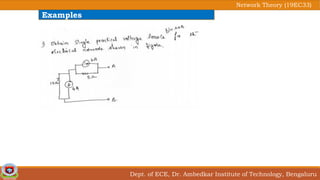
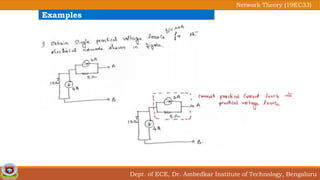
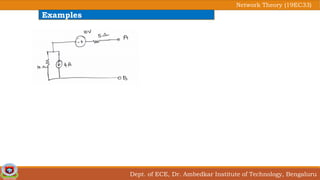
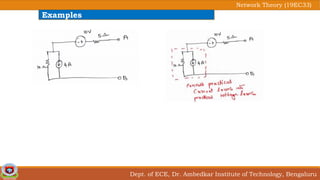
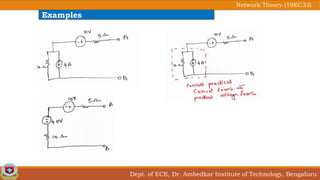
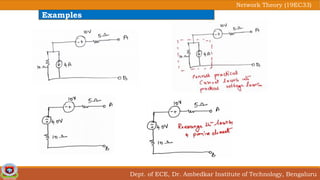
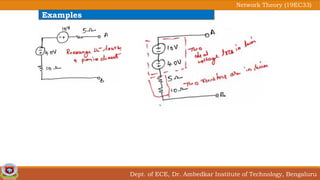
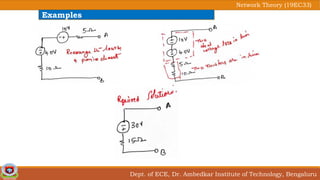
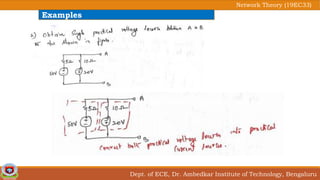
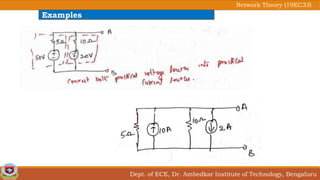
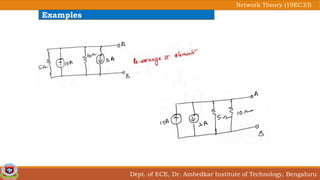
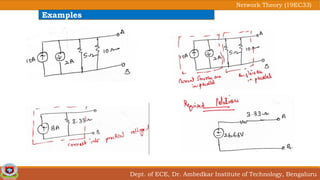
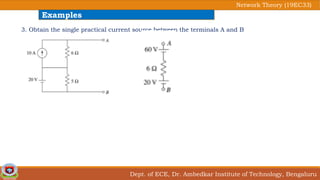
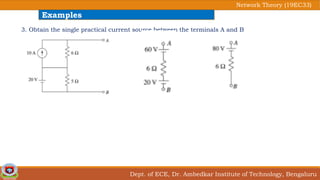
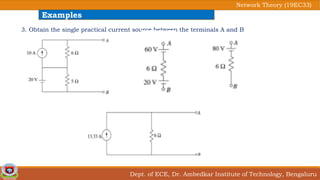
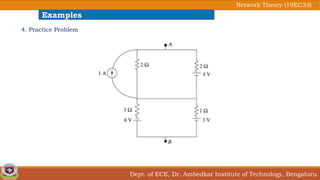
This document discusses source transformation examples in network theory. It begins with key points about applying source transformation to practical sources. Next, it outlines the procedure for simplifying electrical networks using source transformation and source shifting. The remainder of the document works through examples of simplifying circuits using these techniques to obtain equivalent single voltage or current sources between load terminals. It concludes with a practice problem and disclaimer about content taken from other sources.