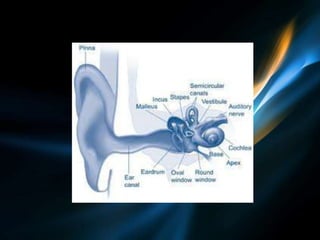
This document discusses sound and its properties. It defines sound as a form of energy that creates the sensation of hearing. It describes sound as a longitudinal wave that propagates through a medium by particles colliding. It discusses the characteristics of sound waves including frequency, amplitude, speed and how these properties vary based on the medium. The document also covers topics like reflection, reverberation, the human range of hearing, SONAR and the anatomy of the human ear.
















![[MCQs]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/soundbypratikshayadav-140206103515-phpapp02/85/Sound-by-Pratiksha-Yadav-18-320.jpg)











