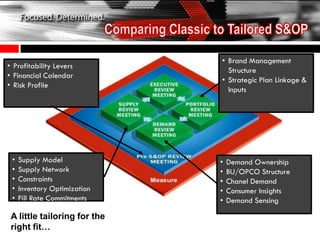
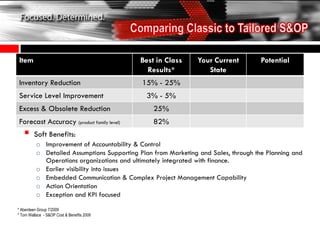
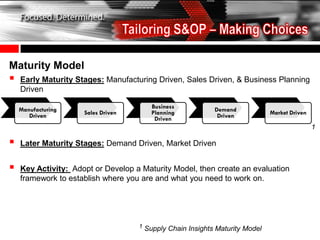
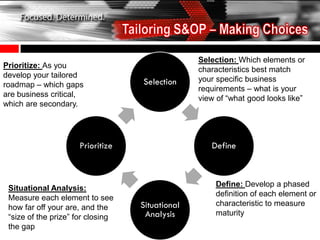
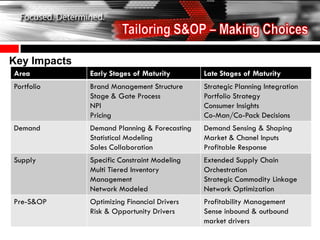
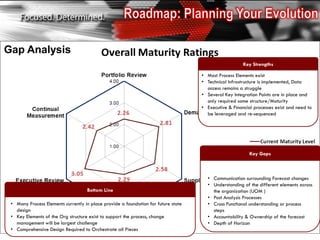
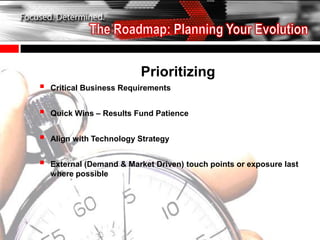
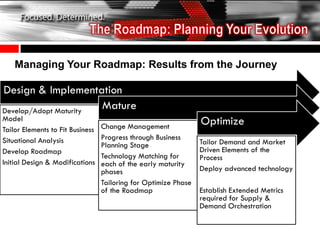
The document discusses the tailoring of Sales and Operations Planning (S&OP) processes to better fit individual business needs, emphasizing the importance of customization to reduce change management challenges. It outlines the evolutionary stages of S&OP maturity, highlighting key components such as inventory management, demand forecasting, and organizational structure. The goal is to create a roadmap that aligns with the specific requirements of the business while improving performance and accountability.