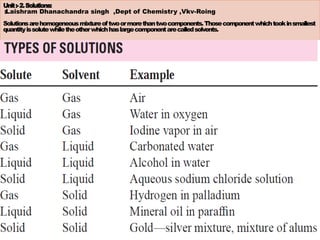
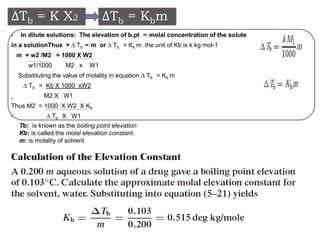
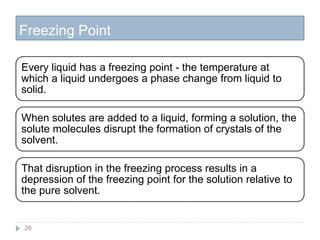
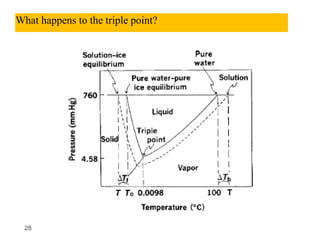
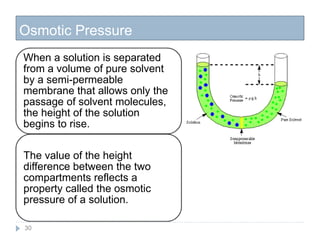
1. Solutions are homogeneous mixtures of two or more components, where the component present in smaller amounts is called the solute and the primary liquid component is the solvent.
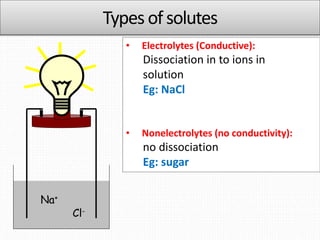
2. Solutes can be electrolytes, which dissociate into ions, or nonelectrolytes, which do not dissociate. Common methods to express the concentration of solutions include molarity, molality, mole fraction, and percent composition.
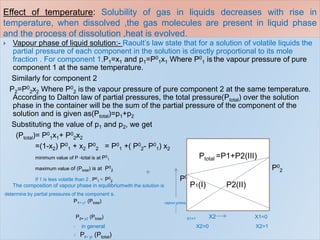
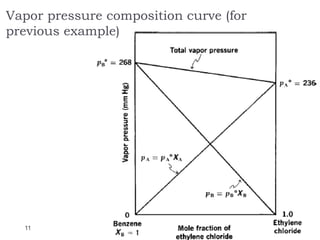
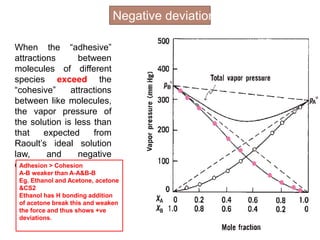
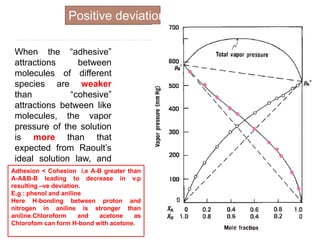
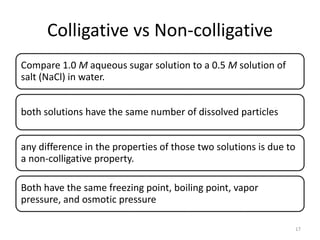
3. The solubility of solids in liquids and gases in liquids depends on factors like temperature, pressure, and the nature of the solute and solvent. Henry's law and Raoult's law describe gas solubility and vapor pressure lowering in solutions. Ideal solutions follow