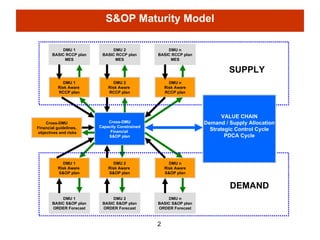
The document describes a maturity model for Sales and Operational Planning (S&OP) with three levels - basic, intermediate, and advanced. At the basic level, each decision making unit (DMU) creates an independent S&OP plan. The intermediate level adds supply chain risk management and financial perspectives. The advanced level enables cross-DMU decision making and optimization based on key performance indicators and financial targets. The model is implemented through a S&OP simulator that decomposes planning into hierarchical decision making and scenario analysis.