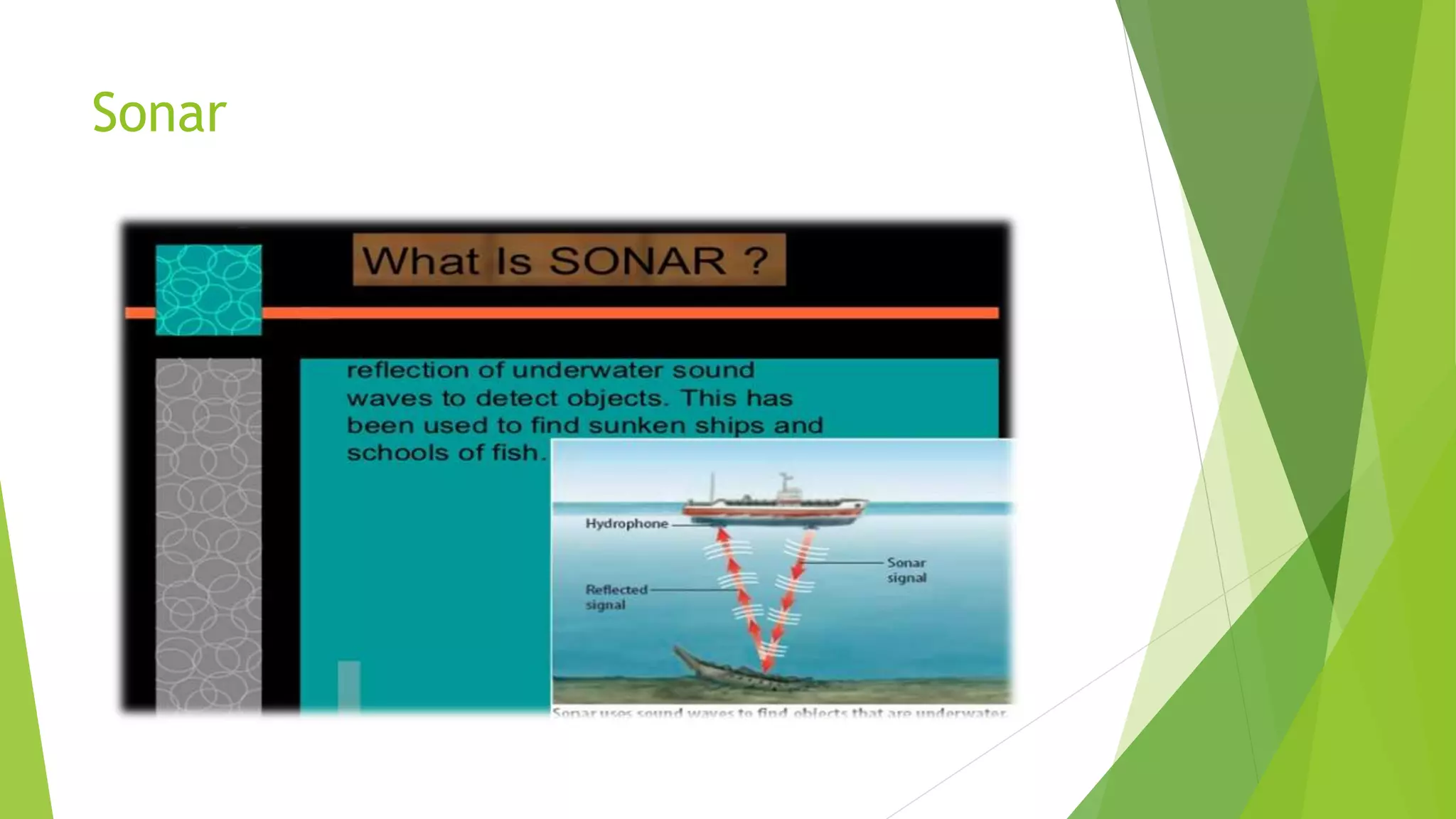
Sound is a vibration that propagates through compressible media such as air or water as mechanical waves of pressure and displacement. It can be audible or inaudible. Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time and is an important parameter used to specify the rate of oscillatory phenomena including sound signals. The human ear receives sound waves, and the wavelength is the spatial period of a wave - the distance over which its shape repeats. Sound travels through various media as longitudinal or transverse waves and can be studied through the fields of acoustics, which deals with mechanical waves in gases, liquids and solids, and sonar, which uses sound waves to navigate or detect objects underwater.





![WAVE LENGTH
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the
wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.[1] It is usually
determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding
points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings and is a
characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other
spatial wave patterns. Wavelength is commonly designated by the Greek
letter lambda (λ). The concept can also be applied to periodic waves of non-
sinusoidal shape. The term wavelength is also sometimes applied to
modulated waves, and to the sinusoidal envelopes of modulated waves or
waves formed by interference of several sinusoids. The SI unit of wavelength
is the meter.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sound-150104070434-conversion-gate01/75/Sound-and-wavelength-6-2048.jpg)