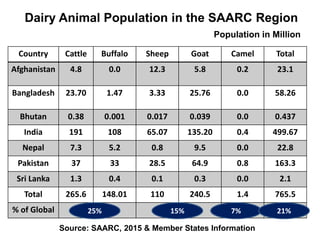
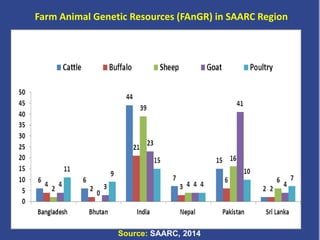
The document discusses the challenges and priorities of livestock in South Asia, highlighting its role in poverty alleviation, food security, health, and gender equality. It presents data on livestock populations, productivity, and demand in the SAARC region, along with current challenges such as low productivity, genetic potential, and diseases. Regional collaboration is emphasized for improving livestock production systems and addressing issues like antimicrobial resistance.