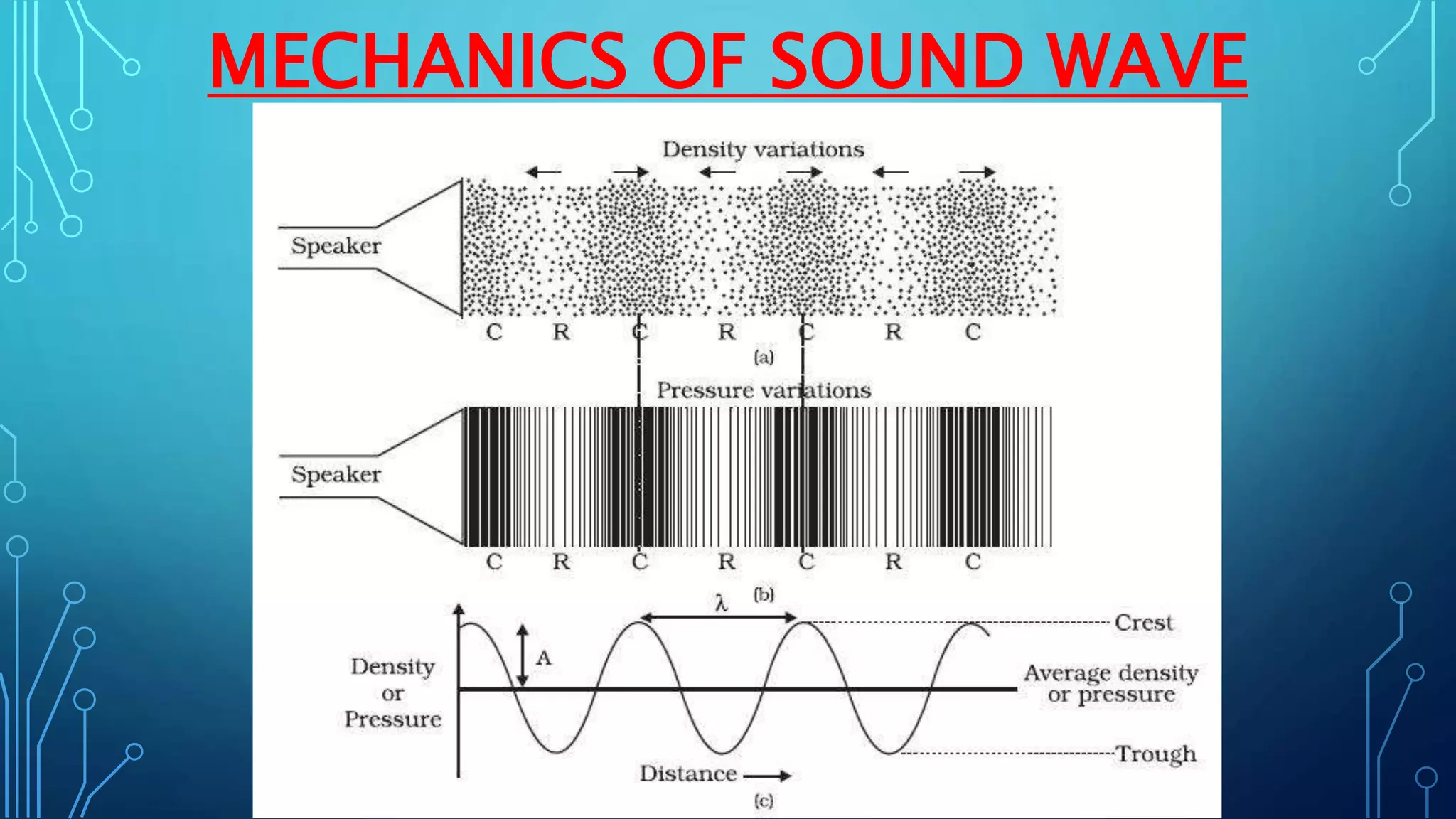
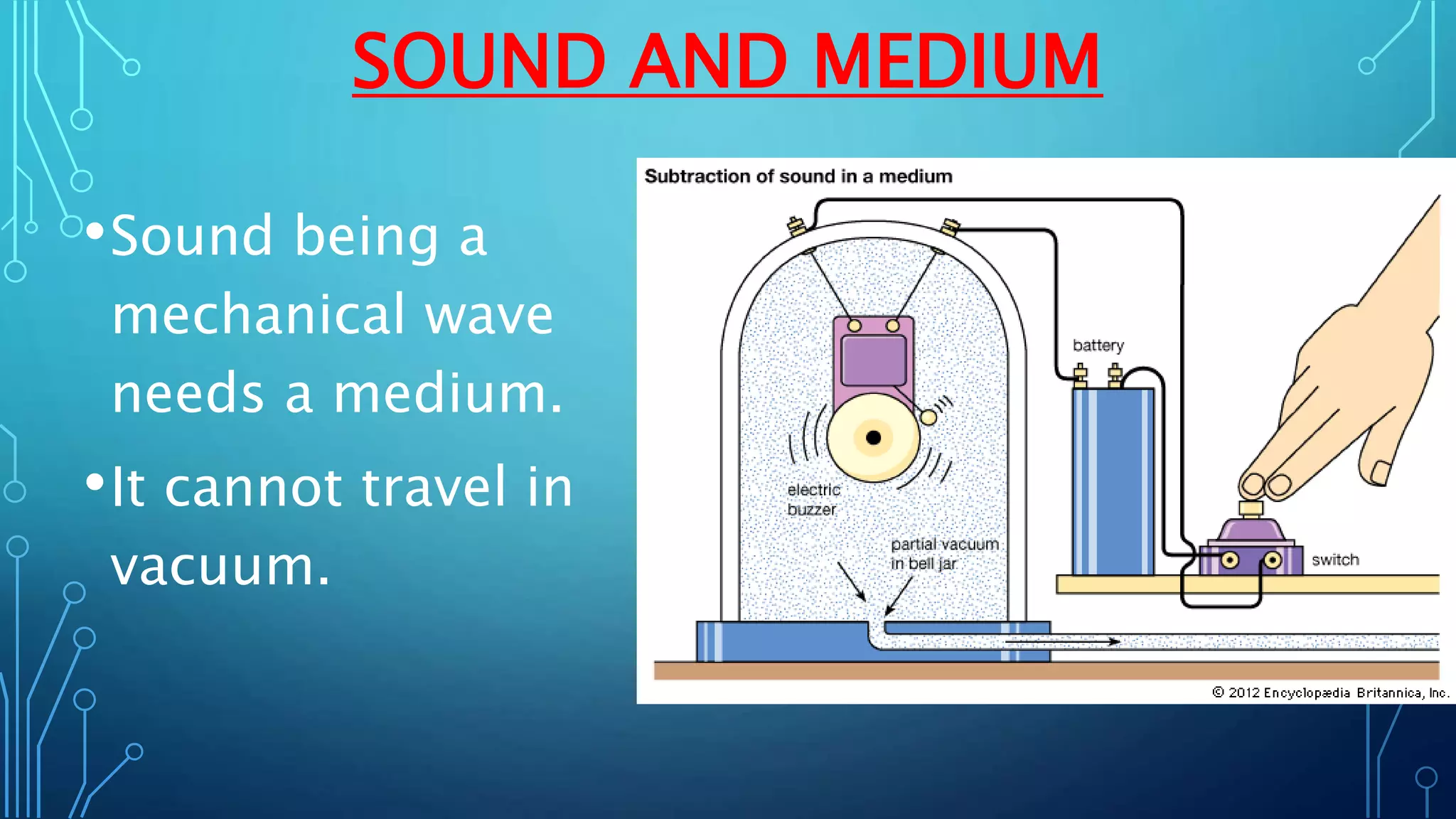
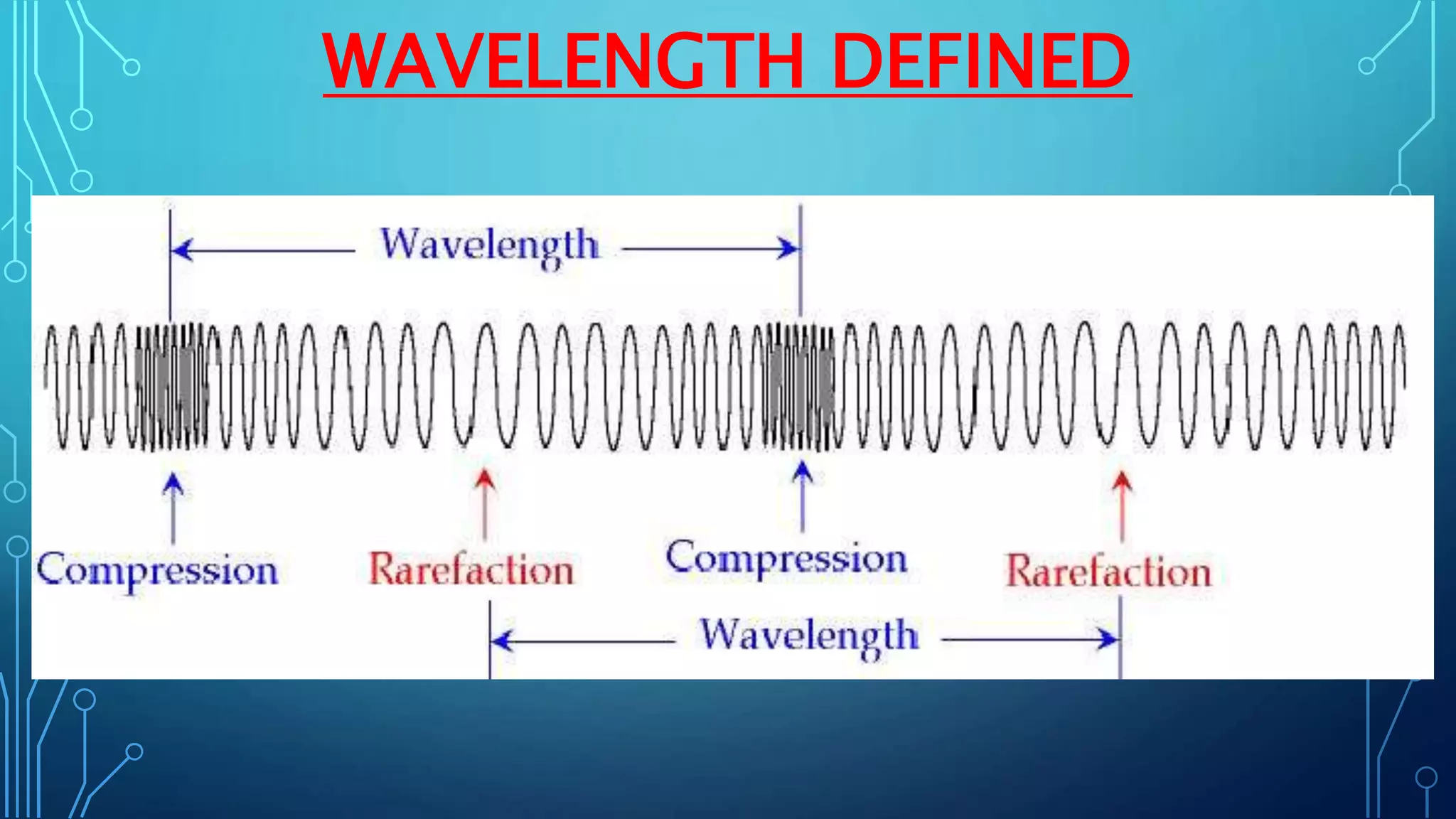
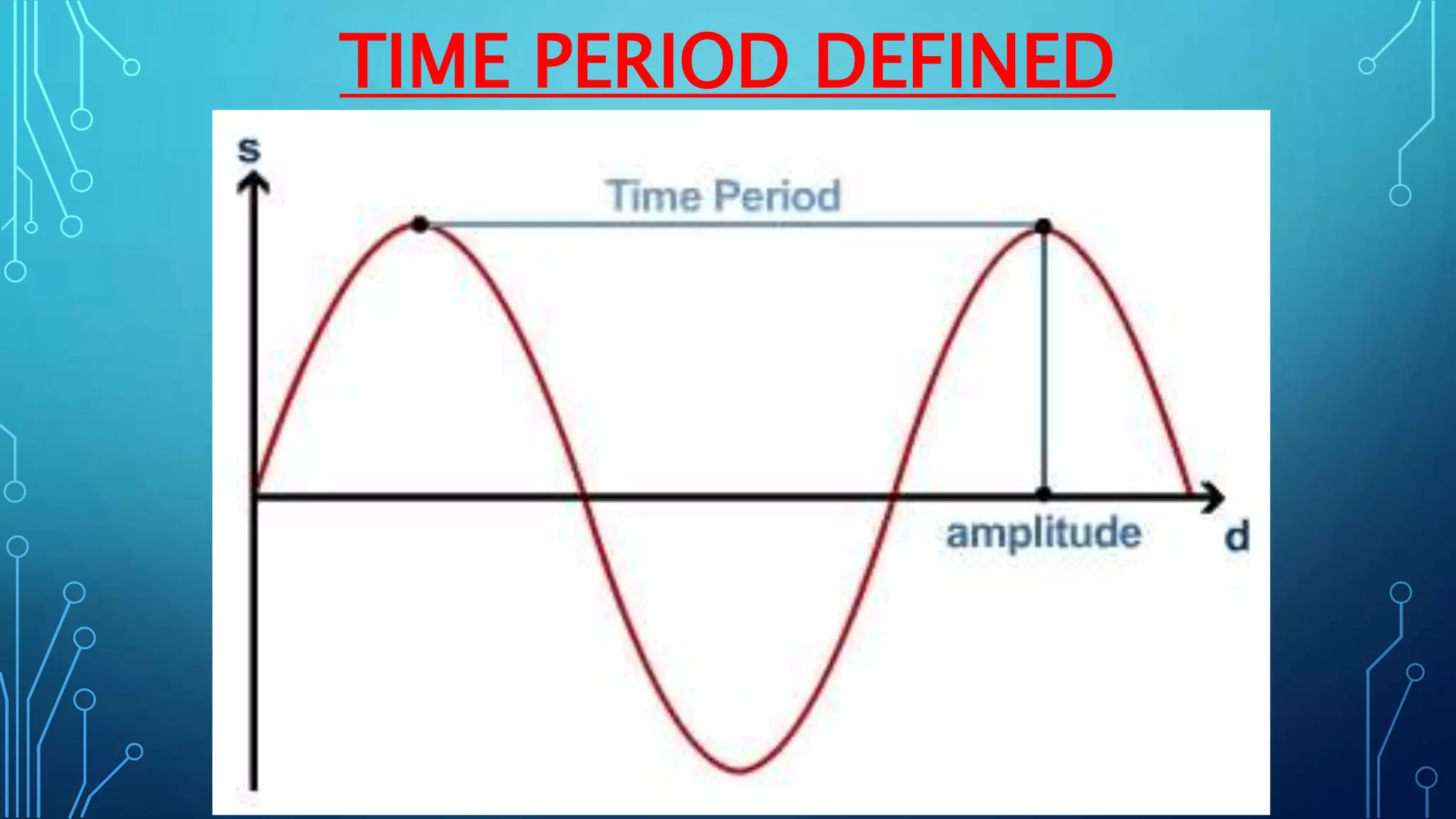
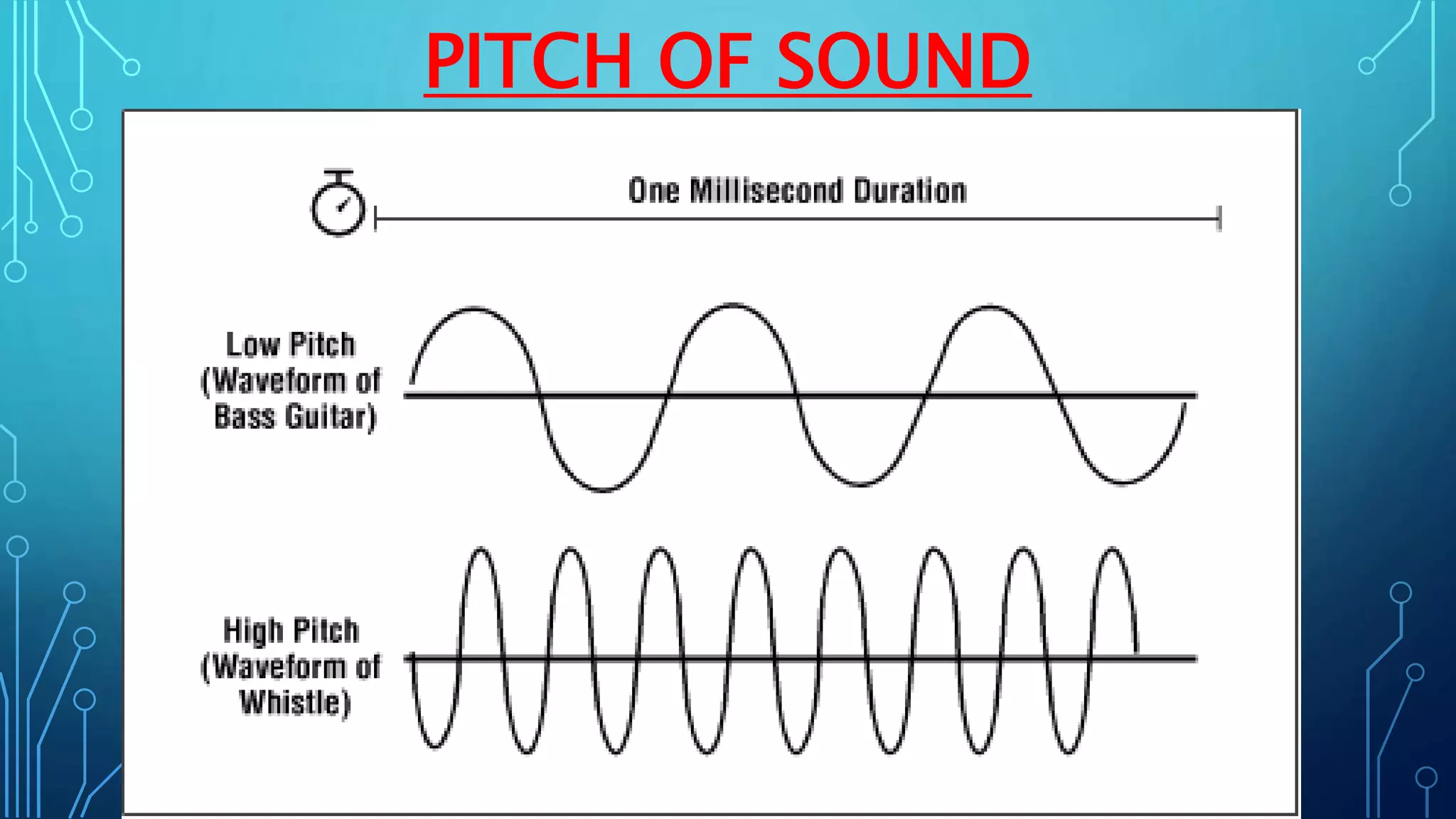
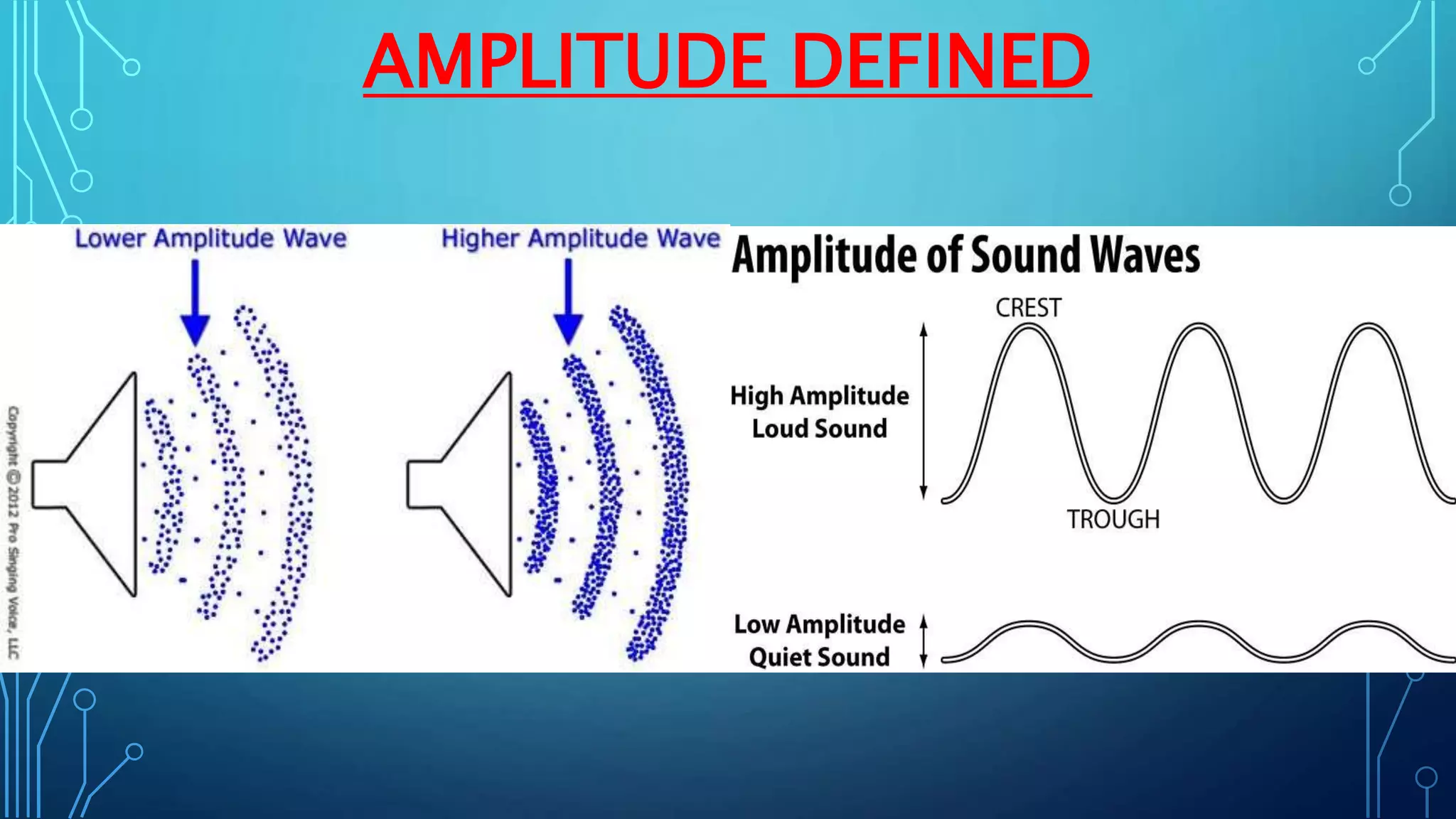
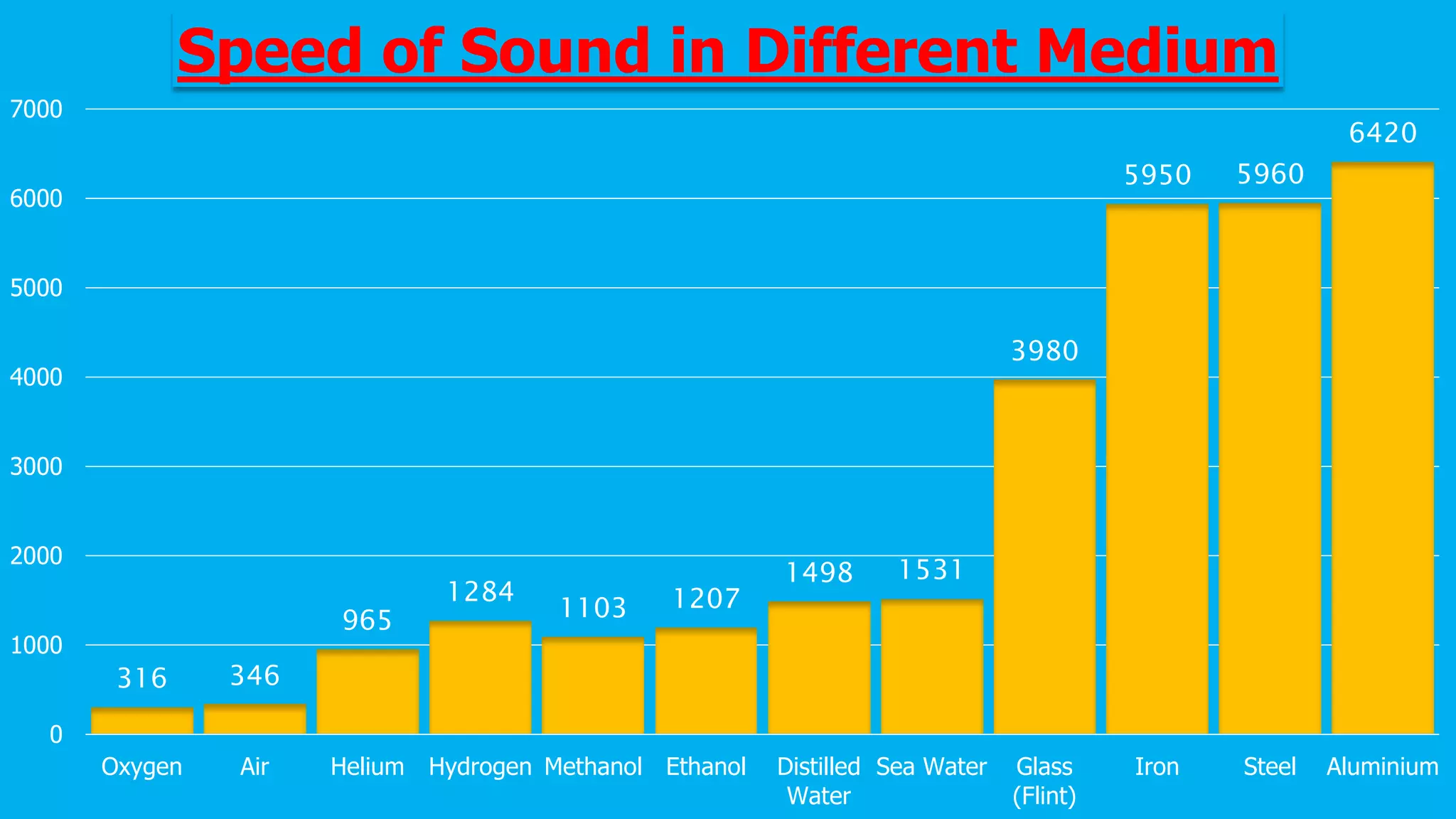
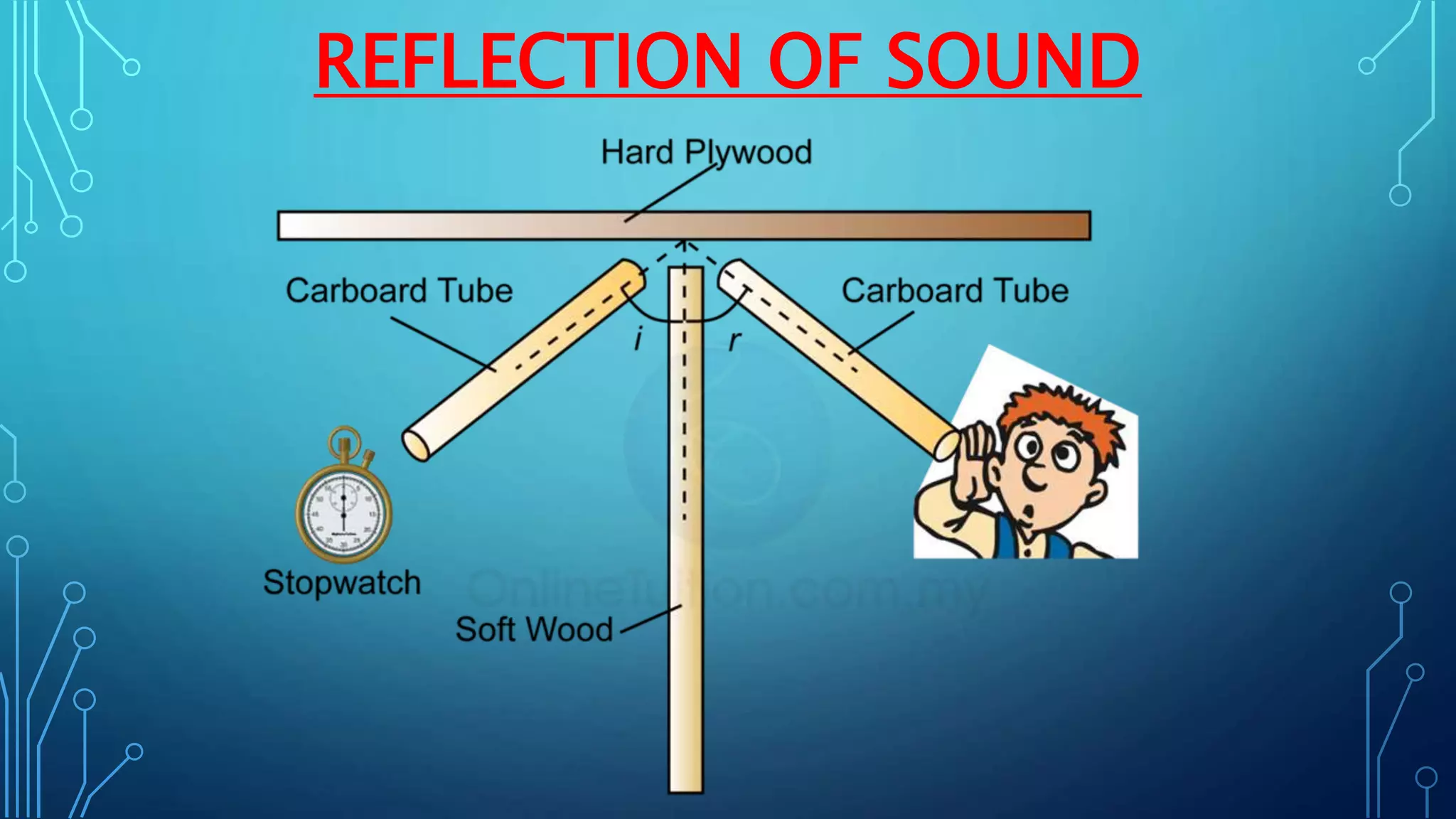
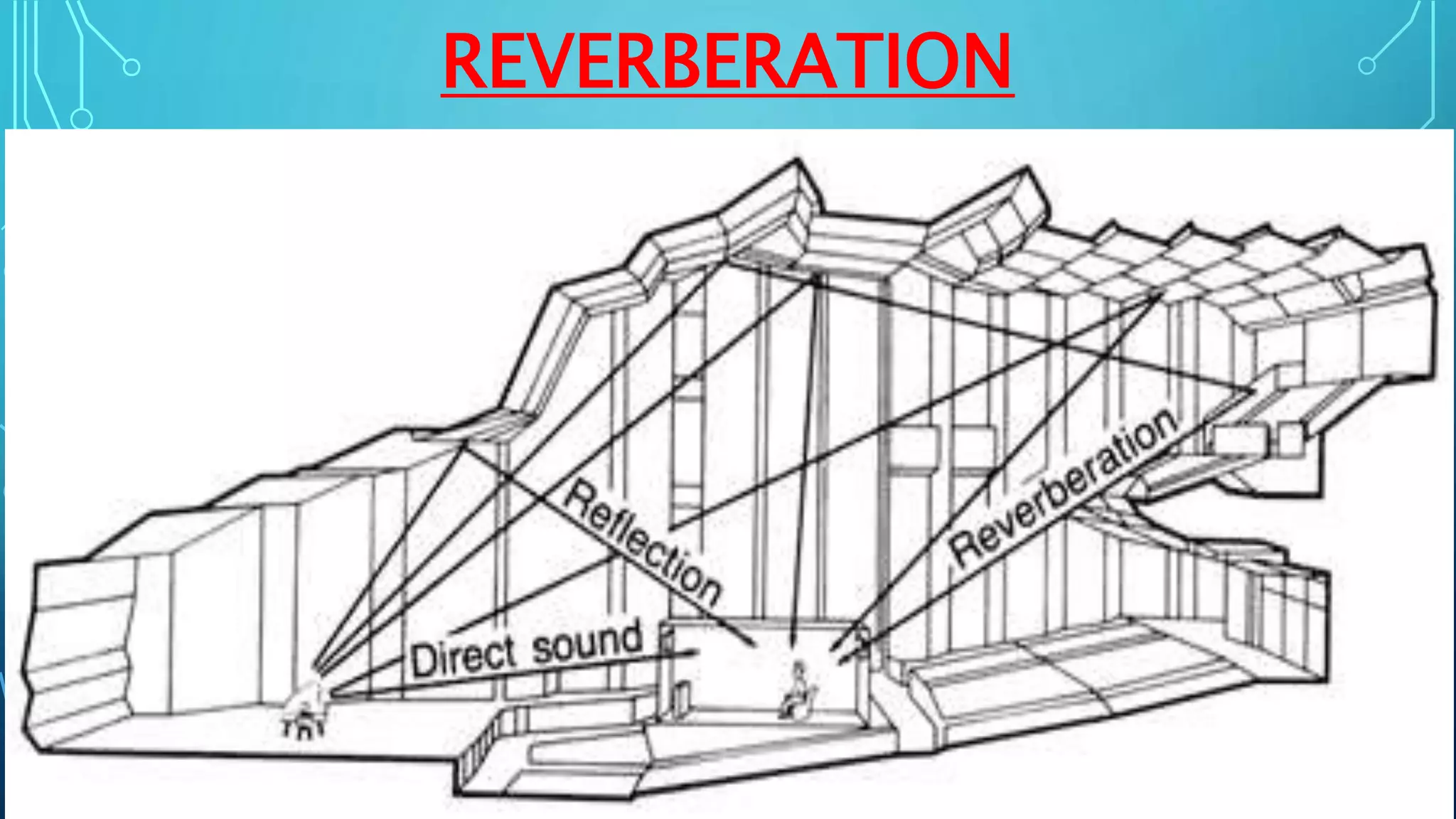
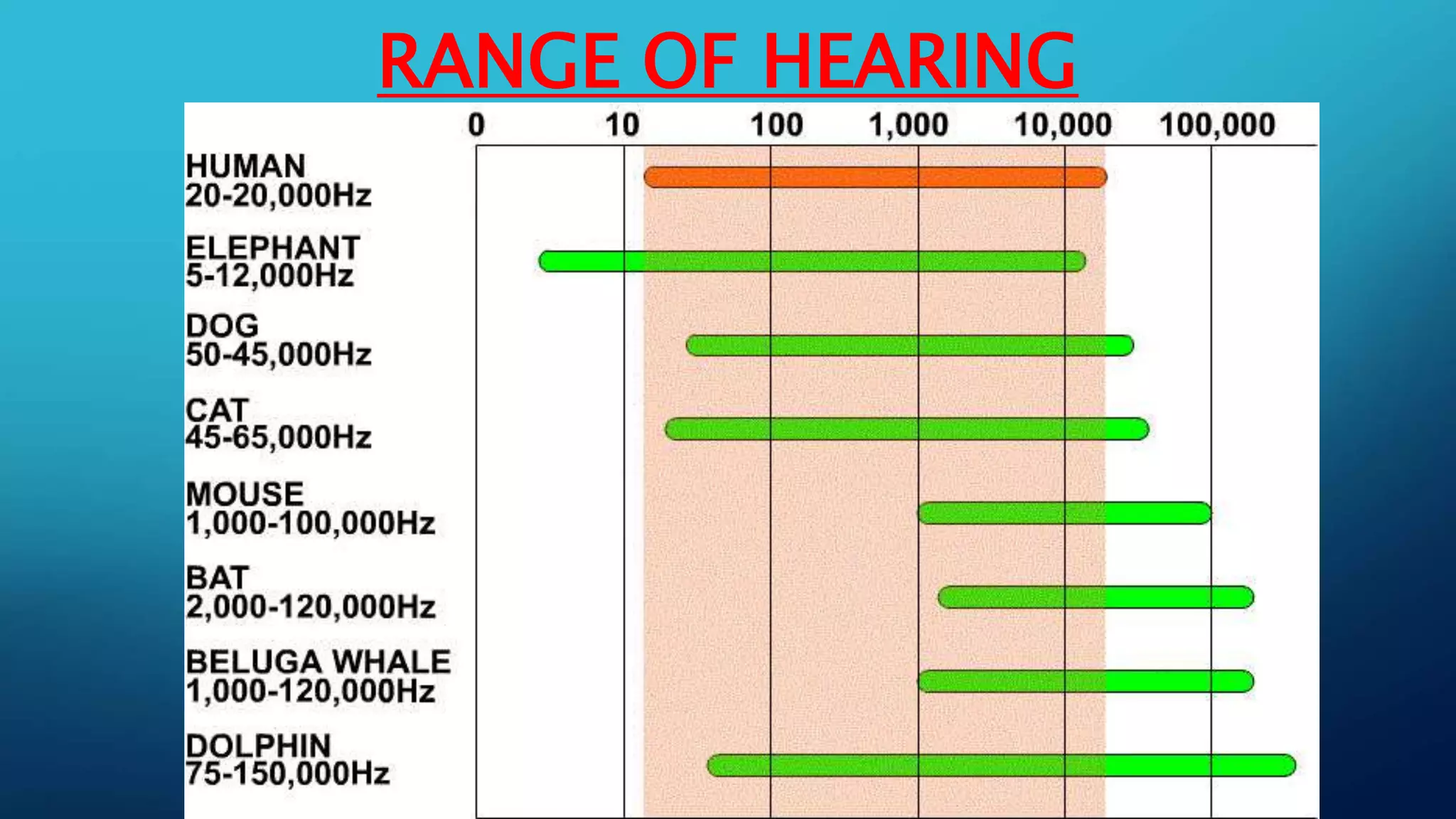
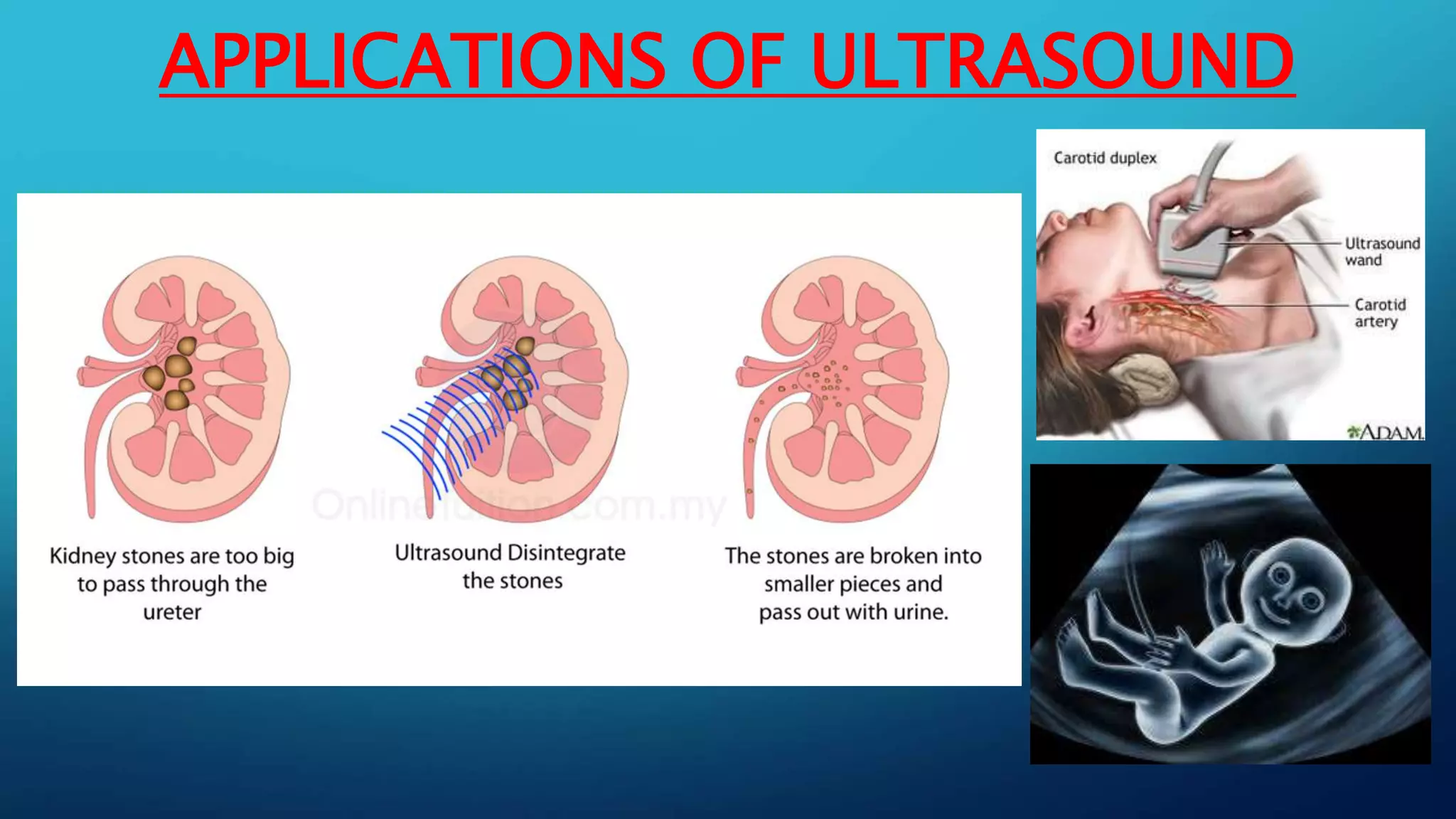
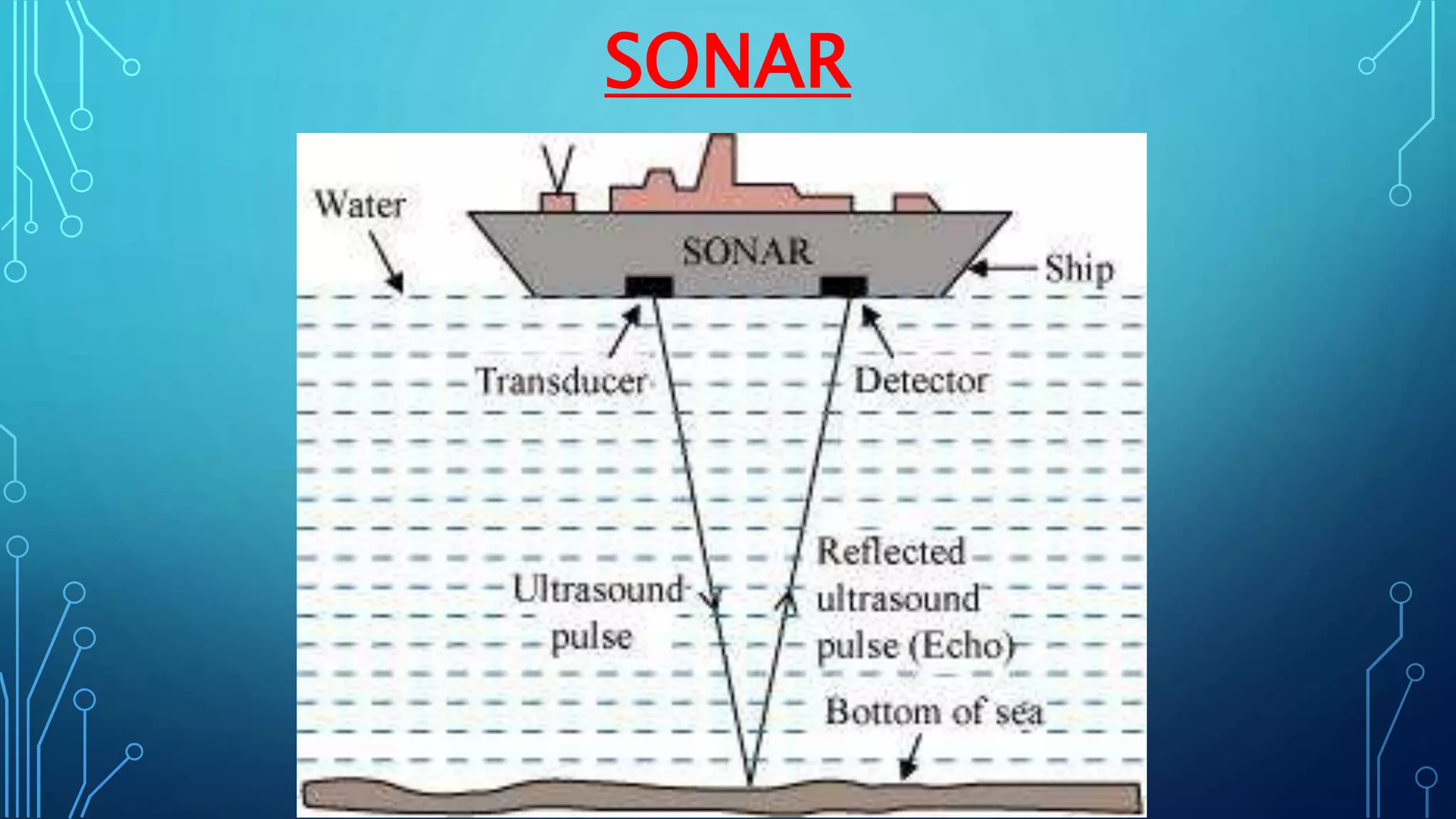
Sound is a mechanical wave produced by vibrating objects that requires a medium—solid, liquid, or gas—for propagation. It travels in longitudinal waves characterized by frequency, amplitude, and wavelength, with properties influenced by the medium's density and temperature. Applications of sound include ultrasound for medical imaging and cleaning, and the use of sonar for navigation underwater.